Definition, Types, Methods used for identification of microbes, Types of specimen collection - Micro organism | 11th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Nursing - Infection Control
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Nursing - Infection Control
Micro organism
Micro organism
Definition
Microorganism or microbe is a
living thing that is too small which is invisible to the naked eye but it can
be visible under microscope. The study of microbes is called as microbiology.
Microorganisms are divided into seven types.
·
Bacteria
·
Archea
·
Protozoa
·
Algae
·
Fungi
·
Viruses
·
Multi
cellular animal parasites (helminthes)
Each type has a characteristic
cellular composition morphology, motility or locomotion, reproduction.
Bacteria are prokaryotic organism.
(single celled microbes). The cell structure is simple than that of other
organism. Bacteria are classified into many groups according to the Morphology
of Bacteria:
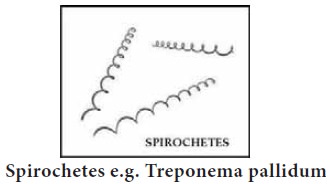
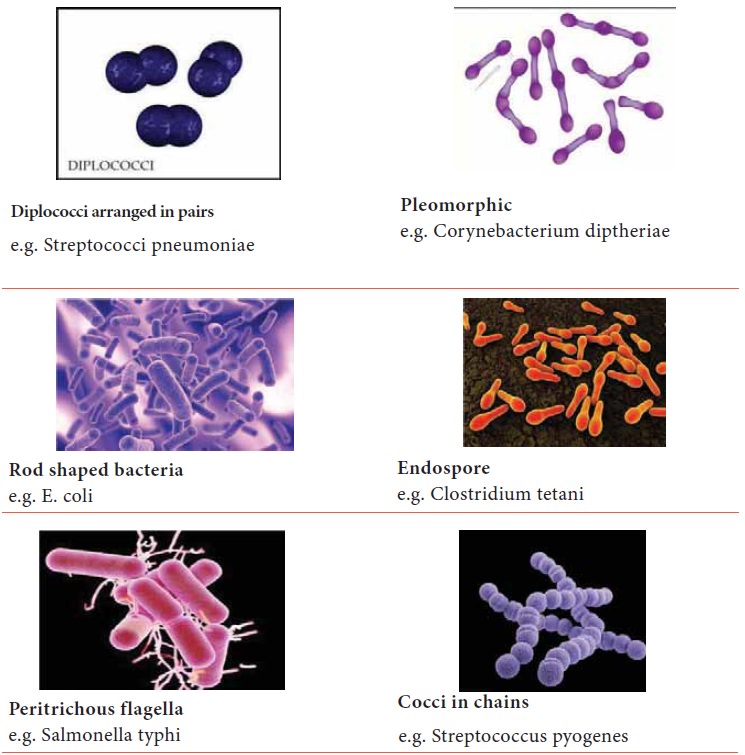
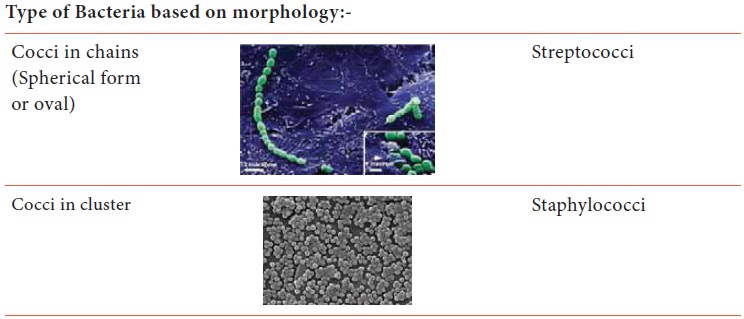
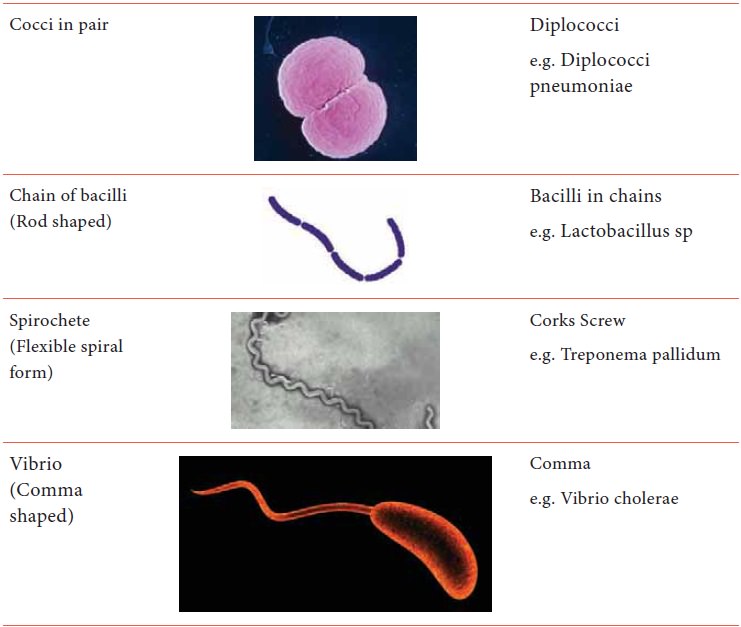
Type of Bacteria based on morphology:-
Bacteria can be divided into two,
1.
Beneficial bacteria
2.
Harmful
bacteria (pathogenic bacteria)
Beneficial bacteria in the body is
plays an important role in human survival. Bacteria in the digestive system
break down the food substance and produce Vitamin K (E.coli.) Beneficial bacteria are also called probiotics. The normal
flora are bacteria which are found in or on bodies. The presence may be
temporary or permanent basis without causing any disease.
Harmful bacterial infection
Harmful bacteria are called
pathogenic bacteria because they cause disease and illness in human and
animals.
Classification of bacteria into
gram positive and gram negative based on the cell wall composition.
Gram positive cocci in chains –
Streptococcus pyogenes
Gram positive cocci in Clusters –
Staphylococcus aureus
Gram negative Cocci in pairs–
Neisseria meningitis
Gram positive Bacilli in chains
other bacteria – Bacillus anthracis
Acid fast bacilli – Mycobacterium
tuberculosis
Endospore forming – Clostridium
tetani
Pleomorphic – Corynebacterium
diphtheria
Gram Negative Bacilli –
Escherichia coli When bacteria is present in our
When bacteria is present in our
body in the absence of disease is called as colonizer. However people can get
infection from Pathogenic bacteria through contaminated water, food and air
Skin infection:-
The organism most commonly found
in the skin and mucous membrane. It cause superficial and systemic infections.
e.g. Staphylococcus aureus
Superficial: Boils, impetigo, foliculitis, Pneumonia, Food poisoning, bacteremia.
Respiratory tract infection: - The organism which is more found in the mouth as a normal flora. The infection
may be in the upper tract or lower respiratory tract.
Ex. Streptococcus pyogenes
Upper Respiratory tract – Sore
throat Laryngitis Pharyngitis
Lower Respiratory tract –
Pneumonia and Tuberculosis
Gastro intestinal infection: -
Many different species of gram
negative bacilli normally found in the intestinal tract. It cause inflammation
of the gastrointestinal tract involving both stomach and the small intestine.
Symptoms include diarrhoea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Genitourinary tract infection: -
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is
an infection in any part of urinary system kidney, uterus, bladder, urethra.
However, serious consequences can occur if a UTI spreads to your kidney.
Lower urinary tract – Cystitis
Upper urinary tract –
Pyelonephritis
The most commonly UTI causing
organism is Escherichia coli
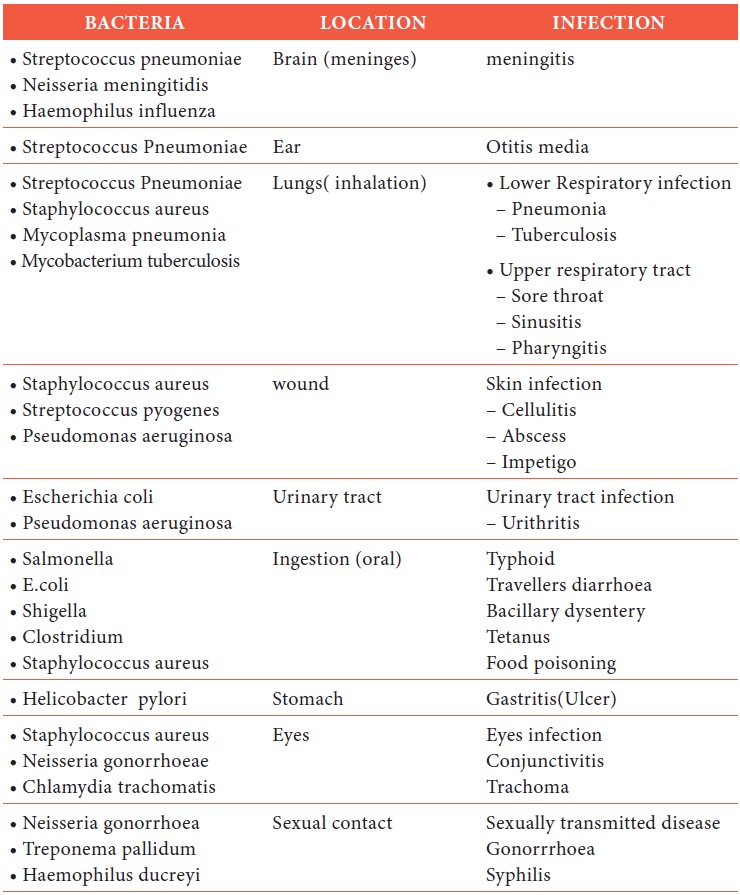
Bacterial Infection
Viruses
Viruses are obligatory
intracellular parasites. They multiply by using the host cells. Synthesizing
machinery to cause the synthesis of specialized elements that can transfer the
viral nucleic acid to other cells. They are ultra-microscopic structure and are
not visible in ordinary microscope. They are visible only under electron
microscope.
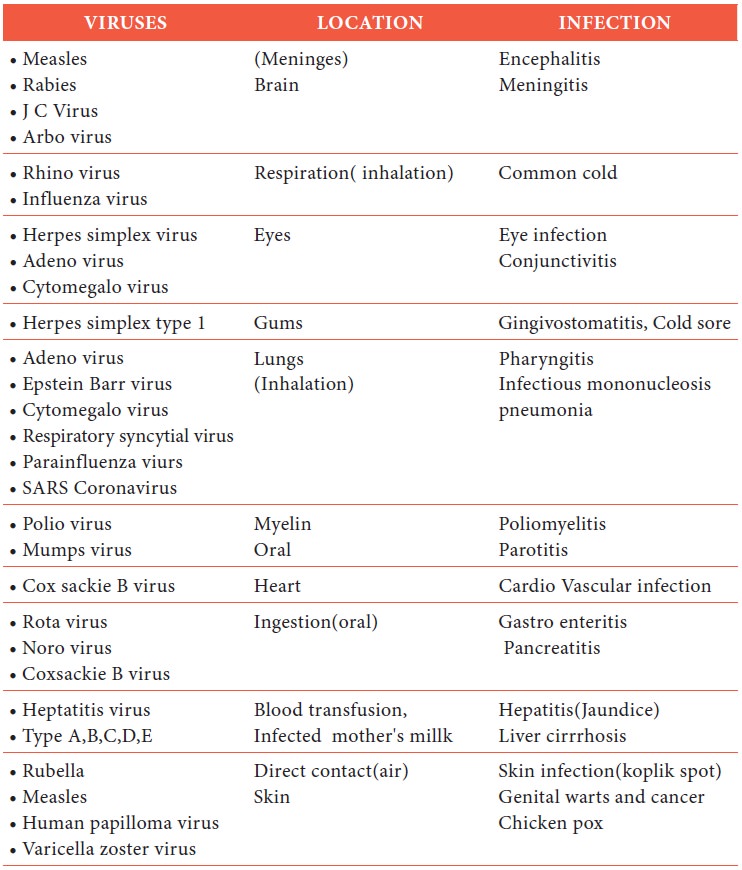
Viral Infection
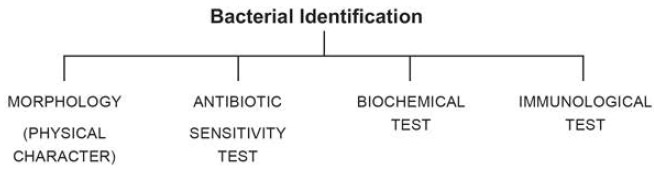
Methods used for identification of microbes:-
Bacteria are single
celled microorganism and are invisible to naked eye. Bacterial identification
is a necessary part of disease diagnosis and treatment without the
identification of causative bacteria is very tough to provide effective
treatment with available antibiotics.
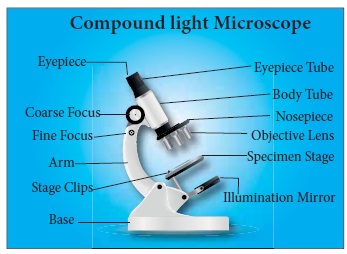
Identification by morphology:-
Microscope is used to
magnify the object and structure. In compound light microscopy which uses two
sets of lenses, ocular, and objective lens. We calculate the total
magnification of an object by multiplying the magnification of the objective
lens and magnification of the ocular lens.
1.
The compound light microscope uses visible light.
2.
The maximum resolving power (ability to distinguish two points)
of a compound light microscope is 0.2 μm
3.
Oil immersion lens is used to reduce the light loss and
increases the resolving power.
Types of Microscope:-
·
Bright field microscope
·
Dark field microscope
·
Phase contrast microscope
·
Flourescence microscope
·
Electron microscope
Compound Light Microscope
Electron Microscope:
Electron microscope
use beam of electrons and it has the magnification power of 10,000 to 1,00,000 x. It
is used to view ultra-structure of viruses and other organisms

Preparation of specimens for light microscopy: -
Preparing smears and staining:
·
A smear is a thin film of material used for microscopic
examination. Place a drop of saline or distilled water and mix the specimen
with a sterile inoculation loop.
·
Spread the specimen uniformly on the slide.
·
Fixing uses air and heat to attach microorganisms on a slide.
Staining: -
·
Gram staining method
·
Acid-fast staining method
Fixing:
After smear
preparation the glass slide should show for 2 to 3 times in a flame. Due to
flaming the specimen get fixed perfectly on a slide and also some chemicals
like formalin, Methyl alcohol, Mercuric chloride is used for fixing the
specimen.
Stains: - Stains is used to make cellular shapes and
arrangements visible. For e.g. The stains used in gram staining – Crystal violet, saffranin)
(decolorizer -Ethyl
alcohol, Mordant agent – grams Iodine).
Hanging Drop Method: - (Glass slit method).
In hanging drop
method, a drop of culture is made to hang between glass slide and slit and
viewed under microscope.
The advantage of
hanging drop method is we can identify mobile bacteria. Some bacteria have
flagella for motility. e.g. Monotrichous, Peritrichous flagella (e.g. Proteus)
By cultural characteristics: -
Here bacteria are
identified as group or culture as a whole and note individual bacteria some
most bacteria grow in colonies and also divide fast. They can be easily grown
into a culture in suitable nutrition media. Based on the characteristics of
culture they can be identified as the size of colonies, type of elevation,
margins, surface of colony, colour of culture.
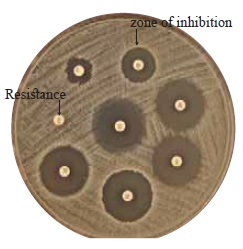
Based on Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotics
(Ex-Penicillin) is added to the culture and measuring the resistance of
microbe. The zone of inhibition surrounding the antiobiotic disc indicating
sensitivity
No zone of inhibition
surrounding the antibiotic disc indicating resistance.
By Biochemical test: -
Sugar fermentation
test
·
Litmus milk test
·
Indole production test
·
Methyl Red test
·
Citrate utilization test
By differential staining: -
The identification
depends on staining of bacteria. And most bacteria can be stained by specific
stain like crystal violet. Gram positive bacteria are stained by gram stain
while Gram negative bacteria don’t take up gram stain.
Mycobacterium
tuberculosis bacteria can be stained by acid fast staining method.
Serological methods: - Here identification of bacteria is done by
use of antibodies and antigens which are specific against the suspected
bacteria. Antigens and antibodies are very specific and bind to single type of
bacteria.

Identification of
bacteria is necessary to
·
Identify the disease
·
Select suitable drug
·
Evaluation of treatment progress
·
For industrial purpose.
·
Storage
Types of specimen collection
Swabs: - It is usually collected in a sterile cotton swab, care
should be taken so as to prevent contaminations of specimen. (e.g. Throat swab,
Eye, Ear, Nose, Mouth, Vaginal, Abscesses swab). Materials should be taken only
from the infected area.
Sputum: - It should be collected in a sterile container
having wide mouth. Sputum should be collected directly after a cough and sent
immediately to the laboratory.
Urine: - Urine specimen remains an important tool for
clinical diagnosis. A correct urine result is influenced by the collection
method, timing and handling (first morning sample, random sample). It should be
collected in a sterile container.
Faeces: - Fresh stool should be collected for bacteriological
examination. Specimen should be well covered and labelled.
For culture and
parasite examination the specimen must be returned to the laboratory within one
hour of collection.
Blood: - It is important that specimens are properly
collected, prepared and preserved. When assisting the physician should adopt
aseptic precautions so as to avoid contamination of specimen.
Always collect the blood
specimen in hygienic area. Blood is carefully transfer from the syringe to the
tube and gently invert 2-3 times to thoroughly mix the anticoagulant with the
blood (heparin)
Related Topics