Changes Around Us | Term 2 Unit 3 | 7th Science - Changes of state | 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 3 : Changes Around Us
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 3 : Changes Around Us
Changes of state
Changes of state
Change of state of a substance is one of the major physical changes we encounter in daily lives. We have read about simple changes of physical state such as melting of ice in our previous classes.
The following are some of the changes of state:
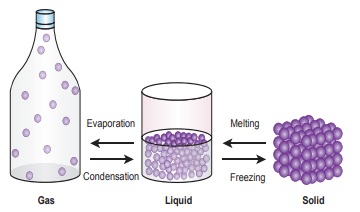
from Solid → to Liquid is Melting
from Liquid → to Gas is Vaporization
from Liquid → to Solid is Freezing
from Gas → to Liquid is Condensation
from Solid → to Gas is Sublimation
Melting, vaporization, and sublimation occur when heated and hence it is called as endothermic process. In an endothermic process, the speed of the molecules is increased hence they move faster.
In contrast, such as in freezing and condensation, heat is removed, resulting in the decreasing the speed of the molecules causing them move slower. Such processes are called as exothermic process.
In the next section we will look at each of these physical changes.
1. Melting
You have seen a puddle of water getting pooled around the glass of ice-cream or a glass of ice cubes when it is kept in room temperature. The ice cubes / ice-cream melt. Right! Can you give reason for that? The ice kept in the beaker receives heat from the surrounding air, to melt and form water.
ACTIVITY 1
Melting of ice and freezing of water
Though ice and water look different, they are both made of water molecules. This means that no new substance is formed during the melting of ice, only a change of state from solid to liquid takes place during the melting of ice. So, the melting of ice to form water is a physical change.

The change which occurs during the melting of ice to form water can be reversed easily by freezing the water to form ice again by keeping a beaker of water in the freezer zone of a refrigerator.
Thus we can find that
Solid --- heating → Liquid
Liquid -- cooling → Solid
Melting is the changing of a solid into its liquid state and it happens by heating, whereas Freezing is the changing of a liquid into its solid state and it happens by cooling.
2. Vapourization
Look at a kettle kept on the fire. The bubbles form and the liquid water becomes water vapour, if you heat it sufficiently.
However, when you put a wet cloth to dry, the water evaporates into air, leaving the clothes dry.
That is there are two types of vaporization: boiling and evaporation, the first one is by heating and the second type of vapourization is natural.
Boiling is the process of conversion of a liquid into vapours on heating. In gaseous state, only the arrangement of molecules changes, there is no change in their chemical composition. So, boiling is a physical change.
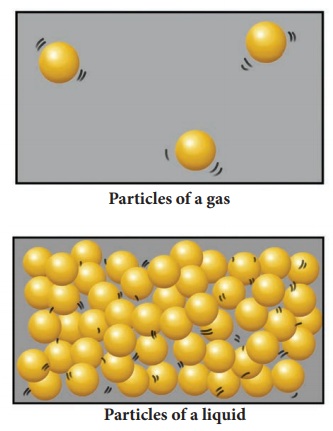
Upon heating a liquid, the particles gain energy and vibrate more vigorously. When the particles possess enough energy, they overcome the strong forces of attraction between one another. The particles break free from one another and move randomly. For example, when liquid water is heated to 100ºC, it boils to become steam. Boiling occurs when the boiling point is reached. The liquid changes to its gaseous state.
Evaporation
Take a glass of water. All the water molecules are moving here and there at different velocities (shown as arrows of different lengths). Some of the molecules, especially at the surface, could be moving in a direction away from the liquid, and have adequate energy to overcome the attractive force (surface tension) of the liquid, then that molecule will escape into the air. Thus slowly and steadily the water molecules escape, or said to evaporate, and the water level in the glass decreases as the time passes. Note that the temperature of the water did not rise to the level of boiling point of water. Nor were there any bubbles formed like boiling.
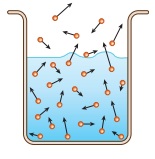
Evaporation is the technique used to separate dissolved solids from a solid-liquid mixture. This is the technique used to extract salt from sea water in salt pans. Shallow level of sea water is impounded. Slowly the water evaporates due to action of Sun. Ultimately salt deposits over the ground we can understand. Evaporation makes use of the fact that the solvent in a solution can vapourise at any temperature, leaving behind a residue of the solid that was dissolved in the liquid.
From drying clothes to drying fish, evaporation is used.
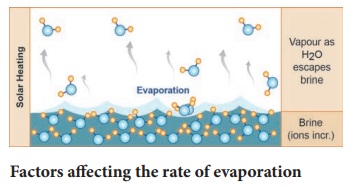
Evaporation is a slow process and occurs only at the surface of the liquid.
ACTIVITY
Activity 2
You must be remembering an activity done in Class six, in which we have taken two same shaped glasses and fill them with equal amount of water from same tap. We kept one under the hot sun and other under the shadow. After three to four hours, we saw that there is difference in water levels. The one kept in the hot place witness more evaporation compared to the one in shade. From this we can conclude that higher the temperature, the rate of evaporation will be more. As the temperature increases, more molecules are able to break free from the surface. Thus the rate of evaporation increases with rising temperature.
Activity 3
Take two pans, one wide and another narrow. Fill hot water in both to the same depth. Keep them in open. Observe after one to two hours. The pan that is wide has cooled more than the narrow one. That is more the surface area; the rate of evaporation is more.
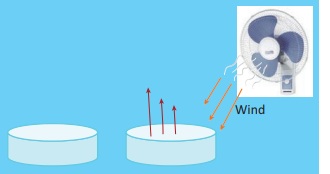
From this, can you guess why we unfurl the clothes while putting them to dry, rather than just drape them over the cloth line?
Greater the surface of conversion of a liquid, more molecules are available for evaporation.
Activity 4
Take sugar solution in a shallow, broad bowl. Place the bowl in hot sun for a few hours. See that the bowl does not get any disturbance for the whole day. You can see that the solvent in the sugar solution evaporates leaving the sugar crystals in the bowl.
3. Freezing
Water in the freezer compartment of a refrigerator gets cooled and solidifies to form ice. In this case, the liquid water changes into solid water called ice.
Only a change in state (from liquid to solid) takes place during the freezing of water to form ice, but no new substance is formed. So, the freezing of water is a physical change.
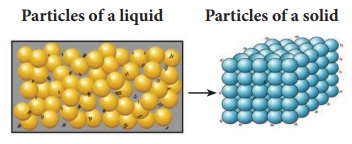
Upon cooling a liquid, the particles loose energy and vibrate less vigorously. When the particles possess less energy, they can experience strong forces of attraction between one another. The particles move closer to each other and movement of particles is also restricted. For example, when liquid water is cooled to 0º C, it freezes to become ice. Freezing occurs when the freezing point is reached. The liquid changes to its solid state.
The arrangement of particles in liquid and solid are diagrammatically represented as follows:
4. Condensation
We would have observed that the plate that covers the cooked food items have water droplets inside. Why?
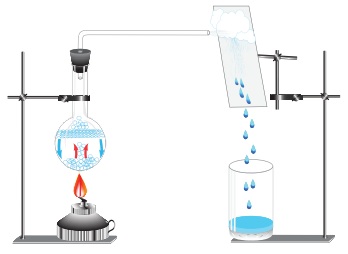
The water vapour emerges from the hot food and goes up. The plate covering the food item is in relative less temperature than the hot food. Thus the more energetic molecules loose energy once they touch the cooler plate. As the molecules lose heat, they lose energy and slow down. They move closer to other gas molecules. Finally these molecules collect together to form a liquid. Condensation happens when molecules in a gas cool down.
In class six, you learnt about water cycle in which you already know how the clouds are formed from water vapour. Water vapour condenses to form clouds.
Condensation is the conversion of gas into its liquid state. The liquid obtained after condensation can be converted back into gas on heating. So, condensation is also a physical process. During this process, only the arrangement of molecules changes from the gaseous state to liquid state. So, condensation is a physical change.
Gas -- Cooling → Liquid
Liquid --heating→ Gas
Condensation is the changing of a gas into its liquid state and it happens by cooling, whereas Evaporation is the changing of a liquid into its gas state and it happens by heating.
5. Sublimation
We have seen camphor being burnt at home, kept in rooms to prevent entry of mosquitoes. Have you ever noticed camphor becoming liquid at any point of time? ..................... It will not.
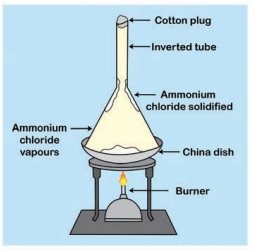
There are certain solid substances like camphor, naphthalene that get converted into gas directly upon heating without becoming liquid. This process in which a solid is converted directly into gas is called sublimation.
In each of the above said processes, there is a change of state due to change in temperature. But there is no change in chemical composition. By changing the temperature all these changes can be reversed. We know that change of a physical state is only a physical change. So, evaporation, boiling, condensation, melting and freezing are all physical processes
ACTIVITY 5
Sublimation
Take some camphor in a porcelain dish and cover it with a clean glass funnel. Close the mouth of the funnel with small amount of cotton wool. Heat the contents in the dish. can you see that camphor changes into vapour state without becoming liquid.
Ammonium chloride is another substance that undergoes sublimation.
6. Crystallization
Though not mentioned earlier, crystallization is also a special form of physical change. The soluble impurities get removed from certain solids by crystallization. The process of cooling a hot, concentrated solution of a substance to obtain crystals is called crystallization.
We also know that sea-water contains salts dissolved in it and the salt can be separated from sea-water by the process of evaporation. The process of evaporation is not a good technique because the soluble impurities do not get removed in the process of evaporation.
ACTIVITY 6
Crystallizing copper sulphate
Take about 100ml of water in a beaker. Heat the water over a burner till it boils. Add impure copper sulphate to the hot water with constant stirring. Continue to add copper sulphate till the solution takes up the added copper sulphate, that is, the added copper sulphate will not dissolve anymore. Filter the contents on a glass plate and allow it to cool. You could see crystals of copper sulphate in a few hours.

Further the crystals of salts obtained by the process of evaporation are small. The shape of crystals cannot be seen clearly. So the solid substances are usually purified by the process of crystallization. Large crystals of pure substances can be obtained from their solutions by the process of crystallization.
Crystallization is a method of separation as well as a method of purification.
Related Topics