Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Anesthetic Management: Anesthesia for Thoracic Surgery
Anesthesia for Thoracic Surgery: The Open Pneumothorax
THE OPEN PNEUMOTHORAX
The lungs are normally kept expanded by
a negative pleural pressure—the net result of the tendency of the lung to
collapse and the chest wall to expand. When one side of the chest is opened,
the negative pleural pressure is lost, and the elastic recoil of the lung on
that side tends to collapse it. Spontaneous ventilation with an open
pneumothorax in the lateral position results in paradoxical respirations and
mediastinal shift. These two phenomena can cause progressive hypox-emia and
hypercapnia, but, fortunately, their effects are overcome by the use of
positive-pressure ventila-tion during general anesthesia and thoracotomy.
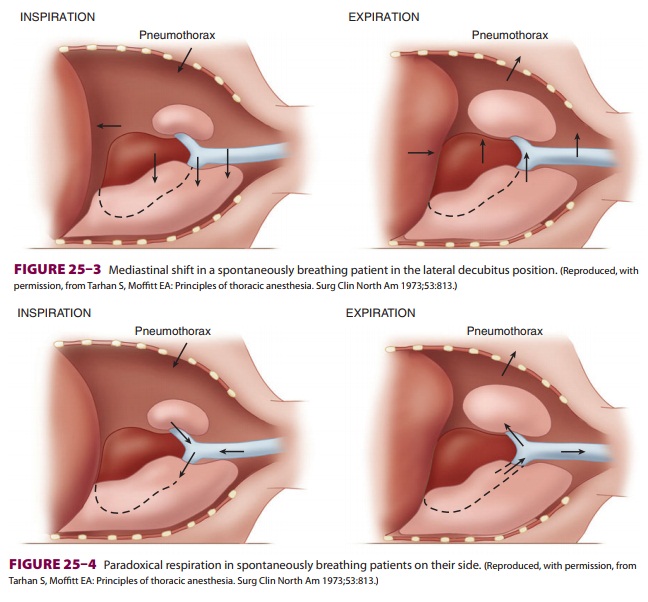
Mediastinal Shift
During spontaneous ventilation in the
lateral posi-tion, inspiration causes pleural pressure to become
more negative on the dependent side, but
not on the side of the open pneumothorax. This results in a downward shift of
the mediastinum during inspiration and an upward shift during expiration (Figure25–3).
The major effect of the mediastinal shift is to decrease the contribution of
the dependent lung to the tidal volume.
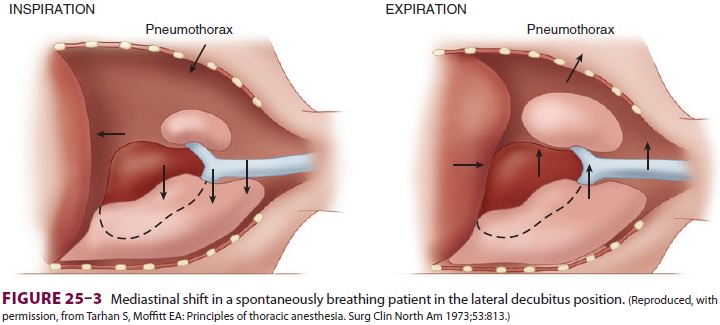
Paradoxical Respiration
Spontaneous ventilation in a patient
with an open pneumothorax also results in to-and-fro gas flow between the
dependent and nondependent lung(paradoxical respiration [pendeluft]). During
inspi-ration, the pneumothorax increases, and gas flows from the upper lung
across the carina to the depen-dent lung. During expiration, the gas flow reverses
and moves from the dependent to the upper lung (Figure 25–4).
Related Topics