Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 17 : Reproduction in Plants and Animals
Sexual Reproduction in Human
Sexual
Reproduction in Human
You have studied the
structural details of the male and female reproductive system in 9th standard.
In human beings the male and female reproductive organs differ anatomically and
physiologically. New individuals develop by the fusion of gametes. Sexual
reproduction involves the fusion of two haploid gametes (male and the female
gametes) to form a diploid individual (zygote).
·
Organs of the reproductive system are divided into primary and
secondary (accessory) sex organs. Primary reproductive organs include the gonads (Testes in male
and Ovaries in female).
·
Accessory sex organs
Male: Vas deferens,
epididymis, seminal vesicle, prostate gland and penis.
Female: Fallopian tubes, uterus,
cervix and vagina.
The secondary
(accessory) sex organs include those structures which are involved in the
·
Process of ovulation
·
Fusion of the male and female gametes (fertilization)
·
Division of the fertilized egg upto the formation of embryo
·
Pregnancy
·
Development of foetus
·
Child birth.
Now let’s see the cells
of the primary reproductive organs in human male and female and their role in
reproduction.
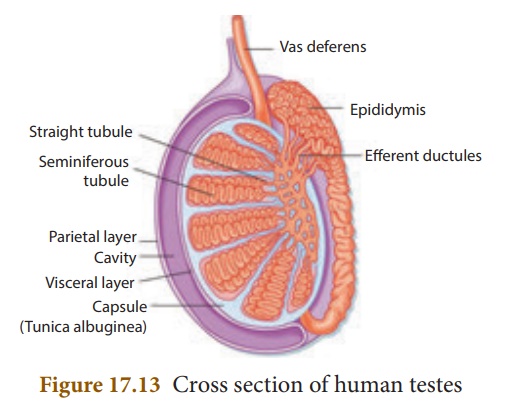
1. Male Reproductive Organ - Structure of Testes
Testes are the
reproductive glands of the male that are oval shaped organs which lie outside
the abdominal cavity of a man in a sac like structure called scrotum.
Now we shall study the various cells which are present in the testes.
Each testes is covered
with a layer of fibrous tissue called tunica albuginea. Many septa from
this layer divide the testes into pyramidal lobules, in which lie seminiferous
tubules, cells of Sertoli, and the Leydig cells (interstitial cells).
The process of spermatogenesis
takes place in the seminiferous tubules. The Sertoli cells are
the supporting cells and provide nutrients to the developing
sperms. The Leydig cells are polyhedral in shape and lie between the seminiferous
tubules and secrete testosterone. It initiates the process of spermatogenesis.![]()
![]()
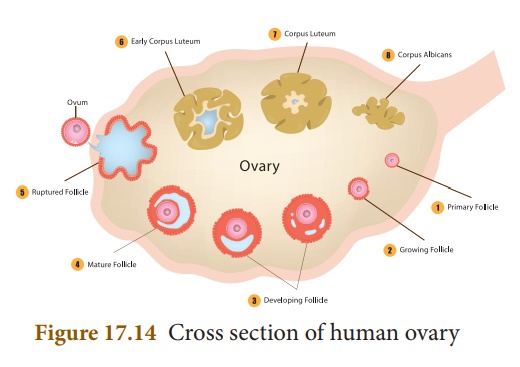
2. Female Reproductive Organ - Structure of Ovary
The ovaries are located
on either side of the lower abdomen composed of two almond shaped bodies, each
lying near the lateral end of fallopian tube. Each ovary is a compact structure
consisting of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The cortex is composed of a
network of connective tissue called as stroma and is lined by the germinal
epithelium. The epithelial cells called the granulosa cells surround
each ovum in the ovary together forming the primary follicle. As the egg grows
larger, the follicle also enlarges and gets filled with the fluid and is called
the Graafian follicle.
Related Topics