Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 17 : Reproduction in Plants and Animals
Fertilization to Foetal Development
Fertilization to Foetal
Development
Fertilization
Fertilization in human
is internal and occurs in the oviduct of the female genital tract. It takes
place usually in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. An oocyte is alive for
about 24 hours after it is released from the follicle. Fertilisation must take
place within 24 hours. The sperm enters into the ovum and fuses with it,
resulting in the formation of a ‘zygote’. This process is called
fertilization. The zygote is a fertilized ovum.
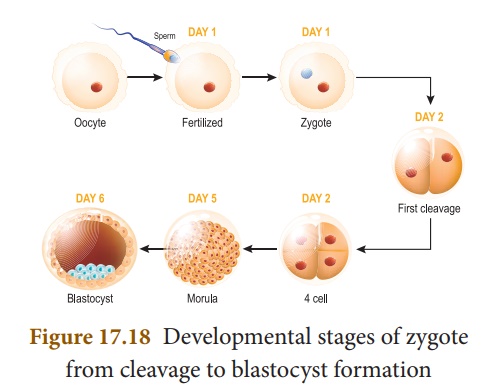
Cleavage and Formation of Blastula
The first cleavage takes
place about 30 hours after fertilization. Cleavage is a series of rapid mitotic
divisions of the zygote to form many celled blastula (Blastocyst) which
comprises an outer layer of smaller cells and inner mass of larger cells.
Implantation
The blastocyst
(fertilized egg) reaches the uterus and gets implanted in the uterus. The
process of attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine wall (endometrium
) is called implantation. The fertilized egg becomes implanted in about 6 to 7
days after fertilization.
Gastrulation
The transformation of
blastula into gastrula and the formation of primary germ layers (ectoderm,
mesoderm and endoderm) by rearrangement of the cells is called
gastrulation. This takes place after the process of implantation.
Organogenesis
The establishment of the
germ layers namely ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm initiates the final phase of
embryonic development. During organogenesis the various organs of the foetus
are established from the different germ layers attaining a functional state.
Formation of Placenta
The placenta is a disc
shaped structure attached to the uterine wall and is a temporary association
between the developing embryo and maternal tissues. It allows the exchange of
food materials, diffusion of oxygen, excretion of nitrogenous wastes and
elimination of carbon dioxide. A cord containing blood vessels that connects
the placenta with the foetus is called the umbilical cord.
Pregnancy (Gestation)
It is the time period
during which the embryo attains its development in the uterus. Normally
gestation period of human last for about 280 days. During pregnancy the uterus
expands upto 500 times of its normal size.
Parturition (Child Birth)
Parturition is the expulsion
of young one from the mother’s uterus at the end of gestation. Oxytocin
from the posterior pituitary stimulates the uterine contractions and
provides force to expel the baby from the uterus, causing birth.
Lactation
The process of milk
production after child birth from mammary glands of the mother is called
lactation. The first fluid which is released from the mammary gland after child
birth is called as colostrum. Milk production from alveoli of mammary
glands is stimulated by prolactin secreted from the anterior pituitary.
The ejection of milk
is stimulated by posterior pituitary hormone oxytocin.
Related Topics