Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
Cervical Plexus (C1 - C4) - Peripheral Nerves
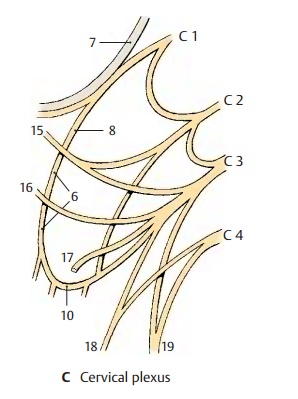
Cervical Plexus (C1 - C4)
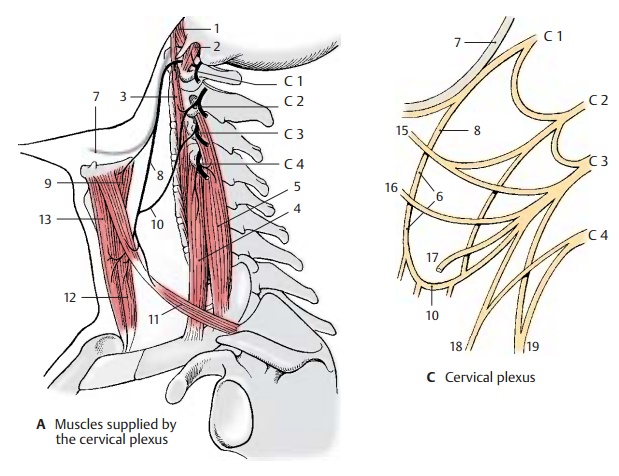
Innervation of the muscles (A).Shortnerves run from the anterior branches directly to the deep
neck muscles, namely, the anterior (A1)
and lateral (A2) rectus capitis
muscles, the long muscle of the head, and the long muscle of the neck (A3). From the anterior branch of C4,
nerves run to the upper part of the anterior scalene muscle (A4) and to the medial scalene muscle (A5).
The anterior branches of C1 – C3
form the deep cervical ansa (C6):
fibers from C1 and C2 temporarily appose the hypoglossal nerve (AC7) and then leave it as the superiorroot (anterior) (AC8); the fibers for the thy-rohyoid
muscle (A9) and the geniohyoid
muscle then continue with the hypoglossal nerve. The superior root combines
with the inferior root (posterior) (AC10) (C2, C3) toform the cervical
ansa, from where branches run to supply the infrahyoid muscles, namely, the
omohyoid muscle (A11), the
sternothyroid muscle (A12), and
sternohyoid muscle (A13).
Innervation of the skin (B, C).The sensorynerves of the plexus
pass behind the sterno-cleidomastoid muscle through the fascia, where they form
the punctum nervosum (B14). From here they spread over head,
neck, and shoulder; the lesser occipital
nerve (BC15) (C2, C3) extends to
the occiput, the greater auricular nerve
(BC16) (C3) into thearea
surrounding the ear (auricula, mastoid process, region of the mandibular
angle). The transverse nerve of the neck
(BC17) (C3) supplies the upper neck
region up to the chin, while the supraclavicular
nerves (BC18) (C3, C4) supply
the subclavicular fossa and the shoulder region.
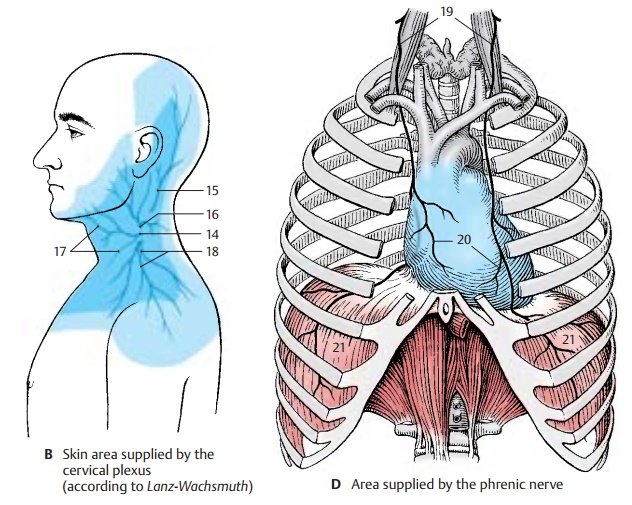
Area innervated by the phrenic nerve (C, D). The phrenic nerve (CD19)
(C3, C4) con-tains fibers of the fourth, and often also ofthe third, spinal
nerve. It crosses the ante-rior scalene muscle and enters into the su-perior
thoracic aperture in front of the sub-clavian artery. It extends through the
medi-astinum to the diaphragm and, on its way, gives off fine branches for
sensory supply to the pericardium, the pericardiac
branches (D20). At the surface
of the diaphragm, it branches and supplies all muscles of the di-aphragm (D21). Fine branches provide the sensory
fibers for the membranes bordering on the diaphragm, that is, cranially the
pleura and caudally the peritoneum of the diaphragm and the peritoneal covering
of the upper intestinal organs.
Clinical Note: Injury to the cervical spinalcord or its roots at the C3 –
C5 levels results in pa-ralysis of the diaphragm and in reduced respira-tion.
In case of paralysis of the thoracic muscles, on the other hand, respiration
can still be main-tained by the cervical spinal cord via the phrenic nerve.
Related Topics