Chapter: Introduction to Botany: Tissues and organs; How the Plant is built
Ecological Forms of Plants
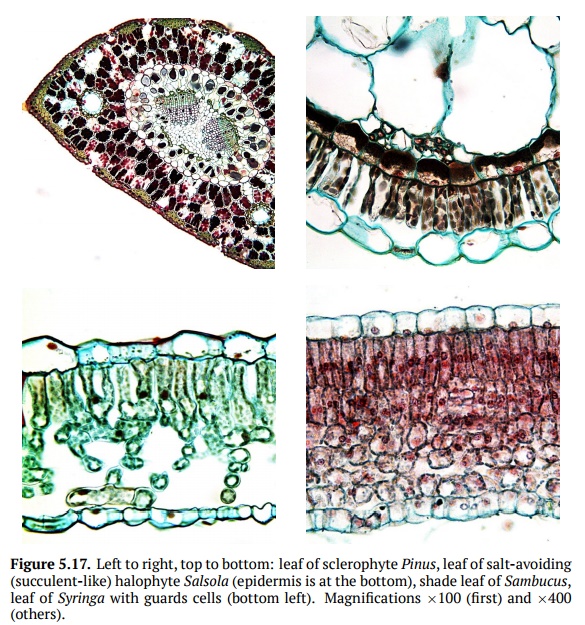
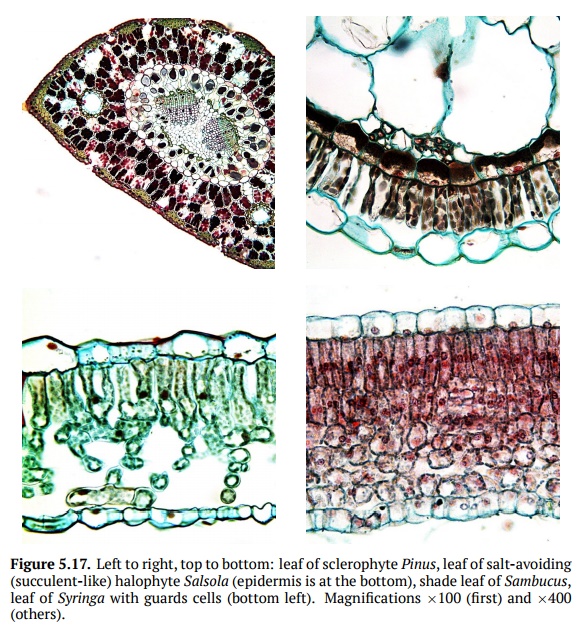
Ecological Forms of Plants
When plants adapt to the particular environment
conditions, leaves usually re-spond first. Conversely, one can estimate the
ecology of plant simply looking on its leaves.
In regards to water, there are four main types
of plants: xerophytes, mesophytes, hygrophytes, and hydrophytes. Xerophytes are adapted to the scarce water
(Fig. 5.17), they could be sclerophytes (usually with prickly and/or rich of scle-renchyma
leaves) and succulents (with
water-accumulating stems or leaves). Mesophytes
are typical plants which adapt to regular water. Hygrophytes live in constantly wet environment, their leaves
adapted to high transpiration and sometimes even to guttation (excretion of
water drops). Hydrophytes grow in
water, their leaves are frequently highly dissected to access more gases
dissolved in water, and their leaf petioles and stems have air canals to supply
underwater organs with gases.
In regards to light, plants could be sciophytes
or heliophytes. Sciophytes prefer
the shade to sunlight, their leaves contain mostly spongy mesophyll. Helio-phytes prefer the full sun and
therefore have leaves filled with palisade meso-phyll. The intermediate group
are “partial shade” plants.
Halophytes, nitrate halophytes, oxylophytes, and
calciphytes are ecological groups adapted to the over-presence of particular
chemicals. Halophyte plants are
frequent, they accumulate (and look similarly to succulents), excrete or avoid
(which looks like sclerophyte) sodium chloride (NaCl). They grow in salty
places: sea shores, salt deserts and solonets prairies. Nitrate halophyte plants grow on soils rich in NaNO3. Oxylophytes grow in acidic soils,
whereas calciphytes grow in basic,
chalk soils rich in CaCO3.
Leaves will also reflect adaptations to the substrate,
ecological forms named psammophytes (grow
on sand), petrophytes (grow on
rocks), and rheophytes (grow in fast
springs). The latter plants frequently have serious simplifications in their
body plan, their leaves and stems are often reduced to form a thallus-like
body.
Parasitic plants could be classified in
mycoparasites, hemiparasites, and phy-toparasites. Mycoparasitic plants feed on soil fungi, phytoparasitic plants are either plant root parasites or plant stem
parasites lacking chlorophyll and pho-tosynthesis. Hemiparasitic plants are those which still have chloroplasts but
take the significant part of water and even organic compounds from the host
plant (like mistletoe, Viscum).
Related Topics