Chapter: Introduction to Botany: Tissues and organs; How the Plant is built
Water and Sugar Transportation in Plants
Water and Sugar Transportation in Plants
Root hairs increase
the surface area where the plant has to absorb the nutrients and water. To take
water, hair cells increase concentration of organic chemicals (the process
which needs ATP) and then use osmosis. There are two ways that water transport
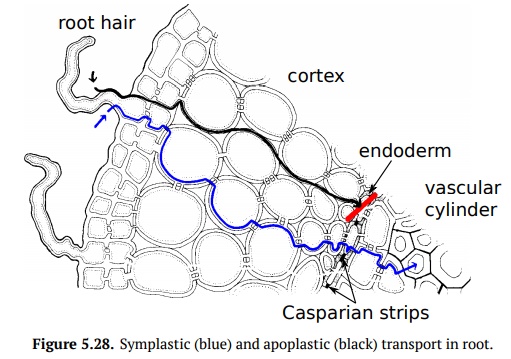
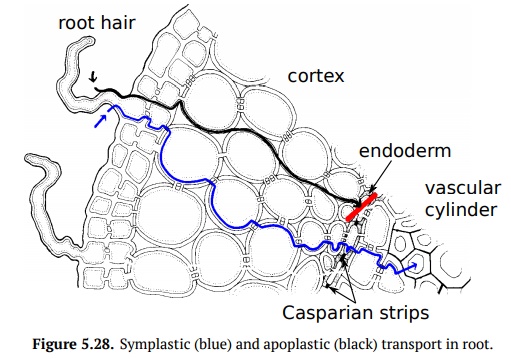
may go: apoplastic or symplastic. Apoplastic transport moves water through the
cell walls of cortex: from the rhizodermis to the endodermis. Endodermis cell
walls bear Casparian strips (rich of
hydrophobic suberin and lignin) which prevent the water from passing through
the cell wall and force symplastic transport (Fig 5.28).
Symplastic transport there is directed to the center of root only and requires
ATP to be spend.
By pumping water
inside vascular cylinder and not letting it out, endodermis cells create the root pressure. It is easy to observe on
tall herbaceous plants cut near the ground: drops of water will immediately
appear on the cutting. Inside tracheary elements of xylem, water moves with the
root pressure, capillary force and the sucking pressure of transpiration. The
latter means that water column does not want to break and if water disappears
from the top (stomata on leaves), it will move water inside plant. The main
direction of water movement is from roots to leaves, i.e. upwards.
Products of
photosynthesis (sugars) are moving inside living cells of phloem; these cells
(sieve tubes) use only symplastic transport to distribute glucose and other
organic compounds among all organs of plants. In fact, phloem transports these
components in all directions: to the flowers (usually upwards), and at the same
time to the roots (usually downwards).
Related Topics