Chapter: Introduction to Botany: Tissues and organs; How the Plant is built
Supportive Tissues: Building Skyscrapers
Supportive Tissues: Building Skyscrapers
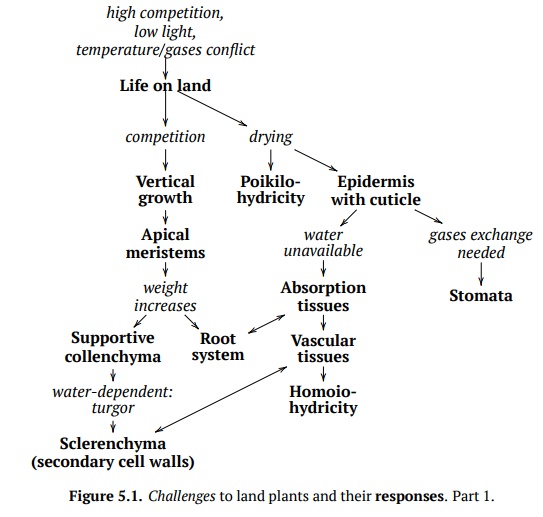
When more and more plants began to move from the water to the land, competition once again became a problem (Fig. 5.1). To solve this, plants grew upwards in order to be able to escape competition for the sunlight and therefore must develop supportive tissues. Collenchyma (Fig. 5.2) is living supportive tissue that has elongated cells and a thick primary cell wall. Its main function is the mechanical support of young stems and leaves via turgor.
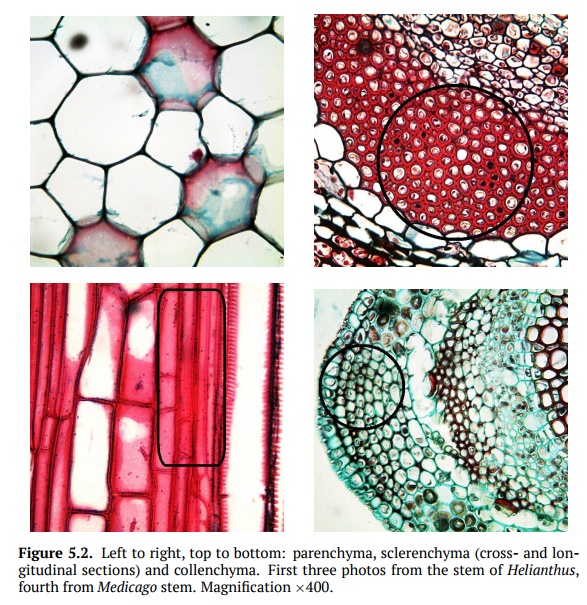
Sclerenchyma (Fig.5.2)is a dead supportive tissue that consists of long fibers orshort, crystal-like cells. Each cell has a thick secondary wall that is rich in lignin. Its main function is a support of older plant organs, and also hardening different parts of plants (for example, make fruit inedible before ripeness so no one will take the fruit before seeds are ready to be distributed). Without sclerenchyma, if a plant isn’t watered, the leaves will droop because the vacuoles will decrease in size which lowers the turgor. Fibers inside phloem (see below) are sometimes regarded as a separate sclerenchyma.
Three times in their evolution plants found the new application for lignin or similar polymers: at first, similar chemicals covered the spore wall which was an adaptation to the spore distribution with wind. Then similar chemicals were used to make cuticle, “epidermal plastic bag” to prevent transpiration outside of stomata. And finally, with acquiring of sclerenchyma, plants found how to use dead cells with completely lignified cell walls.
Cell types and tissues
“Parenchyma” and “sclerenchyma” terms are frequently used in two ways: first, to name tissues (or even classes of tissues) which occur in multiple places of the plant body, and second, to name the cell types which are components of tissues. Therefore, it is possible to say “parenchyma of stem”, “parenchyma of stem pith”, “parenchyma of xylem” and even “leaf mesophyll is a parenchyma”.
Related Topics