Electricity | Chapter 5 | 8th Science - Points to Remember, Glossary, Concept Map | 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Points to Remember, Glossary, Concept Map
Points to Remember
• Opposite charges attract each
other and like charges repel each other.
• Charges can be transferred from
one region to another region by any of the following ways: Transfer by
friction, Transfer by conduction and Transfer by induction.
• Friction between objects results
in transfer of electrons between them.
• When a charged body touches
another body, charges can be transferred from one body to another.
• Induction is a process of charging
an uncharged body by bringing a charged body near to it but not touching it.
• Electroscope is an instrument used
to detect and measure electric charges.
• Earthing is the process of
connecting the exposed metal parts of an electrical circuit to the ground.
• Lightning arrester is a device
used to protect buildings from the effects of lightning.
• A simple circuit consists of four
elements: a source of electricity (battery), a path or conductor through which
electricity flows (wire), a switch to control the circuit and an electrical
resistor (lamp) which is any device that requires electricity to operate.
• The decomposition of molecules of
a solution into positive and negative ions on passing an electric current
through it is called electrolysis.
• A fuse is a strip of alloy wire
which is made of lead and tin with a very low melting point.
GLOSSARY
1.
Battery A device that
stores and produces electricity from chemical cells.
2.
Circuit The path through
which electric current flows.
3.
Electric charge Basic
property of matter carried by some elementary particles. Electric charge can be
positive or negative.
4.
Electric current Flow of
electric charges through a material.
5.
Electron A tiny particle
which revolves around the nucleus of an atom. It has a
negative charge of electricity.
6.
Electroscope A
scientific instrument used to detect the presence of electric charges on a
metal body.
7.
Friction The resistance that
one surface or object encounters when moving over another.
8.
Fuse A strip of wire that melts and
breaks an electric circuit if the current exceeds a safe level.
9.
Volt Unit of electrical force or electric
pressure.
10.
Voltage An electromotive
force that causes electrons to flow.
REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Concept of physics - HC Verma
2. A Text-Book on Static Electricity
- Hobart Mason
3. Fun With Static Electricity - Joy
Cowley
4. Frank New Certificate Physics.
McMillan Publishers.
INTERNET RESOURCES
1. http://sciencenetlinks.com/lessons/static-electricity-2/
2. https://www.stem.org.uk/resources/
community/collection/13389/static-electricity
3. https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/ estatics
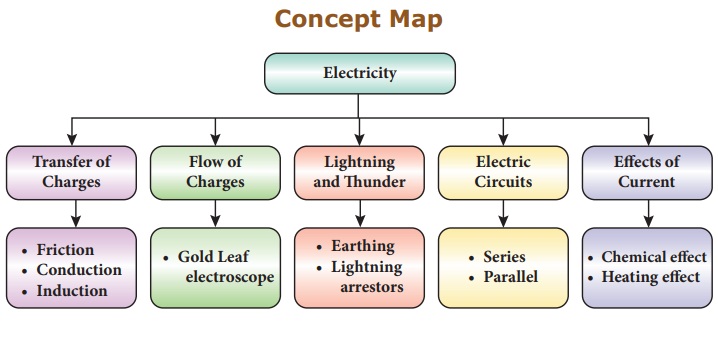
Concept Map
ICT CORNER
Electricity
Through
this activity you will learn the usage of electricity through Interactive
games.

Step
1 Open the Browser and type the URL
given below
Step
2 You will see lot of games which is
related to Electricity
Step
3 Click the Electricity circuits
activity (First activity), you will see the sub topics, like Electricity in
home, Introduction to circuits etc. ..
Step
4 Select the sub topic and play the
game. Likewise play all the games.
Browse in the link:
http://interactivesites.weebly.com/electricity-and-energy.html
*Pictures are indicative only
Related Topics