First Aid - Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) | 11th Nursing : Chapter 9 : First Aid
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 9 : First Aid
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
CPR stands for
cardio-pulmonary resuscitation. It’s a life saving medi-cal procedure which is
given to someone who is in cardiac arrest. It helps to pump blood around the
person’s body when their heart can’t.
To carry out CPR a
person presses up and down on the casualty’s chest (chest compressions) and
gives them a series of rescue breaths to help save their life when they are in
cardiac arrest.
CPR comprises the
following 3 steps, performed in order:
·
Chest compressions
·
Airway
·
Breathing.
Indications and contra indications
CPR should be
performed immediately on any person who has become unconscious and is found to
be pulseless and absence of breathing.
Contra indications
·
The only absolute contra indication to CPR is a
do-not-resuscitate (DNR) order or other advanced directive indicating a
person’s desire to not be resuscitated in the event of cardiac arrest.
6 Major CPR steps
Before starting CPR check is the environment safe for the person.
Step 1: Shake and shout
If the person appears
unconscious tap or shake the shoulders ask loudly are you (ok)? No response
call for help.
Step 2: Check for normal breathing and circulation
·
Check if the person is breathing normally by looking for:
·
regular chest movements listening for breathing
·
feeling for breath on your cheek.
·
Check if the person has circulation by placing the index and
middle fingers on the neck to the side of wind pipe.
·
If there is no pulse and breathing start chest compression and
rescue breathing,
§ If the person is
breathing normally, then put them in the recovery position
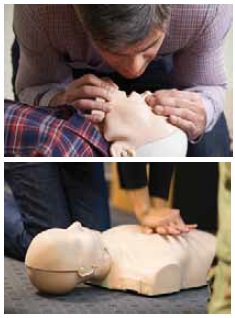
Step 3: Give 30 chest compressions
·
Kneel next to the person.
·
Place the heel of one hand in the centre of their chest. Place
your other hand on top of the first. Interlock your fingers.
·
With straight arms, use the heel of your hand to push the
breastbone down firmly and smoothly, so that the chest is pressed down between
5–6 cm, and release.
·
Do this at a rate of 100 to 120 chest compressions per minute –
that’s around 2 per second.
·
Give 30 chest
compressions.
Step 4: Give two rescue breaths
·
Open the airway Place one hand on the person’s forehead, gently
tilt their head back, then lift their chin using two fingers of your other hand
under their chin – when you do this you open their airway.
§ Take a normal breath,
make a seal around their mouth and breathe out steadily.
§ The person’s chest
should rise and fall. Keeping the person’s head back and the chin lifted, take
your mouth away, take another normal breath, and give a second rescue breath.
The two breaths should take no longer than five seconds.

Step 5: Repeat until an ambulance arrives
Repeat 30 compressions
and two rescue breaths.
Complications of CPR
·
Fractures of ribs or the sternum from chest compression.
·
Gastric insufflations from excessive artificial respiration.
Related Topics