Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Nursing - Infection Control
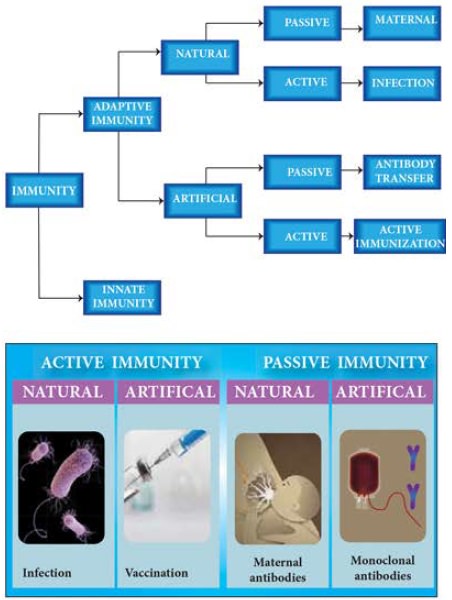
Types of immunity: 3 types of immunity is in human
Types of immunity:- 3 types of immunity is in human.
1. Innate immunity (natural or non specific)
2. Acquired (specific or adaptive) immunity
3. Active and passive immunity.
Innate (natural or Non-specific immunity:-
It refers to the inborn ability of the body to resist and is genetically transmitted from one generation to the next. The immunity offers resistance to any microorganism or foreign material encountered by the host.
Natural immunity results after acquiring certain disease Ex. Measles. This immunity lasts a life time.
Innate immunity can be divided in to species, racial, individual immunity
Acquired immunity (Specific or Adaptive):
Acquired immunity refers to an immunity that is developed by the host in its body after exposure to a suitable antigen or after transfer of antibodies.
Immunity can be described as either active or passive, depending on how it is acquired.
Active immunity: - Active immunity involves the production of antibodies by the body itself and the subsequent development of memory cells.
Passive immunity: - Results from the acquisition of antibodies from another source and hence memory cells are not developed.
Active immunity will result in long-term immunity but passive immunity will not due to the presence or absence of memory cells.
Both active and passive immunity can be induced by either natural or artificial mechanism.
Examples of active immunity: -
Natural – Producing antibodies in response to exposure to a pathogen if infection acquires. (e.g. Chicken Pox, Measles).
Artificial – Producing antibodies in response to the controlled exposure to an attenuated pathogen (e.g. vaccination)
Examples of passive immunity: -
Natural: Receiving antibodies from another host. (e.g. IgG - mother to feters via the placenta; IgA - From mother to new born via breast milk (colostrum)).
Artificial: - Receiving manufactured antibodies via external delivery (Blood transfusion of monoclonal antibodies).
Types of Immunity:-
Example

Types of immunization:-
Active immunization: is the induction of immunity after exposure of an antigen. Antibodies are created by the recipient and may be stored permanently. Artificial active immunization is where the microbe is injected into the person before they are able to take it in naturally.
Passive immunization: - It can be provided when people cannot synthesize antibodies, and when they have been exposed to a particular organ that they do not develop immunity.
Related Topics