Reproduction in Plants - Vegetative Reproduction | 10th Science : Chapter 17 : Reproduction in Plants and Animals
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 17 : Reproduction in Plants and Animals
Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative
Reproduction
In this type, new
plantlets are formed from vegetative (somatic) cells, buds or organs of plant.
The vegetative part of plant (root, stem, leaf or bud) gets detached from the
parent body and grows into an independent daughter plant. It has only mitotic
division, no gametic fusion and daughter plants are genetically similar to the
parent plant.
Vegetative reproduction
may take place through
(i) Leaves: In Bryophyllum small
plants grow at the leaf notches

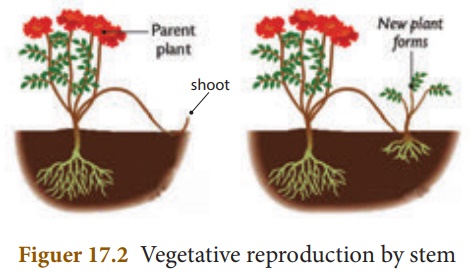
(ii) Stems: In strawberry aerial
weak stems touch the ground and give off adventitious roots and buds.
When the connections with the parent plant is broken, the offspring beomes
independent.
(iii) Root:
Tuberous roots (Asparagus and Sweet potato) can be used for vegetative
propagation.
(iv) Bulbils: In some plants the
flower bud modifies into globose bulb which are called as bulbils, when
these falls on the ground they grow into new plants. e.g. Agave.
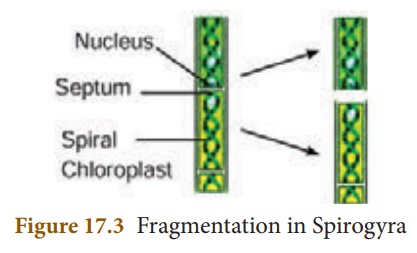
Fragmentation: In filamentous algae,
breaking of the filament into many fragments is called fragmentation.
Each fragment having atleast one cell, may give rise to a new filament of the
algae by cell division e.g. Spirogyra.
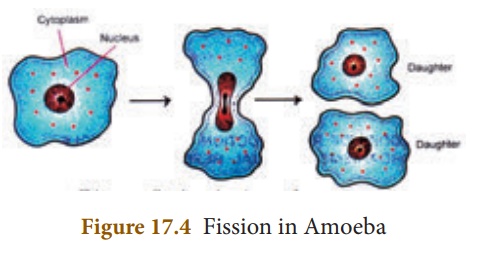
Fission: In this type the parent
cell divides into two daughter cells and each cell develops into a new
adult organism e.g. Amoeba.
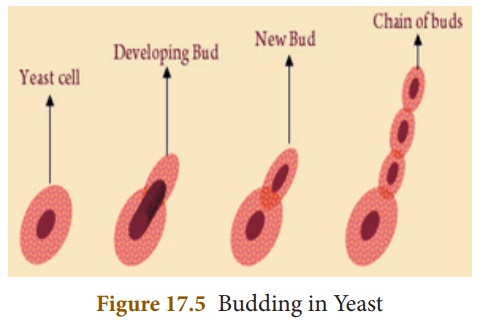
Budding: Formation of a daughter
individual from a small projection, the bud, arising on the parent body
is called budding. e.g. Yeast.
Regeneration: The ability of the lost
body parts of an individual organism to give rise to an whole new
organism is called regeneration. It takes place by specialized mass of cells
e.g Hydra and Planaria.
Related Topics