Reproduction in Plants - Sexual Reproduction in Plants | 10th Science : Chapter 17 : Reproduction in Plants and Animals
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 17 : Reproduction in Plants and Animals
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Sexual
Reproduction in Plants
Sexual reproduction is
the process in which two gametes (male and female) are fused to produce
offspring of their own kind. In such cases both sexes, male and female sex
organs are needed to produce gametes. You have already learnt that the flower
is a reproductive organ of a flowering plant. To understand this further we
need to study the structure of a flower.![]()
![]()
1. Parts of a Typical Flower
A flower is a modified
shoot with limited growth to carry out sexual reproduction. A flower consists
of four whorls borne on a thalamus. These whorls are from outside
a) Calyx – consisting of sepals
b) Corolla – consisting of petals
c) Androecium – consisting of stamens
d) Gynoecium or pistil –
consisting of carpels
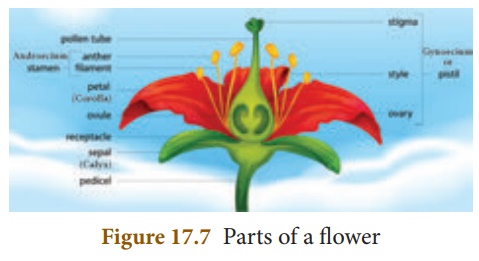
The two outermost
whorls calyx and corolla are non–essential or accessory
whorls as they do not directly take part in the reproduction. The other two
whorls androecium and gynoecium are known as the essential
whorls, because both take part directly in reproduction.
Androecium: Androecium, the male
part of flower is composed of stamens. Each stamen consists
of a stalk called the filament and a small bag like structure called anther
at the tip. The pollen grains are produced in the anther within the pollen sac.
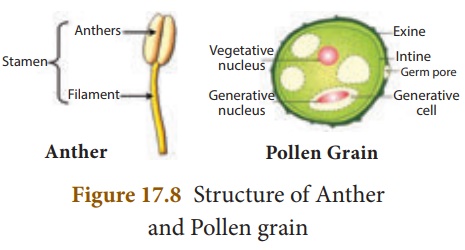
Pollen grain: Pollen grains are
usually spherical in shape. It has two layered wall. The hard-outer
layer is known as exine. It has prominent apertures called germpore. The
inner thin layer is known as intine. It is a thin and continuous layer
made up of cellulose and pectin. Mature pollen grains contain two cells, the vegetative
and the generative cell. Vegetative cell contains a large nucleus.
The generative cell divides mitotically to form two male gametes.
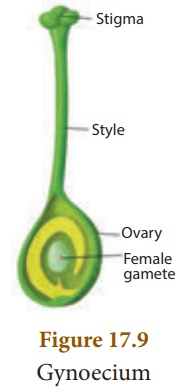
Gynoecium: Gynoecium is the
female part of the flower and is made up of carpels. It has three parts:
1. Ovary
2. Style
3. Stigma
The ovary contains the
ovules.
2. Structure of the Ovule
The main part of the
ovule is the nucellus which is enclosed by two integuments leaving an
opening called as micropyle. The ovule is attached to the ovary wall by
a stalk known as funiculus. Chalaza is the basal part.
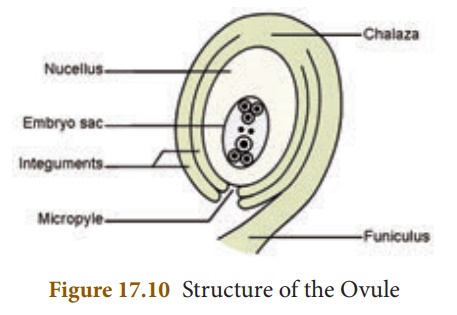
The embryo sac contains
seven cells and the eighth nuclei located within the nucellus. Three
cells at the micropylar end form the egg apparatus and the three cells
at the chalaza end are the antipodal cells. The remaining two nuclei are
called polar nuclei found in the centre. In the egg apparatus one is the
egg cell (female gamete) and the remaining two cells are the synergids.
Process of sexual
reproduction in flowering plants. It involves:
1. Pollination
2. Fertilization
Related Topics