Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Nursing - Infection Control
Infection Process
Infection Process
Infection is the
invasion or colonization of the body by pathogenic microorganisms.
Disease occur when an
infection results in any change from a state of health.
Development of an
infection occurs in a cycle that depends on the following elements.
·
An infectious agent or pathogen Ex. Salmonella
·
A continual source of infection is called a reservoir of
infection (spread of infection)
·
A mode of transmission of disease
·
A portal of entry to a host
·
A susceptible host.
An infection will
develop if this chain remains intact. Nurse use infection prevention and
control practices to break the chain so that infection will not develop.
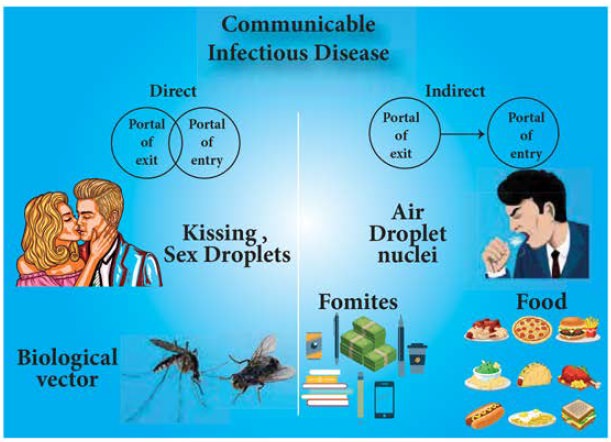
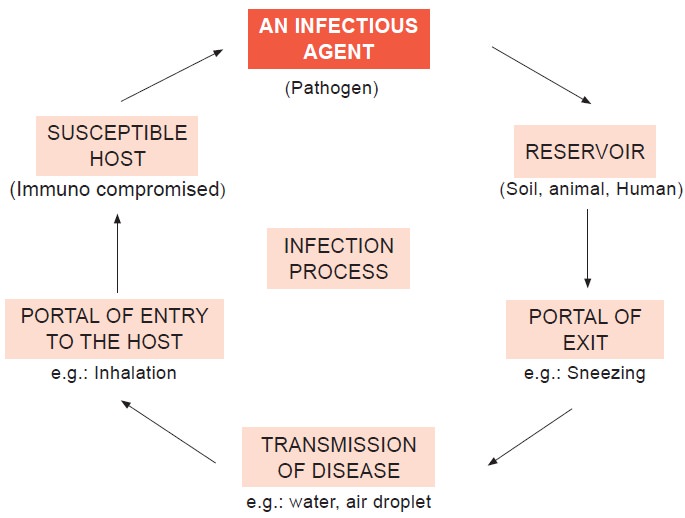
Chains of infection:
Infectious Agent: -
Microorganisms include
bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa. They are common infectious agents or
pathogens. The potential for microorganisms to cause disease is depends on the
following factors.
·
Sufficient number of pathogens (Inoculum) which enter into the
body.
·
Virulence or ability to produce disease.
·
Ability to enter and survive in the host (overcome the immune
system of the host).
·
Susceptibility of host.
Reservoir: - A reservoir is where a pathogen can survive.
·
A continual source of infection is called a reservoir infection.
·
People who have a disease are carriers of pathogenic organisms (human reservoir).
·
Zoonoses can be transmitted to humans from animal reservoirs of
infection.
·
Some pathogenic microorganisms grow in nonliving reservoirs
Ex-Soil, Water.
Portal of exit: -
·
Pathogens have preferred portals of entry, they also have
definite portal of exit.
·
3 common portal of exit.
Respiratory tract – coughing, sneezing
Gastro intestinal tract – Saliva, feaces
Genital tract – Vagina and penis
·
Arthropods and syringes provide a portal of exit for microbes in
blood.
Modes of transmission: -
Mode of transmission
is through direct or indirect contact, droplet infection, vehicle transmission,
air borne, arthropod vector.
Portal of entry: -
Organism can enter the
body through skin, mucous membrane, gastro intestinal tract, intestinal tract,
blood, genital tract.
Compromised host: -
When a person acquires
an infection depends on the susceptibility of an infectious agent.
·
Individual degree of resistance to a pathogen.
·
Patients with burn, surgical wounds, and suppressed immune
system are the most susceptible.
·
According to the virulence of the microbes.

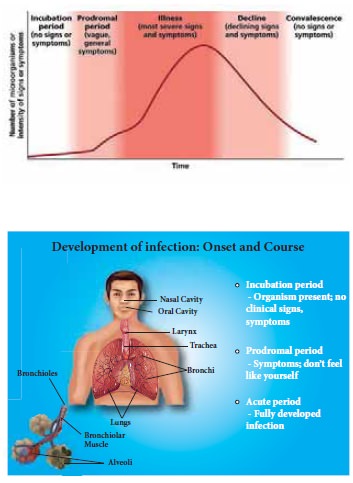
Course of Infection
Once a microorganism
does overcome the defenses of the host, development of the disease follows a
certain sequence of steps that tends to be similar whether the disease be acute
or chronic.
·
Incubation period Proximal stage
·
Period of illness stage
·
Period of decline
·
Period of convalescence
Incubation Period: - The period of incubation is the time
interval between the actual infection and the first appearance of signs and
symptoms interval between entrance of pathogen into body and appearance of
first symptoms.
e.g. Common cold - 1 to 2
days
Mumps
- 18 days
Prodromal Stage: -The prodromal period is characterized by the appearance of the first mild signs and
symptoms (low-grade, fever, fatigue). During this time microorganism grow and
multiply and patient is more capable of spreading disease to others.
Illness Stage: - During this period of illness, the disease is at its height and all disease signs and
symptoms are apparent.
e.g. Common cold - Sore throat, sinus
Mumps
-
Earache, high fever, parotid, salivary gland swelling
The severity of the
patients’ illness depends on the extent of infection, the pathogenicity of the
microorganism, susceptibility of individuals.
Decline Stage: -
During the period of
decline, the signs and symptoms subside.
Convalescence Period: -
During the period of
convalescence, the body returns to its predeceased state, the health is
restored. Length of recovery depends on severity of infection and patients’
general health status. Recovery may take several days to month.
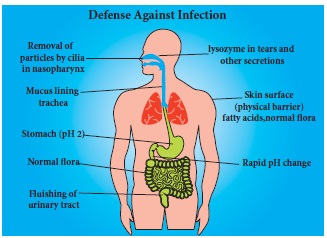
Defense Against Infection: -
1.
The immune system is one portion of the
body’s defense against infection.
2.
Normal body flora that reside inside and outside of the body
protect from several pathogens.
3.
Skin and mucous membrane both prevent pathogens from entering
the body by creating a barrier, mucous traps microorganisms.
4.
Skin & Mucous Membrane
·
Acidity of Skin,
·
Saliva, tears (Ig A) Nostril hairs
·
Stomach Acidity
Provide first line of Defense against
Infection it contains Ig A
·
The inflammatory response is a protective vascular and cellular
reaction that neutralizes pathogens and repair body cells.
·
Inflammatory response – bring blood and therefore more
phagocytes to the area.
·
IgA is predominantly present in secretion (tears, saliva, milk)
is the first line of defense.
·
Lysozyme is present in phagocytes which digest the foreign
particles, break the cell wall of gram positive bacteria
Types of Infection: -
Nosocomial Infection:-It is defined as any infections that
are acquired during the course of stay in a hospital, nursing home, or other health
care facility health care workers.
Iatrogenic Infection:-Iatrogenic
infections are a type
of nosocomial infection resulting from a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure.
i.e. UTI that develops
after catheter insertion
·
Exogenous
·
Endogenous
Exogenous Infection: - Exogenous infection arises from
microorganism external to the individual which do not exist as normal flora
Ex. Salmonella typhi –
Typhoid fever
Endogenous Infection: - Endogenous infection occurs when
part of the patient’s normal flora becomes altered (virulent) and also increase
in number it will become opportunistic infection. Ex. Streptococci in mouth
E. coli in intestine
as normal flora which may cause UTI. When it reach the urinary bladder.
Sites and causes for cross infection: -
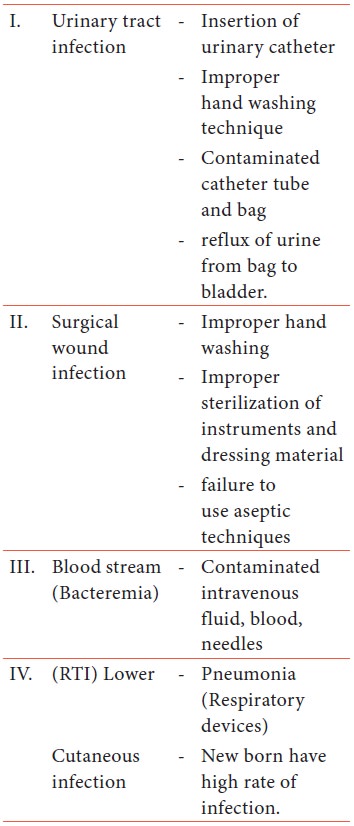
Risk factors for infection
·
Broken skin or mucous membrane Obstructed urine outflow
·
Decreased mobility
·
Reduced hemoglobin level
Related Topics