Electricity | Chapter 5 | 8th Science - Questions Answers | 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Questions Answers
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
I. Choose the best answer.
1.
When an ebonite rod is rubbed with fur, the charge acquired by the fur is
a. negative
b. positive
c. partly positive and partly
negative
d. None of these
[Answer: (b) positive]
2.
The electrification of two different bodies on rubbing is because of the
transfer of
a. neutrons
b. protons
c. electrons
d. protons and neutrons
[Answer: (c) electrons]
3.
Which of the following a simple circuit must have?
a. Energy source, Battery, Load
b. Energy source, Wire, Load
c. Energy source, Wire, Switch
d. Battery, Wire, Switch
[Answer: (d) Battery, Wire, Switch]
4.
An electroscope has been charged by induction with the help of charged glassrod.
The charge on the electroscope is
a. negative
b. positive
c. both positive and negative
d. None of the above
[Answer: (b) positive]
5.
Fuse is
a. a switch
b. a wire with low resistance
c. a wire with high resistance
d. a protective device for breaking
an electric circuit
[Answer: (d) a protective device for breaking an
electric circuit]
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Transfer of electron takes place by rubbing
objects together.
2. The body which has lost electrons
becomes
3. Lightning arrestor is a device that protects
building from lightning strike.
4. Electric fuse has a thin metallic
filament that melts and breaks the connection when the circuit is overheated.
5. Three bulbs are connected end to end
from the battery. This connection is called
III. State true or false. If false, correct the statement.
1. The charge acquired by an ebonite
rod rubbed with a piece of flannel is negative.
2. A
charged body induces an opposite charge on an uncharged body when they are
brought near.
3. Electroscope
is a device used to charge a body by induction.
4. Water
can conduct electricity.
5. In
parallel circuit, current remains the same in all components.
Correct statement: In parallel circuit, voltage
remains the same in all components.
IV. Match the
following.
Two
similar charges - acquires a positive charge
Two dissimilar charges - prevents a
circuit from overheating
When glass rod is rubbed with silk -
repel each other
When ebonite rod is rubbed with fur - attract
each other
Fuse - acquires a negative charge
Answer:
Two similar charges : repel
each other
Two dissimilar charges : attract
each other
When glass rod is rubbed with silk : acquires a positive charge
When ebonite rod is rubbed with fur : acquires a negative charge
Fuse : prevents a circuit
from overheating
V. Give reason for the following.
1. When
a glass rod is rubbed with silk cloth both get charged.
Answer:
Reason : When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth the free electrons
in the glass rod are transferred to silk cloth. It is because the free
electrons in the glass rod are less tightly bound as compared to that in silk
cloth. Since the glass rod looses electrons, it has a deficiency of electrons
and hence acquires positive charge. But, the silk cloth has excess of
electrons. So, it becomes negatively charged.
2.
When a comb is rubbed with dry hair it attracts small bits of paper.
Answer:
Reason: Comb rubbed with hair gains electrons from the hair and
becomes negatively charged. These electrons are accumulated on the surface of
the comb. When a piece of paper is teared into bits, positive and negative
charges are present at the edges of the bits. Negative charges in the comb
attract positive charges in the bits. So, the paper bits are moving towards the
comb.
3.
When you touch the metal disc of an electroscope with a charged glass rod the
metal leaves get diverged.
Answer:
Reason : The leaves of an electroscope diverge because when a glass rod
is touched on the metal disc, the charge travels through the metal rod to the
leaves. Since, like charge repel, the charge travels till the leaves and then
open up as both the leaves have like charges.
4.
In an electroscope the connecting rod and the leaves are all metals.
Answer:
Reason: These are made of metals
so that the electrons become free to move.
5.
One should not use an umbrella while crossing an open field during
thunderstorm.
Answer:
Reason:
(i) Carrying an umbrella is not advisable during thunderstorm.
(ii) As the rod of umbrella and its supporting wires are made up
of metals.
(iii) Thus during thunderstorm, the conducting object should be
avoided.
VI. Consider the statements given below and choose the correct
option.
a. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c. Assertion is true but reason is false.
d. Assertion is false but reason is true.
1.
Assertion: People struck by
lightning receive a severe electrical shock.
Reason: Lightning carries very high
voltage.
[Answer: (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the
correct explanation of assertion.]
2.
Assertion: It is safer to
stand under a tall tree during lightning
Reason: It will make you the target for lightning.
[Answer: The assertion is false but reason is true]
VII. Answer briefly.
1.
How charges are produced by friction?
Answer: Rubbing certain materials with one another can cause the built-up of
electrical charges on the surfaces. So charges are produced by friction. Eg.:
Combing hair charges are transferred from the hair to comb due to friction.
2.
What is earthing?
Answer: Earthing is the process of connecting the exposed metal parts of an
electrical circuit to the ground.
3.
What is electric circuit?
Answer: The path through which electrons flow from one terminal to another
terminal of the source, is called electric
circuit.
4.
What is electroplating?
Answer: The process of depositing a layer of one metal over the surface of
another metal by passing electric current is called electroplating.
5.
Give some uses of electroplating.
Answer: Electro plating is applied in many fields :
(i) We use iron in bridges and automobiles to provide strength.
(ii) A coating of zinc is deposited on iron to protect it from
corrosion and formation of rust.
(iii) Chromium has a shiny appearance. It does not corrode.
(iv) It resists scratches.
VIII. Answer in detail.
1.
Explain three ways of charge transfer.
Answer:
Transfer of charges takes place in the following three ways.
Transfer by Friction
Transfer by Conduction
Transfer by Induction
(a) Transfer
by Friction : This method of charging
an uncharged body by rubbing it against another body is called charging by
friction. Eg.: While combing hair charges are transferred from the hair to comb
due to friction.
(b) Transfer
by conduction : Charges can be
transferred to on object by bringing it in contact with a charged body. This
method of transferring charges from one body to other body is called transfer by conduction. Eg. : When the
ebonite rod is rubbed with woollen cloth, electrons from the woollen cloth are
transferred to the ebonite rod. Now ebonite rod will be negatively charged.
(i) When it is brought
near the paper cylinder, negative charges in the rod are attracted by the
positive charges in the cylinder.
(ii) When the cylinder is touched by the rod, some negative
charges are transferred to the paper. Hence, the negative charges in the rod
are repelled by the negative charges in the cylinder.
(c)
Transfer by Induction : The process of
charging an uncharged body by bringing a charged body near to it but without
touching it is called induction. Eg.: we can charge an uncharged object when we
touch it by a charged object. But, it is also possible to obtain charges in a
body without any contact with other charges.
2.
What is electroscope? Explain how it works.
(i) An electroscope is a scientific instrument used to detect
the presence of electric charge on a body.
(ii) An electroscope is made out of conducting materials,
generally metal.
(iii) It works on the principle that like charges repel each
other.
(iv) In a simple electroscope two metal sheets are hung in
contact with each other.
(v) They are connected to a metal rod that extends upwards, and
ends in a knob at the end.
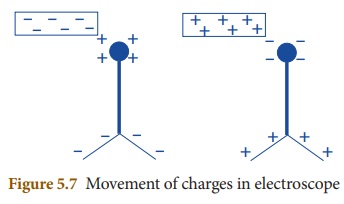
(vi) If you bring a charged object near the knob, electrons will
either move out of it or into it.
(vii) This will result in charges on the metal leaves inside the
electroscope.
(viii) If a negatively charged object is brought near the top
knob of the electroscope, it causes free electrons in the electroscope to move
down into the leaves, leaving the top positive.
(ix) Since both the leaves have negative charge, they repel each
other and move apart.
(x) If a positive object is brought near the top knob of the
electroscope, the free electrons in the electroscope start to move up towards
the knob.
(xi) This means that the bottom has a net positive charge. The
leaves will spread apart again.
3.
Explain series and parallel circuit.
Answer:
Series
Circuit
(i) A series circuit is one that has more than one resistor
(bulb) but only one path through which the electrons can travel.
(ii) From one end of the battery the electrons move along one
path with no branches through the resistors (bulbs) to the other end of the cell.
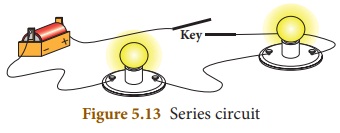
(iii) All the components in a series circuit are connected end
to end.
(iv) So, current through the circuit remains same throughout the
circuit.
(v) But, the voltage gets divided across the bulbs in the
circuit.
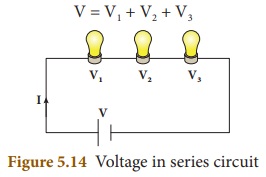
(vi) In the following
series circuit two bulbs are used as resistors.
(vii) Let I be the current through the circuit and V1,V2,
V3 be the voltage across each bulb.
(viii) The supply voltage V is the total of the individual voltage drops across the resistances. V= v1 + v2 + v3
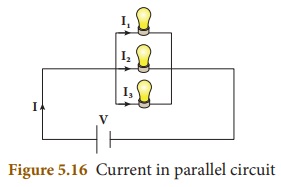
Parallel
Circuit:
(i) In a parallel circuit, there is more than one resistor
(bulb) and they are arranged on many paths.
(ii) This means charges (electrons) can travel from one end of
the cell through many branches to the other end of the cell.
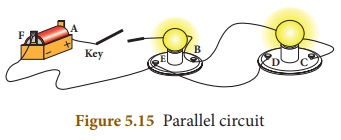
(iii) Here, voltage across the resistors (bulbs) remains the
same but the current flowing through the circuit gets divided across each
resistor.
(iv) Let us consider three bulbs connected in series.
(v) Let V be the voltage across the bulbs and I1,I2,I3
be the current across each bulb.
(vi) The current I from the battery is the total of the
individual current flowing through the resistances. I = I1+I2+I3
4.
How lightning takes place?
Answer:
(i) Lightning is produced by discharge,of electricity from cloud
to cloud or from cloud to ground.
(ii) During thunderstorm air is moving upward rapidly.
(iii) This air which moves rapidly, carries small ice crystals
upward.
(iv) At the same time, small water drops move downward.
(v) When they collide, ice crystals become positively charged
and move upward and the water drops become negatively charged and move
downward.
(vi) So the upper part of the cloud is positively charged and
the lower part of the cloud is negatively charged.
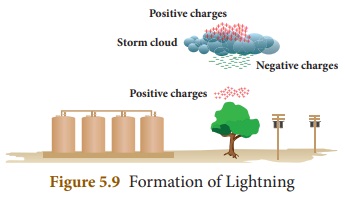
(vii) When they come into contact, electrons in the water drops
are attracted by the positive charges in the ice crystals. Thus, electricity is
generated and lightning is seen.
(viii) Sometimes the lower part of the cloud which is negatively charged comes into contact with the positive charges accumulated near the mountains, trees and even people on the earth. This discharge produces lot of heat and sparks that results in what we see as lightning.
5.
What is electroplating? Explain how it is done.
Answer:
Electroplating
(i) Electroplating is one of the most common applications of
chemical effects of electric current.
(ii) The process of depositing a layer of one metal over the
surface of another metal by passing electric
current is called electroplating.
(iii) Take a glass jar and fill it with copper sulphate
solution.
(iv) Take a copper metal plate and connect it to the positive
terminal of battery.
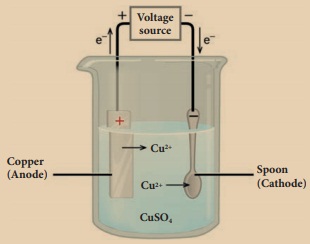
(v) Connect an iron spoon to the negative terminal of the
battery.
(vi) Now, dip them in the copper sulphate solution.
(vii) When electric current is passed through the copper
sulphate solution, you will find that a thin layer of copper metal is deposited
on the iron spoon and an equivalent amount of copper is lost by the copper
plate.
Related Topics