Chemistry - Chemical Kinetics: Summary | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 7 : Chemical Kinetics
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 7 : Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics: Summary
Summary
·
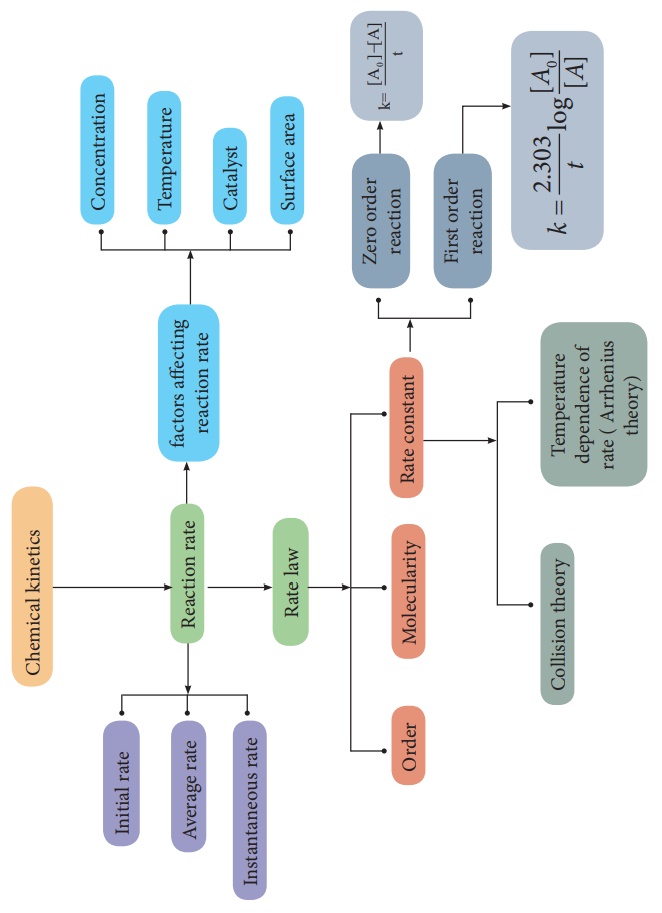
Chemical kinetics is the study of the rate and the mechanism of
chemical reactions, proceeding under given conditions of temperature, pressure,
concentration etc.
·
The change in the concentration of the species involved in a
chemical reaction per unit time gives the rate of a reaction.
·
The rate of the reaction, at a particular instant during the
reaction is called the instantaneous rate. The shorter the time period, we
choose, the closer we approach to the instantaneous rate,
·
The rate represents the speed at which the reactants are converted
into products at any instant.
·
The rate constant is a proportionality constant and It is equal to
the rate of reaction, when the concentration of each of the reactants in unity
·
Molecularity of a reaction is the total number of reactant species
that are involved in an elementary step.
·
The half life of a reaction is defined as the time required for
the reactant concentration to reach one half its initial value. For a first
order reaction, the half life is a constant i.e., it does not depend on the
initial concentration.
·
According to collision theory, chemical reactions occur as a
result of collisions between the reacting molecules.
·
Generally, the rate of a reaction increase with increasing
temperature. However, there are very few exceptions. The magnitude of this
increase in rate is different for different reactions. As a rough rule, for
many reactions near room temperature, reaction rate tends to double when the
temperature is increased by 10 0 C .
·
According to Arrhenius, activation energy of the reaction is the
minimum energy that a molecule must have to posses to react.
·
The rate of a reaction is affected by the following factors.
1. Nature and state of
the reactant
2. Concentration of the
reactant
3. Surface area of the
reactant
4. Temperature of the
reaction
5. Presence of a catalyst
Related Topics