Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Foundamentals of Communication Enginnering
Principles of Amplitude modulation
Principles
of Amplitude modulation
Amplitude Modulation (AM) plus frequency
division multiplexing (FDM) is one way of solving above problem. Each
conversation is shifted to a different part of the frequency spectrum by using
a high-frequency waveform to "carry" each individual speech signal.
These high frequencies are called carrier frequencies .
Amplitude modulation is the process of varying
the amplitude of the sinusoidal carrier wave by the amplitude of the modulating
signal, and is illustrated in Fig.
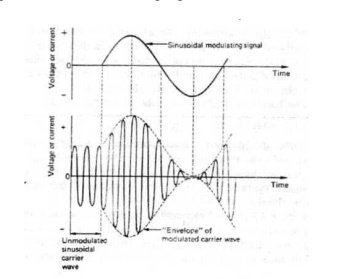
The unmodulated carrier wave has a constant
peakvalueand a higher frequency than the modulating signal , but, when the
modulating signal is applied, the peak value of the carrier varies in
accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal, and the
outline wave shape or "envelope" of the modulated wave's peak values
is the same as the original modulating signal wave shape. The modulating signal
waveform has been superimposed on the carrier wave.
When a sinusoidal carrier wave of frequency fc
Hz is amplitude - modulated by a sinusoidal modulating signal of frequency fm
Hz , then the modulated carrier wave contains three frequencies .
1) fc
Hz : Original carrier frequency
2) ( fc + fm
) Hz :
The sum of carrier and modulating signal frequencies
3) ( fc - fm
) Hz :
The difference between carrier and modulating signal
This is
illustrated in Fig
It should be noted that two of these
frequencies are new, being produced by the amplitude-modulation process, and
are called side-frequencies. The sum of carrier and modulating signal
frequencies is called the upper side-frequency. The difference between carrier
and modulating signal frequency is called the lower side-frequency. This is
illustrated in the frequency spectrum diagram of Fig.
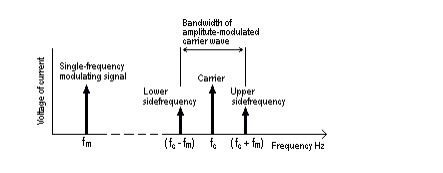
The bandwidth of the modulated carrier wave is
( fc + fm ) - ( fc - fm ) = 2 fm
i.e.
double the modulating signal frequency
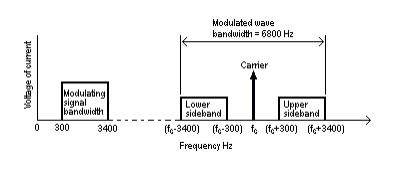
The complete amplitude-modulated wave band of
lower sideband plus carrier plus upper sideband shown in Fig. 8 takes up more
frequency bandwidth than is really necessary to transmit the information signal
since all the information is carried by either one of the sidebands alone . The
carrier component is of constant amplitude and frequency so does not carry any
of the information signal at all . It is possible by using special equipment to
suppress both the carrier and one sideband and to transmit just the other
sideband with no loss of information. This method of working is called single
sideband working ( SSB ) . This method is not used for domestic radio
broadcasting , but it is used for some long-distance radio telephony systems
and for multi-channel carrier systems used in national telephone networks.
Related Topics