Chapter: Basic Concept of Biotechnology : Biotechnology in Forensic Sciences
Short Tandem Repeats (STRs) - Biotechnology in Forensic Sciences
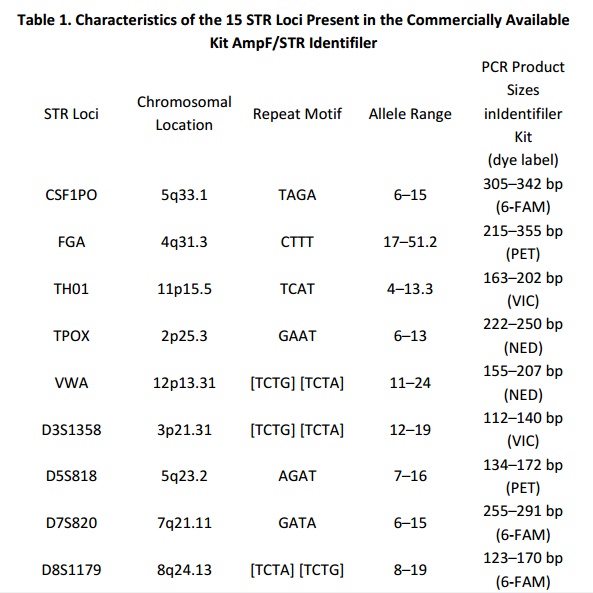
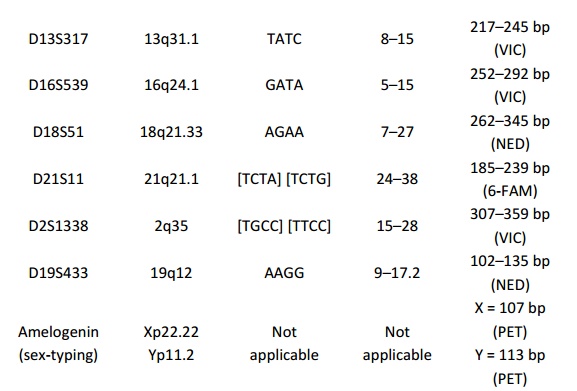
Short Tandem Repeats (STRs)
STRs, sometimes referred to as microsatellites or simple sequence repeats (SSRs), are found as short sequences of DNA, length of 2-5 base pairs, repeated many times in a head and tail manner, viz. the 20bp sequence of “GATAGATAGATAGATAGATA” would represent 5 head and tail copies of the tetramer “GATA”. The dissimilar number of copies of the repeat element in a population leads to the polymorphisms in STRs.DNA fingerprinting relies upon the analysis of these short tandem repeats (STRs).Only few STR markers, which express a high degree of polymorphism, making them of specific use, are used in forensic DNA profiling.
STR markers are generally of three types – simple (identical length repeats), compound (two or more neighbouring repeats) or complex (numerous different length repeats). They are found on autosomal and allosomal chromosomes. Inaccuracy of DNA polymeraseenzyme in copying the region causes the variability in STRs.Tetra- and pentad-nucleotide repeats are preferred for STRs used in forensic science as they provide a high degree of fault free data and suffer less environmental degradation Commercial kits are available to produce DNA profiles containing these main STR loci (Table 1).
Performing STR Analysis
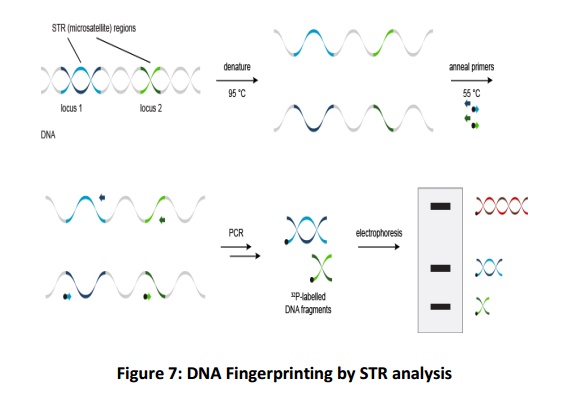
This method differs from RFLP since in STR analysis DNA is not cut with restriction enzymes. Probes are attached to preferred regions on the DNA, and a PCR is employed to discover the lengths of the short tandem repeats.
The whole process for STR typing comprisesof collection of sample, extraction of DNA, quantisation of DNA, amplification of multiple STR loci by PCR, separation and sizing of STR allele, STR typing followed by profile interpretation, and possibly a report of the statistical significance of a match. Current forensic systems apply 10 (e.g. United Kingdom) or 13 (e.g. United States) STR loci. Kits with PCR primers for the standard STR loci are available commercially.
Numerous PCR reactions are performedconcurrently in a single tube at different STR loci, which give several products (two for each locus). The required components are as follows:
§ A DNA sample, e.g. blood or buccal cells from a suspect or a tissue, hair, nail from the scene of a crime
§ Two oligonucleotide PCR primers: one unlabelled reverse primer and one primer labelled at the 5′-end with 32P
§ A DNA polymerase (thermos table)
§ Four deoxynucleoside triphosphates which are as follows: dATP, dGTP, dCTP, dTTP.
The labelled PCR products separate according to size when run on a polyacrylamide gel. DNA ladder is obtained and works as characteristic of an individual (Fig.7).
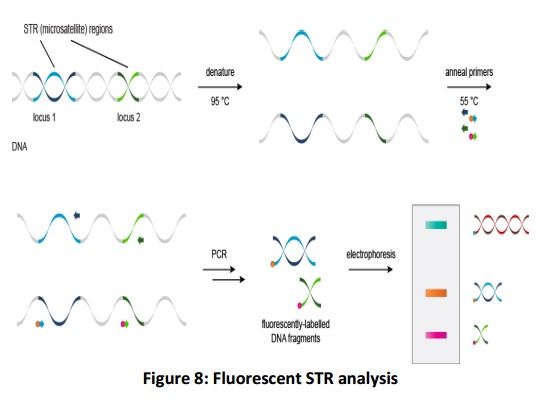
Fluorescent STR analysis
In an advanced variant of STR analysis, PCR primers are labelled with different fluorescent dyes(Fig.8).Still, only a limited number of fluorescent dyes with adequate spectral characteristics have been developed, three different types of fluorescent dyes are used.The use of different fluorescent labels facilitates the distinction between the products and bands originating from different STR loci.
Paternity testing
DNA paternity testing helps in parental dispute cases. DNA paternity test is either an inclusion (the alleged father is regarded as the biological father with 99.9% accuracy) or an exclusion (the alleged father is not the biological father with the accuracyof 100%). The tested parties include the alleged father, the mother and a child.
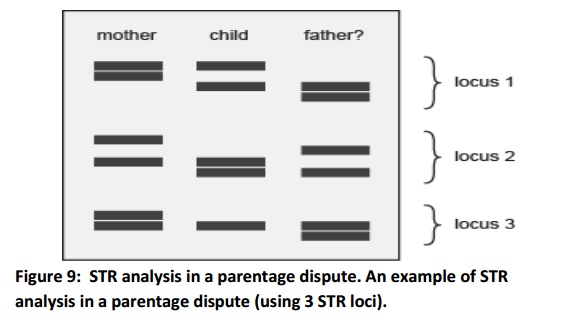
Benefits of STR Analysis
Presently, it is a standard method for genetic profiling. STR analysis used today includes four to five nucleotide repeats. It allows scientists to achievecomparativelyaccurate information.
In the September 11, 2001 attack on the World Trade Centre (WTC), New York, thousands of people were killed.Forensic scientists faced the difficulty of ascertaining victims with degraded samples and required advanced and refined forms of DNA analysis.
Value of Technology to Identify Victims
In this comparatively newer approach, the concept involved smaller STR assays. The advantage of the smaller size is that a damaged DNA sample will still have fragments in the thirteen locations that differ among humans that are usable and can be analysed.
Understanding the DNA Analysis Used for September 11 Victims
These small fragments are called as DNA primers which bind to particular sequences of base pairs. The primers helps scientists procuresome of the DNA fragments to copy it to provide a sample of anadequately large size.
Related Topics