Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : The Ear
Auditory Ossicles - Structure of Middle Ear
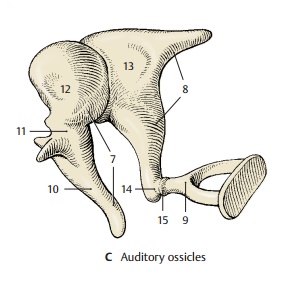
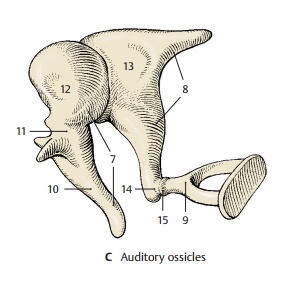
Auditory Ossicles
The three auditory ossicles, or ear bones, form together with the eardrum the sound-conducting apparatus. They are called the hammer, ormalleus(CD7), the anvil, orincus(CD8), and the stirrup, or stapes (CD9). The manubrium of the malleus (ACD10) is firmlyattached to the eardrum and connected via its neck (C11) to the head of the malleus (C12). The malleus has a saddle-shaped ar-ticular surface that contacts the body of theincus (C13). Its lenticular process (AC14),which is attached to the long limb of the incus and projects at a right angle, carries the articular surface for the head of thestapes (C15). The footplate of the stapescloses the vestibular window; it is attached at the margin by the annular ligament of the stapes (D16). Several ligaments (A17) con-nected to the wall of the tympanic cavity keep the ossicles in place.
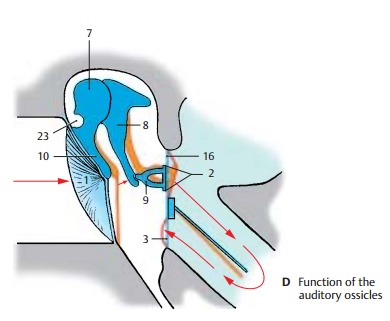
The auditory ossicles transmit to the inner ear the vibration of the eardrum caused by sound waves. For this purpose, malleus andincus act like an angular lever, and the stapes performs a tilting movement. The footplate of the stapes transmits the vibra-tion to the fluid of the inner ear. The move-ment of the fluid through the cochlea is simplified in diagram (D); in reality, it takes a spiral course inside the cochlea. Tension in the system is controlled by two muscles with antagonistic effects, namely, the tensor tympani muscle (A18) and the stapedius muscle (A19).
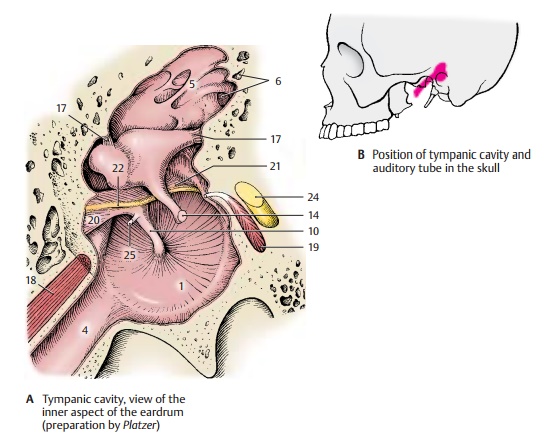
The mucosa lining the tympanic cavity and covering the auditory ossicles forms various folds, such as the anterior (A20) and poste-riormallear folds (A21) which envelope the chorda tympani (A22). The folds form several mucosal pouches. The superiorrecess of the tympanic membrane, Prussak’spouch (D23), lies between the pars flaccida of the eardrum and the neck of the malleus; it plays an important role in ear infections.
A24 Facial nerve.
A25 Tendon of the tensor tympani muscle.
Related Topics