Chapter: Basic Concept of Biotechnology : Biotechnology in Forensic Sciences
X-chromosomal short tandem repeats (ChrX STRs)
X-chromosomal short tandem repeats (ChrX STRs)
X-chromosome short tandem repeat (X-STR) markers (Fig.11) have lead over autosomal and Y chromosome markers in kinship cases. It is used where the alleged father is absent and the child is female.Female individuals receive one X from the mother and the other X from the father while male individuals inherit one X-Chr from mother. Thus, female individuals from same father share their paternal chromosome X.
X-STRs are particularly helpful in paternity testing and kinship analyses, such as mother-son, father-daughter, kinship testing of putative sisters and grandmother-granddaughter kinship testing. When second and third degree kinships are considered, extremely polymorphic STRs are required.
A girl who disappeared for several years, X-STRs were used for the identification.A man suspected to be the murderer of another woman, was found to have a head scarf similar to the one belonging to the girl in his house. Inside the head scarf some hair was found.Therelationship between the hair found and the mother and the sister of the girl was verified in the absence of any biological sample.
For the identification of a biological material supposed to be belonging to a girl who disappeared for several years X-STRs were used.In fact in the house of a man suspected to be the cause of another woman’s murder, a head scarf similar to the one belonging to the girl and inside it some hair was found. In the absence of any biological sample belonging to the girl who disappeared, the relationship between the hair above and the mother and the sister of the girl was verified. DNA typing of hair exposed that all of them were from a female and that they disclosed the same X-STR profile.The present case establishes that X-STR markers are beneficial even in special reverse paternity test.
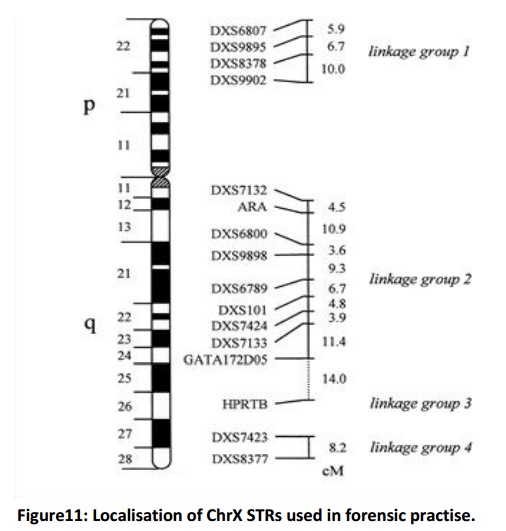
The order and approximate position of STRs on the ChrX ideogram is based upon publicised map data (Marshfield, NCBI) and RH and genetic mapping studies. Pair-wise genetic distances (in cM) are calculated from maximum likelihood estimates of pair- wise recombination fractions using the Kosambi mapping function.
Power of ChrX markers in stain analysis
With a few exemptions, AS (Autosomal) markers are more powerful than ChrX markers. In a mixed stain of male and female, the probability of all male alleles being incorporated in the female component is greater for ChrX than for AS markers. So, it is not suitableto use ChrX markers to assess male traces where female contamination is present. But, to identify female traces present in male contamination, ChrX markers are more competent than AS markers since the female alleles can be fully included in the male component only if the female is coincidentally homozygous at all loci. Examination of female traces on a male rape suspect with the help of ChrX typing has already been performed efficaciously in practice.
Related Topics