Chapter: Medical Physiology: Membrane Physiology, Nerve, and Muscle : Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
Recording Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
Recording Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
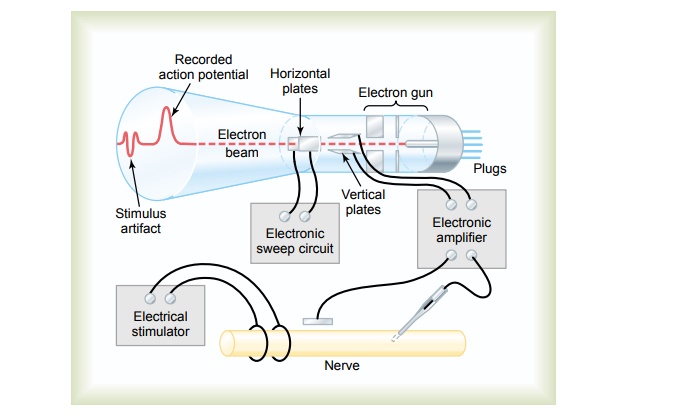
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope. Earlier, we noted that the membrane potential changes extremely rapidly during the course of an action potential. Indeed, most of the action potential complex of large nerve fibers takes place in less than 1/1000 second. In some figures, an electrical meter has been shown recording these potential changes. However, it must be understood that any meter capable of recording most action potentials must be capable of responding extremely rapidly. For practical purposes, the only common type of meter that is capable of responding accurately to the rapid membrane potential changes is the cathode ray oscilloscope.
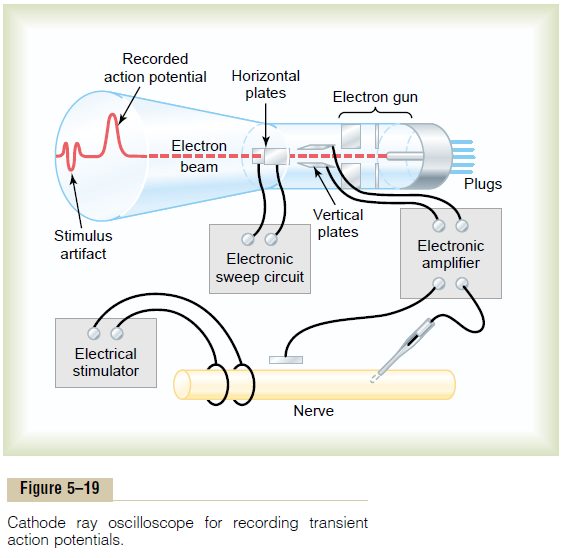
Figure 5–19 shows the basic components of a cathode ray oscilloscope. The cathode ray tube itself is composed basically of anelectron gun and a fluorescent screen against which electrons are fired. Where the electrons hit the screen surface, the fluorescent material glows. If the electron beam is moved across the screen, the spot of glowing light also moves and draws a fluorescent line on the screen.
In addition to the electron gun and fluorescent surface, the cathode ray tube is provided with two sets of electrically charged plates—one set positioned on the two sides of the electron beam, and the other set posi-tioned above and below. Appropriate electronic control circuits change the voltage on these plates so that the electron beam can be bent up or down in response to electrical signals coming from recording electrodes on nerves. The beam of electrons also is swept horizontally across the screen at a constant time rate by an internal electronic circuit of the oscilloscope. This gives the record shown on the face of the cathode ray tube in the figure, giving a time base horizontally and voltage changes from the nerve electrodes shown vertically. Note at the left end of the record a smallstimulus arti-fact caused by the electrical stimulus used to elicit thenerve action potential. Then further to the right is the recorded action potential itself.
Related Topics