Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disorders
Nursing Process: The Patient With Hyperthyroidism
NURSING
PROCESS:THE PATIENT WITH HYPERTHYROIDISM
Assessment
The
health history and examination focus on symptoms related to accelerated or
exaggerated metabolism. These include the pa-tient’s and family’s report of
irritability and increased emotional reaction and the impact these changes have
had on the patient’s interaction with family, friends, and coworkers. The
history in-cludes other stressors and the patient’s ability to cope with
stress.
The
nurse assesses the patient’s nutritional status and the pres-ence of symptoms.
Symptoms related to excessive nervous system output and changes in vision and
appearance of the eyes are noted. The nurse periodically assesses and monitors
the patient’s cardiac status, including heart rate, blood pressure, heart
sounds, and peripheral pulses.
Because
emotional changes are associated with hyperthyroid-ism, the patient’s emotional
state and psychological status areevaluated, as are such symptoms as
irritability, anxiety, sleep dis-turbances, apathy, and lethargy, all of which
may occur with hyper-thyroidism. The family may also provide information about
recent changes in the patient’s emotional status.
Diagnosis
NURSING DIAGNOSES
Based
on all the assessment data, the major nursing diagnoses of the patient with
hyperthyroidism include the following:
· Imbalanced nutrition,
less than body requirements, related to exaggerated metabolic rate, excessive
appetite, and in-creased gastrointestinal activity
· Ineffective coping
related to irritability, hyperexcitability, apprehension, and emotional
instability
· Low self-esteem related
to changes in appearance, excessive appetite, and weight loss
· Altered body temperature
COLLABORATIVE PROBLEMS/POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS
Based
on assessment data, potential complications may include the following:
· Thyrotoxicosis or
thyroid storm
· Hypothyroidism
Planning and Goals
The
goals for the patient may be improved nutritional status, im-proved coping
ability, improved self-esteem, maintenance of nor-mal body temperature, and
absence of complications.
Nursing Interventions
IMPROVING NUTRITIONAL STATUS
ENHANCING COPING MEASURES
The
patient with hyperthyroidism needs reassurance that the emotional reactions
being experienced are a result of the disorder and that with effective
treatment those symptoms will be con-trolled. Because of the negative effect
these symptoms have on family and friends, they too need reassurance that these
symp-toms are expected to disappear with treatment.
It is
important to use a calm, unhurried approach with the patient. Stressful
experiences are minimized; therefore, if hospi-talized, the patient is not
placed in a room with very ill or talka-tive patients. The environment is kept
quiet and uncluttered. Noises, such as loud music, conversation, and equipment
alarms, are minimized. The nurse encourages relaxing activities if they do not
overstimulate the patient.
If
thyroidectomy is planned, the patient needs to know that pharmacologic therapy
is necessary to prepare the thyroid gland for surgical treatment. The nurse
instructs and reminds the patient to take the medications as prescribed.
Because of hyperexcitability and shortened attention span, the patient may
require repetition of this information and written instructions.
IMPROVING SELF-ESTEEM
The
hyperthyroid patient is likely to experience changes in ap-pearance, appetite,
and weight. These factors, along with the pa-tient’s inability to cope well
with family and the illness, may result in loss of self-esteem. The nurse
conveys an understanding of the patient’s concern about these problems and
assists the patient to develop effective coping strategies. The patient and
family need to know that these changes are a result of the thyroid dysfunction
and are, in fact, out of the patient’s control.
If
changes in appearance are very disturbing to the patient, mirrors may be
covered or removed. In addition, the nurse re-minds family members and
personnel to avoid bringing these changes to the patient’s attention. The nurse
explains to the pa-tient and family that most of these changes are expected to
dis-appear with effective treatment.
If the
patient experiences eye changes secondary to hyper-thyroidism, eye care and
protection may become necessary. The patient may need instructions about
instillation of eye drops or ointment prescribed to soothe the eyes and protect
the exposed cornea.
The
patient may be embarrassed by the need to eat large meals. Therefore, the nurse
arranges for the patient to eat alone if desired and avoids commenting on the
patient’s large dietary intake while making sure that the patient receives
sufficient food.
MAINTAINING NORMAL BODY TEMPERATURE
The
patient with hyperthyroidism frequently finds a normal room temperature too
warm because of an exaggerated metabolic rate and increased heat production.
The nurse maintains the en-vironment at a cool, comfortable temperature and
changes bed-ding and clothing as needed. Cool baths and cool or cold fluids may
provide relief. The reason for the patient’s discomfort and the importance of
providing a cool environment are explained to the family and staff.
![]()
MONITORING AND MANAGING POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS
The
nurse closely monitors the patient with hyperthyroidism for signs and symptoms
that may be indicative of thyroid storm. Car-diac and respiratory function are
assessed by measuring vital signs and cardiac output, ECG monitoring, arterial
blood gases, and pulse oximetry. Assessment continues when treatment is
initiated because of the potential side effects on cardiac function. Oxygen is
administered to prevent hypoxia, to improve tissue oxygena-tion, and to meet
the high metabolic demands. Intravenous flu-ids may be necessary to maintain
blood glucose levels and to replace lost fluids. Antithyroid medications (PTU
or methima-zole) may be prescribed to reduce thyroid hormone levels. In
ad-dition, propranolol and digitalis may be prescribed to treat cardiac
symptoms. If shock develops, treatment strategies must be implemented.
Hypothyroidism
is likely to occur with any of the treatments used to treat hyperthyroidism.
Therefore, the nurse periodically monitors the patient. Most patients report a
greatly improved sense of well-being after treatment of hyperthyroidism, and
some fail to continue to take prescribed thyroid replacement therapy.
Therefore, part of patient and family teaching is instruction about the
importance of continuing therapy indefinitely after discharge and a discussion
of the consequences of failing to take medication.
PROMOTING HOME AND COMMUNITY-BASED CARE
Teaching Patients Self-Care
The
nurse teaches the patient with hyperthyroidism how and when to take prescribed
medication, and provides instruction about the essential role of the medication
in the broader thera-peutic plan. Because of the hyperexcitability and
decreased at-tention span associated with hyperthyroidism, the nurse provides a
written plan for the patient to use at home. The type and amount of information
given depend on the patient’s stress and anxiety levels. The patient and family
members receive verbal and writ-ten information about the actions and possible
side effects of the medications. The nurse identifies adverse effects that
should be reported if they occur (Chart 42-5).
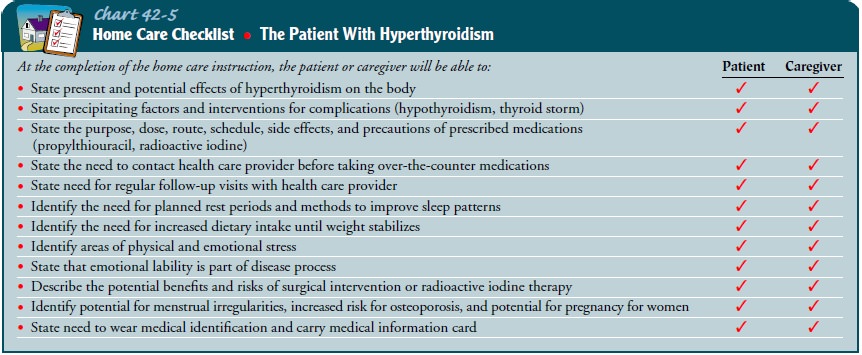
If a
total or subtotal thyroidectomy is anticipated, the patient needs information
about what to expect. This information is re-peated as the time of surgery
approaches. The nurse also advises
Ppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppp
the
patient to avoid stressful situations that may precipitate thy-roid storm.
Continuing Care
Referral
for home care, if indicated, allows the home care nurse to assess the home and
family environment and the patient’s and family’s understanding of the
importance of adhering to the ther-apeutic regimen and the recommended
follow-up monitoring. The nurse reinforces to the patient and family the
importance of long-term follow-up because of the risk for hypothyroidism after
thyroidectomy or treatment with antithyroid medications or ra-dioactive iodine.
The nurse also assesses the patient for changes indicating return to normal
thyroid function and signs and symp-toms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
Further, the nurse reminds the patient and family about the importance of health
promotion activities and recommended health screening.
Evaluation
EXPECTED PATIENT OUTCOMES
Expected
patient outcomes may include:
1) Improves nutritional
status
a)
Reports adequate dietary intake and decreased
hunger
b)
Identifies high-calorie, high-protein foods;
identifies foods to be avoided
c)
Avoids use of alcohol and other stimulants
d)
Reports decreased episodes of diarrhea
2) Demonstrates effective
coping methods in dealing with family, friends, and coworkers
a)
Explains reasons for irritability and emotional instability
b)
Avoids stressful situations, events, and people
c)
Participates in relaxing, nonstressful activities
3) Achieves increased
self-esteem
a)
Verbalizes feelings about self and illness
b)
Describes feelings of frustration and loss of
control to others
c)
Describes reasons for increased appetite
4) Maintains normal body
temperature
5) Absence of complications
a)
Serum thyroid hormone and TSH levels are within
normal limits
b)
Identifies signs and symptoms of thyroid storm and
hypo-thyroidism
c)
Vital signs and results of ECG, arterial blood
gases, and pulse oximetry are within normal limits
d)
States importance of regular follow-up and lifelong
maintenance of prescribed therapy
Related Topics