Chapter: Environmental Biotechnology: Genetic Manipulation
Bioenergy
Bioenergy
The concept of obtaining energy from biomass material was mentioned
earlier, in respect of the biological waste treatment methods involving
anaerobic digestion and fermentation, and represents nothing particularly novel
in itself. Methane and ethanol have been long established as fuels in many
parts of the world, their production and utilisation being well documented.
Both of these may be described as derived fuels, biochemically obtained from
the original biomass. However, to many people around the globe, the most
familiar forms of biofuel are far more directly utilised, commonly via direct
combustion and, increasingly, pyrolysis. Around half the world’s population
relies on wood or some other form of biomass to meet daily domestic needs,
chiefly cooking. Estimates put the average daily consumption of such fuels at
between 0.5 – 1.0 kg per person (Twidell and Weir 1994a). This equates to
around 150 W which is an apparently high figure, but one largely explained by
the typical 5% thermal efficiency of the open-fire method most commonly
encountered.
The energy demands of the
developed world are well known to be enormous. In the USA alone, the
requirement for electricity has grown by 2.7% on average per year over the past
10 years (Perkowitz 2000). The Executive
Order on BiobasedProducts and Bioenergy, August 1999, set out the goal of
tripling US biomassuse by 2010, which has been estimated to be worth around $15
billion of new income, while at the same time reducing carbon emissions by the
equivalent of removing some 70 million cars from the road (Feinbaum 1999). The
European Commission has also suggested that the EU as a whole should aim to
double the current contribution made by renewable energy sources, taking it to
12%, also by 2010. Under this proposal, biomass energy was to provide an
additional 90 million tonnes of oil equivalent (Mtoe) per year, raising its
overall share to 137 Mtoe. Half of this would come from specifically farmed
energy crops, while other biofuel forms would account for the rest..
The energy of all biofuels
derives ultimately from the sun, when incident solar radiation is captured
during photosynthesis. This process collects around 2 × 1021 joules
of energy, or 7 × 1013 watts, each year, throughout the biosphere as
a whole. During biomass combustion, as well as in various metabolic processes
described elsewhere, organic carbon reacts with oxygen, releasing the energy
once more, principally as heat. The residual matter itself feeds back into
natural cycles for reuse. It has been calculated that a yearly total of some
2.5 × 1011 tonnes of dry matter circulates around the biosphere, in
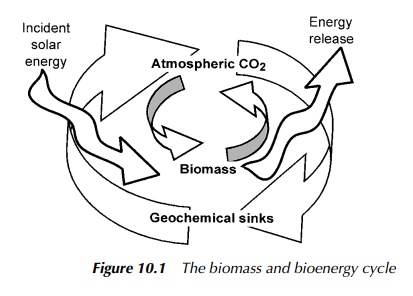
This relationship of energy
and matter within the biospheric system, shown schematically in Figure 10.1, is
of fundamental importance to understanding the whole question of biomass and
biofuels. Before moving on to examine how inte-grated technologies themselves
combine, it is worth remembering that the crux of this particular debate
ultimately centres on issues of greenhouse gases and global warming.
Increasingly the view of biomass as little more than a useful long-term carbon
sink has been superseded by an understanding of the tremendous potential
resource it represents as a renewable energy. Able to substitute for fossil
fuels, bioenergy simply releases the carbon it took up during its own growth.
Thus, only ‘modern’ carbon is returned, avoiding any unwanted additional
atmospheric contributions of ancient carbon dioxide.
Related Topics