Chapter: Mechanical : Robotics : Sensors and Machine Vision
Applications of Sensor
Applications
of Sensor
(i)
Optical encoders
(ii)
Laser range meters
(iii)
Capacitive type touch sensors
(iv)
Ultrasonic proximity sensors
(i)Optical
encoders:
The
absolute optical encoder employs the same basic construction as incremental
optical
encoders except that there are more tracks of stripes and a corresponding
number
of receivers and
transmitters.
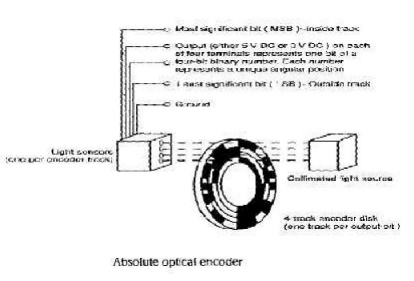
Usually, the stripes
are arranged to provide a binary number proportional to the shaft angle. The
first track might have two stripes, the second four, the third eight, and so
on. In this way the angle can be read directly from the encoder without any
necessary counting.
(ii)
Laser range meters:
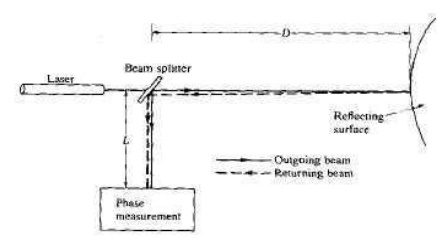
A pulsed-laser system described by larvis [produces
a two-dimensional array with values proportional to distance. The
two-dimensional scan is accomplished by deflecting the laser light via a
rotating mirror.
The
66 working range of this device is on the order of I to 4 m, with an accuracy
of ± 0. 25 cm. Figure shows a collection of three-dimensional objects, and
Figure is the corresponding sensed array displayed as art image in which the
intensity at each point is proportional to the distance between the sensor and
the reflecting surface at that point (darker is closer).
The bright areas around the object boundaries
represent discontinuity in range determined by post processing in a computer An
alternative to pulsed light is to use a continuous-beam laser and measure the
delay (i.e., phase shift) between the outgoing and returning beams.
(iii)
Capacitive type touch sensors:
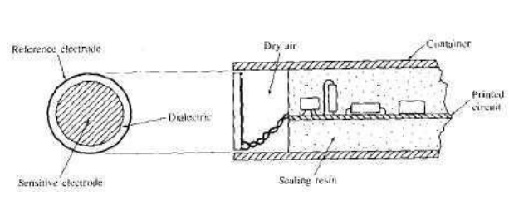
Unlike inductive and Hall-effect sensors
which detect only ferromagnetic materials, capacitive sensors are potentially
capable (with various degrees of sensitivity) of detecting all solid and liquid
materials.
As their name implies, these sensors are based
on detecting a change in capacitance induced by a surface that is brought near
the sensing element.
The basic components of a capacitive sensor
are shown in Figure. The sensing element is a capacitor composed of a sensitive
electrode and a reference electrode. These can be, for example, a metallic disk
and ring separated by a dielectric material.
A
cavity of dry air is usually placed behind the capacitive element to provide
isolation.
The rest of the sensor consists of electronic
circuitry which can be included as an integral part of the unit, in which case
it is normally embedded in a resin to provide sealing and mechanical support.
There are a number of electronic
approaches for detecting proximity based on a change in capacitance.
One of the simplest includes the
capacitor as part of an Oscillator circuit designed so that the oscillation
starts only when the capacitance of the sensor exceeds a predefined threshold
value.
The start of oscillation is then translated
into an output voltage which indicates the presence of an object. This method
provides a binary output whose triggering sensitivity depends on the threshold
value.
A
more complicated approach utilizes the capacitive element as part of a circuit
which is continuously driven by a reference sinusoidal waveform.
A
change in capacitance produces a phase shift between the reference signal and a
signal derived from the capacitive element.
The phase shift is proportional to the
change in capacitance and can thus be used as a basic
mechanism for proximity detection.
(iv)
Ultrasonic proximity sensors:
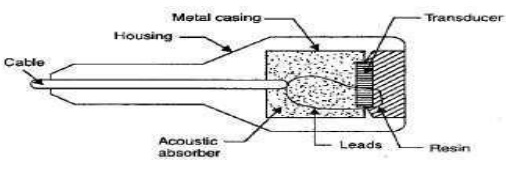
The previously discussed proximity sensors are
useful for detection of ferro-magnetic matter only. If the robot has to handle
other type of materials ultrasonic sensors find the application.
Construction:
The main part in this type of sensor is the
transducer which can act both as transmitter and receiver. The sensor is
covered by a resin block which protects from dust and humidity.
For the acoustic damping, absorber
material is provide as shown in Figure. Finally a metallic housing gives
general protection.
Related Topics