Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Reproductive System
Uterine tubes - Female Reproductive System
Uterine tubes
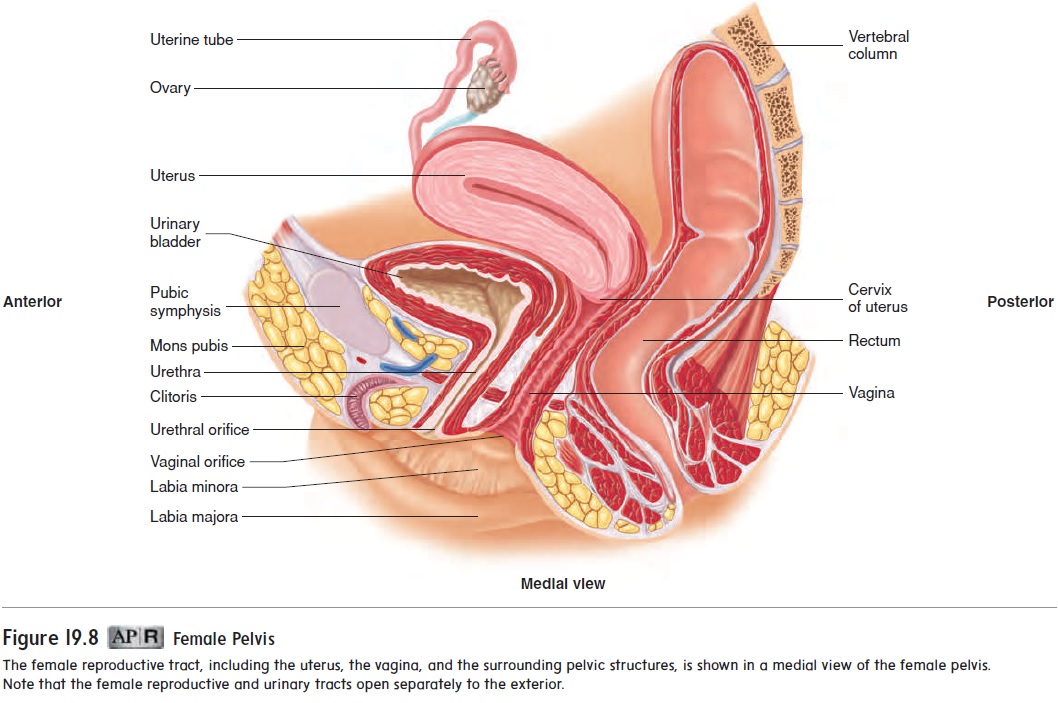
A uterine tube, also called a fallopian (fa-lō ′ pē -an) tube or oviductoviduct (ō ′ vi-d̆u ct), is associated with each ovary. The uterine tubes extend from the area of the ovaries to the uterus. They open directly into the peritoneal cavity near each ovary and receive the secondary oocyte. The opening of each uterine tube is surrounded by long, thin processes called fimbriae (fim′ brē -ē ; fringes) (see figure 19.9).
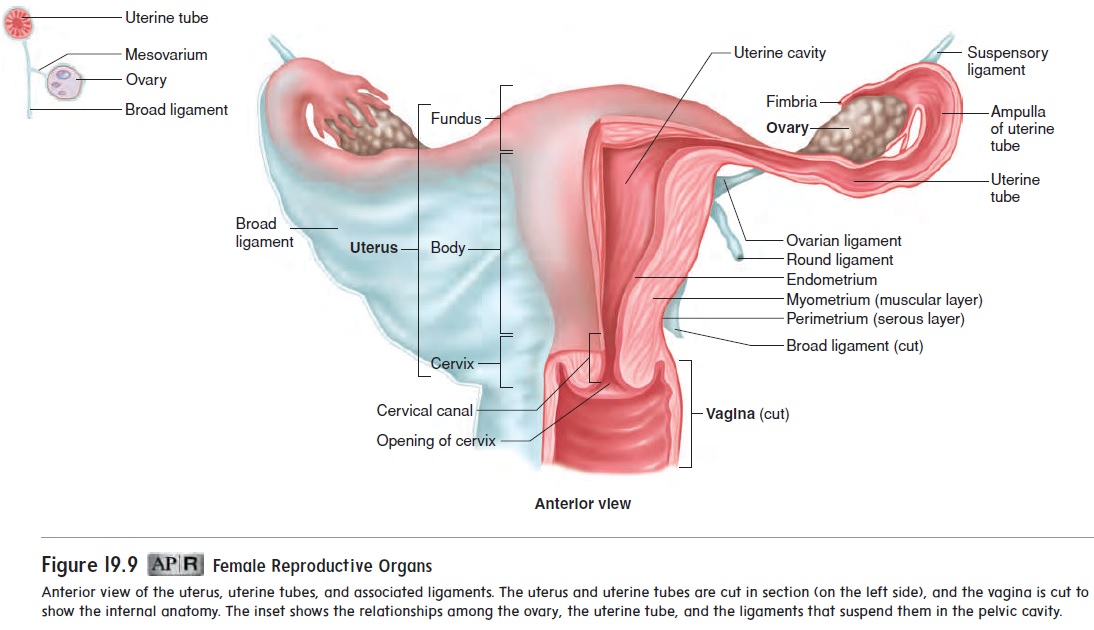
The fimbriae nearly surround the surface of the ovary. As a result, as soon as the secondary oocyte is ovulated, it comes into contact with the surface of the fimbriae. Cilia on the fimbriae surface sweep the oocyte into the uterine tube. Fertilization usu-ally occurs in the part of the uterine tube near the ovary, called the ampulla (am-pul′ l ă). The fertilized oocyte then travels to the uterus, where it embeds in the uterine wall in a process called implantation.
Related Topics