Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Foundamentals of Communication Enginnering
Types of signal: Analog signal and digital signal
Types of signal
Analog signal and digital signal
Definitions of Analog vs Digital signals
An Analog signal is any continuous signal
for which the time varying feature (variable) of the signal is a representation
of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying
signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the
signal which are meaningful.
A digital signal uses discrete
(discontinuous) values. By contrast, non-digital (or analog) systems use a
continuous range of values to represent information. Although digital
representations are discrete, the information represented can be either
discrete, such as numbers or letters, or continuous, such as sounds, images,
and other measurements of continuous systems.
Properties of Digital vs Analog signals
Digital
information has certain properties that distinguish it from analog
communication methods. These include
Synchronization – digital communication uses specific synchronization sequences for determining synchronization.
Language – digital communications requires a language which should be
possessed by both sender and
receiver and should specify meaning of symbol sequences.
Errors – disturbances in analog communication causes errors in actual
intended communication but
disturbances in digital communication does not cause errors enabling error free
communication. Errors should be able to substitute, insert or delete symbols to
be expressed.
Copying – analog communication copies are quality wise not as good as their
originals while due to error free
digital communication, copies can be made indefinitely.
Granularity – for a continuously variable analog value to be represented in
digital form there occur
quantization error which is difference in actual analog value and digital
representation and this property of digital communication is known as
granularity.
Differences
in Usage in Equipment
Many
devices come with built in translation facilities from analog to digital.
Microphones and speaker are perfect examples of analog devices. Analog technology is cheaper but there
is a limitation of size of data that can be transmitted at a given time.
Digital technology has
revolutionized the way most of the equipments work. Data is converted into binary code and then reassembled
back into original form at reception point. Since these can be easily
manipulated, it offers a wider range of options. Digital equipment is more
expensive than analog equipment.
Comparison
of Analog vs Digital Quality
Digital
devices translate and reassemble data and in the process are more prone to loss
of quality as compared to analog devices. Computer advancement has enabled use
of error detection and error correction techniques to remove disturbances
artificially from digital signals and improve quality.
Differences
in Applications
Digital
technology has been most efficient in cellular phone industry. Analog phones
have become redundant even though sound clarity and quality was good.
Analog
technology comprises of natural signals like human speech. With digital
technology this human speech can be saved and stored in a computer. Thus
digital technology opens up the horizon for endless possible uses.
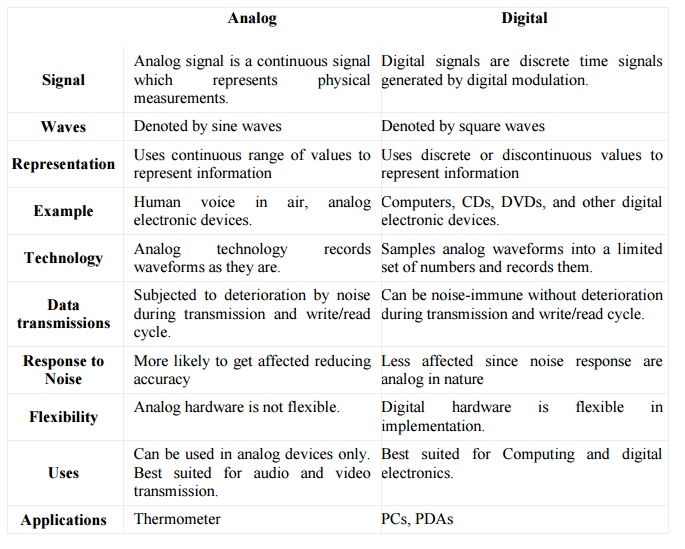
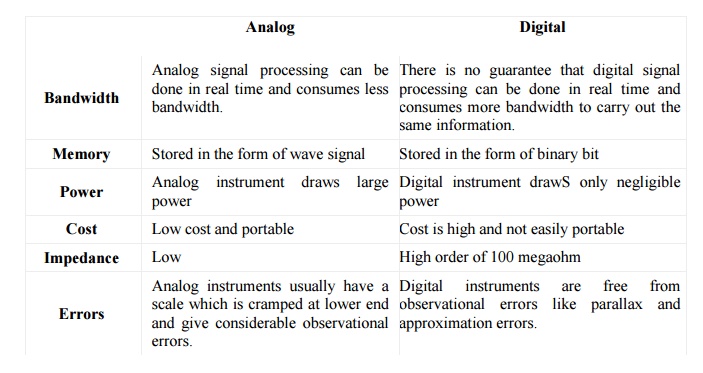
Comparison
chart
Related Topics