Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Reproductive System
Vagina - Female Reproductive System
Vagina
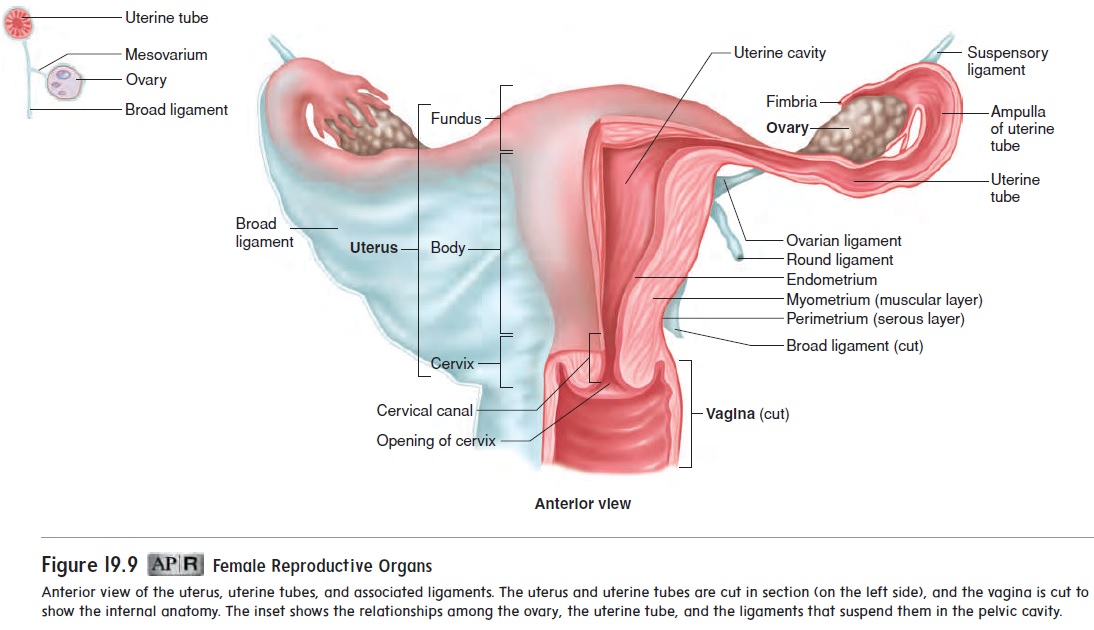
The vagina (vă-j ı̄′ nă) is the female organ of copulation; it receives the penis during intercourse. It also allows menstrual flow and childbirth. The vagina extends from the uterus to the outside of the body (see figures 19.8 and 19.9). The superior portion of the vagina is attached to the sides of the cervix, so that a part of the cervix extends into the vagina.
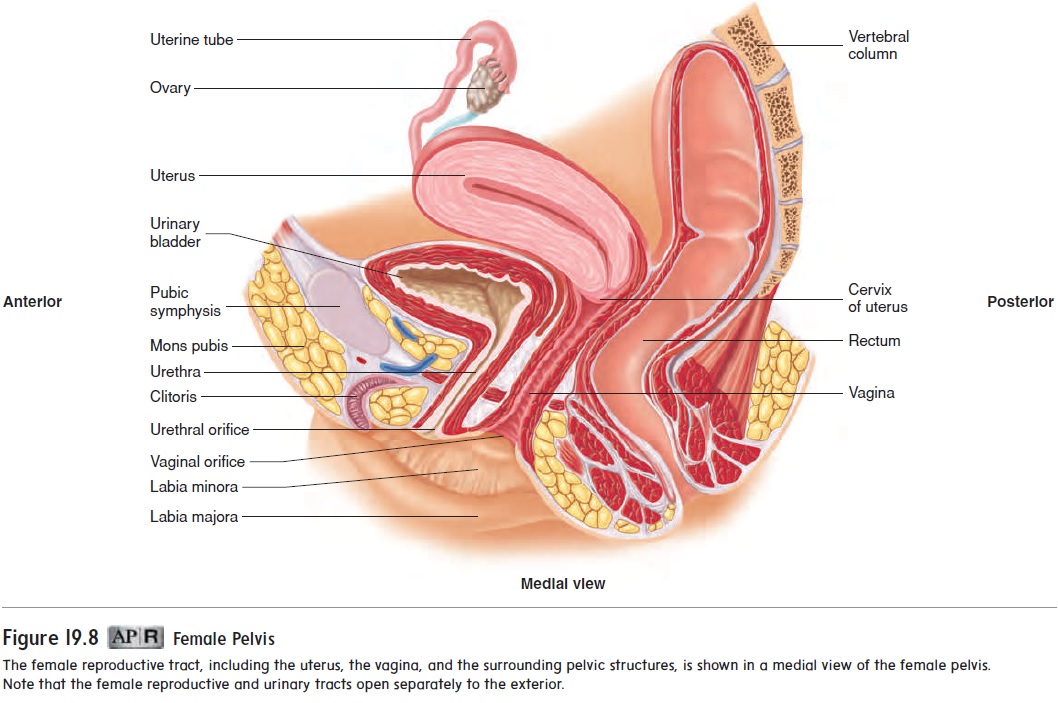
The wall of the vagina consists of an outer muscular layer and an inner mucous membrane. The muscular layer is smooth muscle and contains many elastic fibers. Thus, the vagina can increase in size to accommodate the penis during intercourse, and it can stretch greatly during childbirth. The mucous membrane is moist stratified squamous epithelium that forms a protective surface layer. Lubricating fluid passes through the vaginal epithelium into the vagina.
In young females, the vaginal opening is covered by a thin mucous membrane called the hymen (hı̄′ men; membrane). In rare cases, the hymen may completely close the vaginal orifice and it must be removed to allow menstrual flow. More commonly, the hymen is perforated by one or several holes. The openings in the hymen are usually greatly enlarged during the first sexual intercourse. The hymen can also be perforated or torn earlier in a young female’s life during a variety of activities, including strenu-ous exercise. The condition of the hymen is therefore an unreliable indicator of virginity.
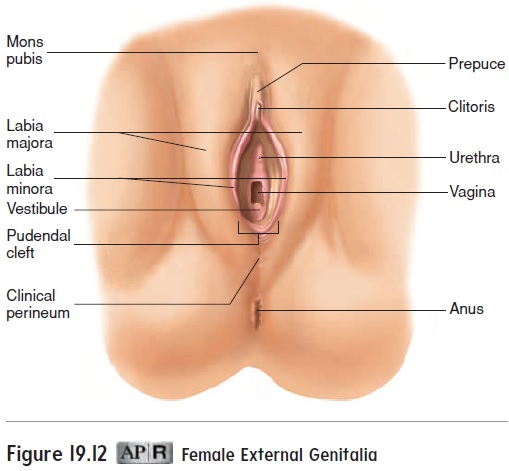
The region between the vagina and the anus is the clinicalperineum (per′i-nē′um; area between the thighs). The skin andmuscle of this region can tear during childbirth. To prevent such tearing, an incision called an episiotomy (e-piz-ē-ot′ ō-mē) is sometimes made in the clinical perineum. Traditionally, this clean, straight incision has been thought to result in less injury, less trouble in healing, and less pain. However, many studies report less injury and pain when no episiotomy is performed.
Related Topics