Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Foundamentals of Communication Enginnering
Satellite communication
Satellite communication
A
communications satellite or comsat is an artificial satellite sent to space for
the purpose oftelecommunications. Modern communications satellites use a
variety of orbits including geostationary orbits, Molniya orbits, elliptical
orbits and low (polar and non- polar) Earth orbits.
For fixed
(point-to-point) services, communications satellites provide a microwave radio
relay technology complementary to that of communication cables. They are also
used for mobile applications such as communications to ships, vehicles, planes
and hand-held terminals, and for TV and radio broadcasting.
Communications
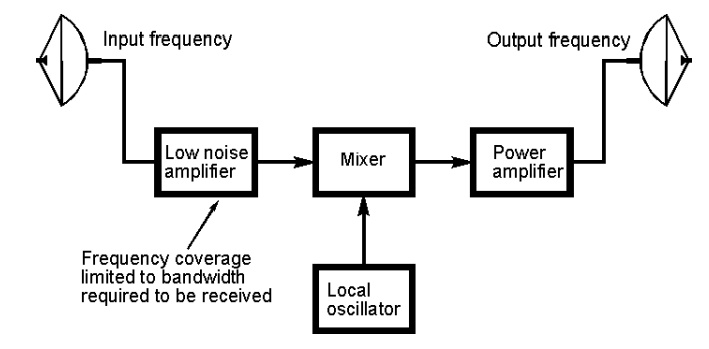
Satellites are usually composed of the following subsystems: Communication
Payload, normally composed of transponders, antenna, and switching systems
Engines used to bring the satellite to its desired orbit
Station
Keeping Tracking and stabilization subsystem used to keep the satellite in the
right orbit, with its antennas pointed in the right direction, and its power
system pointed towards the sun Power subsystem, used to power the Satellite
systems, normally composed of solar cells, and batteries that maintain power
during solar eclipse
Command
and Control subsystem, which maintains communications with ground control
stations. The ground control earth stations monitor the satellite performance
and control its functionality during various phases of its life-cycle.
The
bandwidth available from a satellite depends upon the number of transponders
provided by the satellite. Each service (TV, Voice, Internet, radio) requires a
different amount of bandwidth for transmission. This is typically known as link
budgeting and a network simulator can be used to arrive at the exact value.
Related Topics