Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Nucleic Acid and Chromosome Structure
Generating DNA with Superhelical Turns
Generating DNA with Superhelical Turns
To understand how we may experimentally vary Lk, and consequently the degree of
supercoiling, let us consider the lambda phage DNA. The molecules of this DNA
are about 50,000 base pairs long and possess what are called sticky ends; that
is, the ends of the DNA duplex are not flush. As shown in Fig. 2.9, the 5’ ends
protrude in a single-stranded region of 12 bases. The sequence of the left end
is complementary to the sequence of the right end. These sticky ends can be
reassociated together to form a circle, which sometimes is called a Hershey
circle after its discoverer. The phosphodiester bonds are not contiguous around
the Hershey circle; hence its other name, a nicked circle. Circles having a
break in only one of their backbones also are called nicked.
Nicks can be covalently sealed with DNA ligase.
This enzyme seals the phosphodiester backbone of DNA between nicks that have a
5’-phos-phate and a 3’-hydroxyl. Following ligation which forms circles, Lk cannot be altered without breaking
the backbone of one of the two strands. Hence, the sum of Tw, the right-helical turns, and Wr, the number of superhelical turns, is fixed. If under fixed
buffer and tem-perature conditions, we were to anneal the ends of the lambda
DNA together and then seal with ligase, the number of superhelical turns would
be zero and Lk would be about 5,000,
about one turn per ten base
Figure
2.9 Association of the
self-complementary single-stranded ends oflambda phage DNA to form a nicked
circle
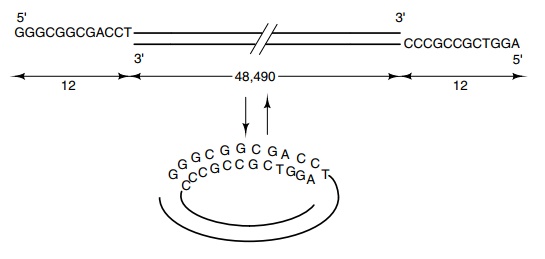
pairs. For convenience let us say that the number
is exactly 5,000. Furthermore, if we were to introduce distortion or even to
wrap this DNA around a protein, the sum of Tw
and Wr must still remain 5,000.
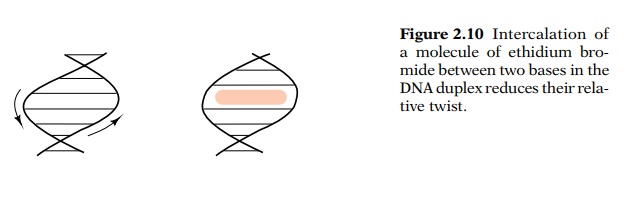
Suppose instead, the annealing and sealing had been
done in the presence of ethidium bromide. Its intercalation between bases
pushes the bases apart and partly untwists the DNA in this region because the
phosphodiester backbone of the DNA cannot lengthen (Fig. 2.10). Hence the
amount by which one strand wraps around another is decreased by the
intercalation of the ethidium bromide. In the common B form of DNA, the bases
are twisted about 34° per base, but the intercalation of an ethidium bromide
molecule removes 24° of this twist. The number of helical turns in a lambda DNA
molecule sealed in the presence of a particular concentration of ethidium
bromide might be about 100 less than the number contained in a lambda DNA
molecule sealed in the absence of ethidium bromide. Treating with DNA ligase
under these conditions would produce a molecule with no writhe, Wr = 0, and with Lk = Tw = 4,900. If the
ethidium bromide were then removed byextraction with an organic solvent, Tw would return to near its standard
value of 5,000; but because of the requirement that Tw + Wr = 4,900 be a
constant, Wr would become -100 and
the circular DNA would writhe. It would have 100 negative superhelical turns,
or σ or -100/5000 = -0.02.
Related Topics