Electricity | Chapter 5 | 8th Science - Transfer of Charges | 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Transfer of Charges
Transfer of Charges
As we saw earlier, electrons
(negative electric charges) in the outermost orbit of an atom can be easily
removed. They can be transferred from one substance to another. The substance
which gains electrons become negatively charged and the substance which looses
electrons becomes positively charged. Transfer of charges takes place in the
following ways.
* Transfer by Friction
* Transfer by Conduction
* Transfer by Induction
1. Transfer by
Friction
Activity 1
Take a comb and place
it near some pieces of paper. Are they attracted by the comb? No. Now comb your
dry hair and place it near them. What do you see? You can see that the paper
pieces are attracted by the comb now. How is it possible?

Answer: Comb attracts a bits of paper because Comb is charged object
and paper is in neutral so, to be charged one must be in neutral and Comb is
negative charged as it gains electrons from hair. Since ,when Comb is placed
near to a bits of paper then papers get charged due to induction.
Comb rubbed with hair gains
electrons from the hair and becomes negatively charged. These electrons are
accumulated on the surface of the comb. When a piece of paper is teared into
bits, positive and negative charges are present at the edges of the bits.
Negative charges in the comb attract positive charges in the bits. So, the
paper bits are moving towards the comb. While combing hair, charges are
transferred from the hair to comb due to friction. If the hair is wet, the
friction between the hair and the comb reduces which will reduce the number of
electrons transferring from hair to comb. Hence, rubbing certain materials with
one another can cause the build-up of electrical charges on the surfaces. From
this it is clear that charges are transferred by friction.
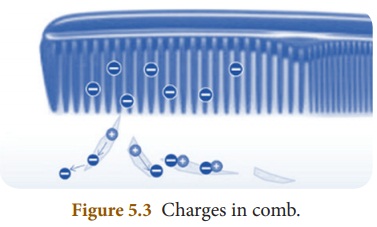
A neutral object can
become positively charged when electrons get transferred to another object; not
by receiving extra positive charges.
Similar effect can be seen when we
rub few materials with one another. When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk
cloth the free electrons in the glass rod are transferred to silk cloth. It is
because the free electrons in the glass rod are less tightly bound as compared
to that is in silk cloth. Since the glass rod looses electrons, it has a
deficiency of electrons and hence acquires positive charge. But, the silk cloth
has excess of electrons. So, it becomes negatively charged.
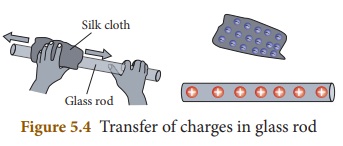
When an ebonite rod (rod made by
vulcanized rubber) is rubbed with fur, the fur transfers electrons to the
ebonite rod because the electrons in the outermost orbit of the atoms in fur
are loosely bound as compared to the ebonite rod. The ebonite rod which has
excess electrons becomes negatively charged and the fur which has deficiency of
electrons is positively charged.
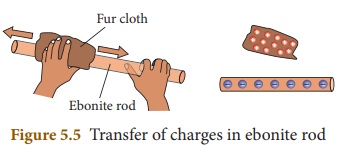
From these we know that when two
materials are rubbed together, some electrons may be transferred from one
material to the other, leaving them both with a net electric charge.
If a positively
charged glass rod is brought near another glass rod, the rods will move apart
as they repel each other. If a positively chargedglass rod is brought close to
a negatively charged ebonite rod, the rods will move toward each other as they
attract. The force of attraction or repulsion is greater when the charged
objects are closer.
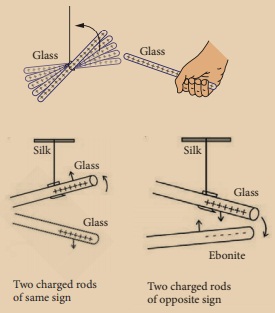
2. Transfer by
Conduction
Activity 2
Take a sheet of paper.
Turn it into a hollow cylinder. Tie one end of the cylinder with a silk thread
and hang it from a stand. Now take an ebonite rod and charge it by rubbing it
with a woollen cloth. Bring this charged ebonite rod near the paper cylinder.
The cylinder will be attracted by the rod. If you touch the paper cylinder by
the charged rod, you will see the paper cylinder repelling the rod. Can you say
the reason?
Answer: When the cylinder is touched by the rod, some negative charges are
transferred to the paper. Hence, the negative charges in the rod are repelled
by the negative charges in the cylinder.
When the ebonite rod is rubbed with
woollen cloth, electrons from the woollen cloth are transferred to the ebonite
rod. Now ebonite rod will be negatively charged. When it is brought near the
paper cylinder, negative charges in the rod are attracted by the positive
charges in the cylinder. When the cylinder is touched by the rod, some negative
charges are transferred to the paper. Hence, the negative charges in the rod
are repelled by the negative charges in the cylinder.
Thus, we can say that charges can be
transferred to an object by bringing it in contact with a charged body. This
method of transferring charges from one body to other body is called transfer
by conduction.
The materials which allow
electric charges to pass through them easily are called conductors of electricity.
For example,metals like aluminium, copper are good conductors of electricity.
Materials which do not allow electric charges to pass through them easily are
called insulators. Rubber, wood and plastic are insulators.
3. Transfer by
Induction
We saw that we can charge an
uncharged object when we touch it by a charged object. But, it is also possible
to obtain charges in a body without any contact with other charged body. The
process of charging an uncharged body by bringing a charged body near to it but
without touching it is called induction. The uncharged body acquires an
opposite charge at the near end and similar charge at the farther end.
Activity 3
Bring a negatively
charged plastic rod near a neutral rod. When the negatively charged plastic rod
is brought close to the neutral rod, the free electrons move away due to
repulsion and start piling up at the farther end. The near end becomes
positively charged due to deficit of electrons. When the neutural rod is
grounded, the negative charges flow to the ground. The positive charges at the
near end remain held due to attractive forces and the electrons inside the
metal becomes zero. When the rod is removed from the ground, the positive
charges continue to be held at the near end. This makes the neutral rod a positively
charged rod.
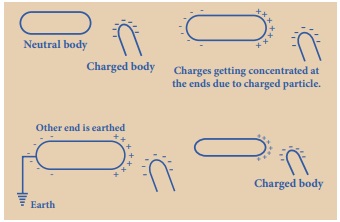
Similarly, when a positively charged
rod is brought near an uncharged rod, negatively charged electrons are
attracted towards it. As a result there is excess of electrons at nearer end
and deficiency of electrons at the farther end. The nearer end of the uncharged
rod becomes negatively charged and far end is positively charged.
Related Topics