Definition, Disinfection, Methods | Infection Control - Sterilization | 11th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Nursing - Infection Control
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Nursing - Infection Control
Sterilization
Sterilization:-
Definition
It is a process of
making something free from bacteria or other living organism either in
vegetative or spores. The removal of all microorganism from an object or
surface.
Disinfection
The process of
cleaning something. Especially with a chemical in order to destroy or kill
bacteria, but not necessarily spores.
·
Physical method
·
Chemical method Radiation
·
Filtration
·
Mechanical
Methods of disinfection and Sterilization:
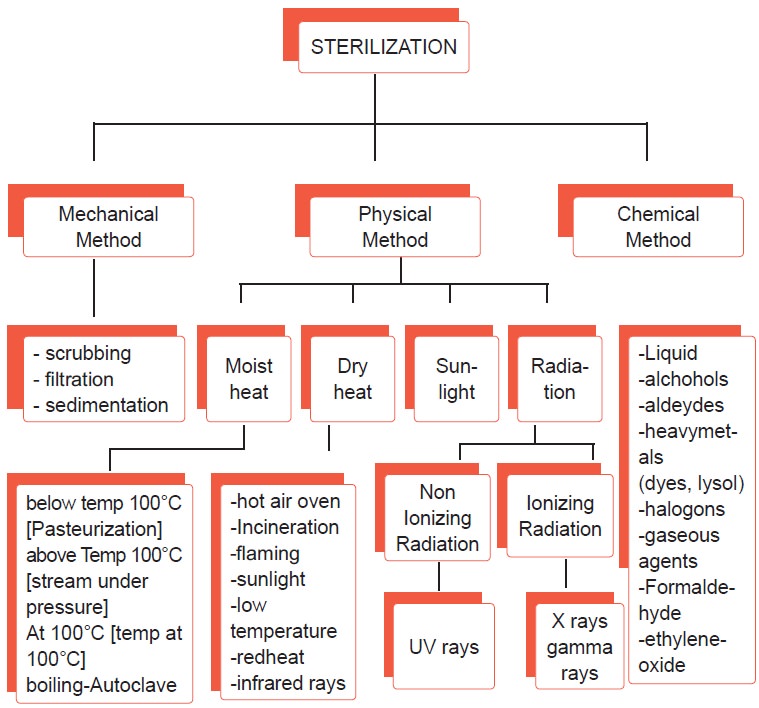
. . . Mechanical Method
Scrubbing: Hand washing is one of the important procedures
of a nurse in order to control and prevent self-infection as well as cross
infection.
Filtration: Filtration is the passage of a liquid fluid or gases
through a filter with pores small enough retain microbes – vaccine, toxins, enzymes.
e.g. - HEPA filter,
Membranes filters (nitrocellulose)
Sedimentation: - It is used in the purification of water by this method the suspending material
together with bacteria settles down in the bottom of liquid.
. . . hysical methods
Sunlight: Sunlight contains UV rays which cause thymine
dimer in the DNA of bacterial cells. These UV says stops the replication of DNA
in bacterial cells. These rays has more antimicrobial action e.g. Blanket,
Pillows.
Dry heat: -
Direct flaming: -
·
Very effective method of sterilization.
·
Burning contaminants to ashes.
·
This is used to sterilizing inoculation loops and sterilizing
needles and instruments killing organisms.
Incineration: All hospital wastages like dressing,
garbage, contaminated materials are completely bunt by incineration. It is very
effective to kill all organism.
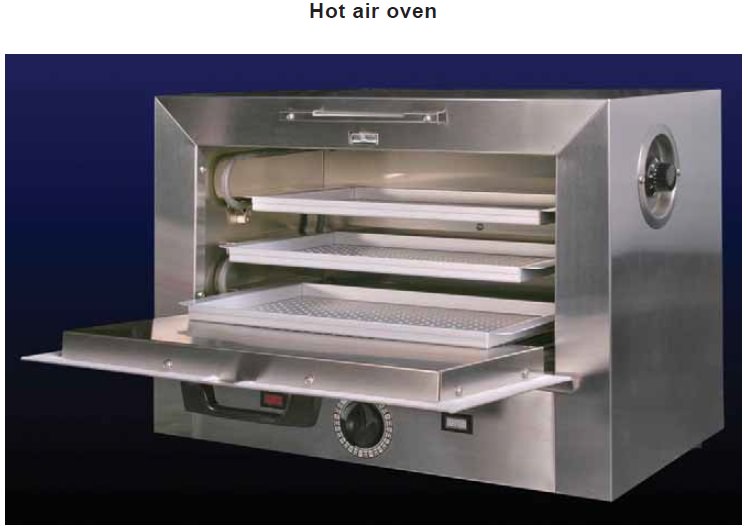
Hot air oven: This instrument is used to sterilize
glassware, syringes, needles, culture tubes and enhance the growth of micro
organism in culture media The vegetative forms of bacteria can be killed by
this at 160°C for1 hour.

Moist heat Sterilization
Boiling: At a temperature of 100°C boiling for 3 to 5 minutes
kill microorganisms except spore bearing organisms.
·
This method is suitable for enamel, metal, glass, rubber wares.
Points to remember
·
The article must be cleaned by scrubbing to remove the organic
matter.
·
Great care should be taken for glass articles and they should be
wrapped with cloth and put in cold water and then brought to boil.
·
The organic matter which will coagulate around the organism and
protect them.
·
Testing material to check effectiveness of sterilization.
Autoclaving (Above 100°C temperature)
Spore bearing organism
Ex. Clostridium tetani are killed by steam under pressure.
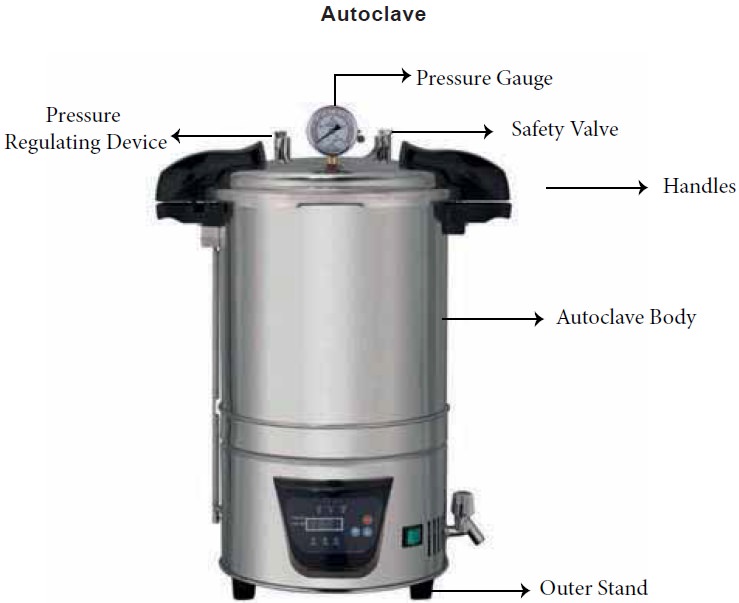

Autoclave is an apparatus used for
sterilization of articles by steam under pressure.
·
It
is a metal chamber with an outer jacket and a lid, which can be firmly clamped.
Steam is generated by heating water in a boiler or in the outer jacket.
In this the steam is allowed to
circulate in a closed container and it is compressed and there by raises the temperature
above the boiling point of water (at 121°C for 15 to 30 minute). Then the heat
is turned off. The steam is evacuated.
Ses
The materials sterilized by
autoclaving method are dressing, gloves, lines, syringes, certain instruments
and culture Medias.
points to remember
·
All
articles should be clean and dry before packing. Any organic matter such as
blood or pus prevents penetration of steam.
·
The
holes in drum must be open when placing into the auto clave, and closed
immediately on taking them out.
·
Rubber
gloves cannot stand high temperature and long sterilizing. Autoclave those
separately at 15 lbs. pressure for 15 minutes.
·
To
auto clave bottles of fluids loosen the screw caps, evacuate the steam slowly.
Pasteurization: (Temperature at 62.8°C)
In pasteurization a high
temperature is used for a short time (72°C for 15 minutes) to destroy pathogens
without altering the flavor of the food. This process is used to kill all the
pathogenic organisms in milk, cream, and certain alcoholic beverages.
Chemical Methods
Certain chemicals are
used in disinfection of articles like thermometer and also the disinfection of
floor and de-contamination of infected linen.
Chemical Substance which are commonly used:
1.
Dettol: This is widely used chemical for Sterilization of
instruments, thermometer etc. 5 to 50% of solution is used for drawings and
wound irrigation.
2.
Savlon: 1:30 solution is used to destroy or kill vegetative
bacteria.
3.
Chloride of lime (bleaching powder): This is used for
disinfection of drinking water, stools, urine, sputum. As it decomposes quickly
when exposed to air. Solutions must be prepared fresh for each use.
4.
Formalin: - A 40% solution is used to disinfect faces, urine and
sputum. It is not used for the skin and tissue, as it is an irritant.
5.
Tincture of Iodine: - 1-2% iodine is used for cleaning skin and
treating injuries to the skin.
6.
Hydrogen peroxide: 1-5% of solution is used in cleaning wounds
and to remove pus from infected ears. Hydrogen peroxide is also used to clean
the mouth. It is an oxidizing agent.
7.
Potassium Permanganate: - It is an oxidizing agent used for
cleaning the mouth with 1:1000 strength. It is also used for irrigation of
wounds.
8.
Carbolic acid (Phenol): - It is a good designating for feces,
pus, blood and sputum. It is a skin irritant and a poison. Dissolves early in
hot water. For thermometer 1:20 solution for a duration of 10 minutes.
9.
Lysol: This is a phenol preparation mixed with soap. It is less
poisonous than a carbolic acid but has a greater bactericidal action. 2% of
solution for 6-8 hours is wed for disengaging livens.
10. Ethyl Alcohol: 70% is
effective for skin disinfection. Certain gases like formaldehyde and
glutaral-dehyde are used in disinfection of rooms.
Radiation
The effects of
radiation depend on its wave length, intensity, duration.
Ionizing radiation
·
Gamma rays and
x-rays are both types of high energy electron (high
frequency ) electromagnetic radiation
·
These rays can cause destruction of the DNA in microbes.
·
The principal effect of ionizing radiation is the ionization of
water, which forms highly reactive hydroxyl radicals.
on Ionizing radiation rays
UV light damages the
DNA of the exposed cells. It causes bonds to form between adjacent thymine
dimers in DNA chain and inhibit replication.
USES
The radiations are
used for sterilizing pharmaceutical and medical dental carries. (cold
sterilization)
·
Practical application is the UV lamp (germicidal property) in
the microbiological laboratories.
Fumigation (or) Gas Sterilization
Fumigation is a
process of gaseous sterilization which is used for killing of microorganisms
and prevention of microbial growth in air, surface of wall or floor.
·
It is generally used in the pharmaceutical, operation theatres.
Hospitals, and offices.
·
For effective fumigation process is done according to the
density. Humidity 60% and temperature never below 18° C in opened area around
at a time of 1 hour to o16 hours it may be differ the gas kill all the spores,
vegetative cells etc.,
Gaseous agents
·
Formaldehyde
·
Ethylene oxide
·
Glutaraldehyde
·
Propiolactone
Disadvantage: These gas may cause irritant to the eyes, and mucous membranes and un wanted odors.
Low temperature:
Cold has the effect of
decreasing or completely stopping the growth of bacteria constant freezing will
destroy and inhibit the growth of bacteria.
In freeze condition
the organisms growth may be delayed or inhibited. The organisms can be
destroyed often is freeze conditions.
Principles to be observed:
1.
All articles contaminated with blood, feces, pus, sputum or
other substances must be rinsed with cold water to prevent coagulation of
protein material.
2.
Use soap and water for cleaning the instruments and use a brush
whenever necessary.
3.
Allow sufficient time for articles to be disinfected or
sterilized by physical or chemical agents.
4.
It is importance to select the right disinfectant, the right
strength and the right time.
5.
Use the right procedure to render instruments and other articles
safe for further use in order to prevent the spread of infection.
Related Topics