Electricity | Chapter 5 | 8th Science - Effects of Current | 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Effects of Current
Effects of Current
When current is flowing through a
conductor it produces certain effects. These are known as effects of electric
current. These effects result in conversion of electrical energy into different
forms of energies such as heat energy, mechanical energy, magnetic energy,
chemical energy and so on.
1. Chemical effect of
current
Activity 5
Take two pieces of
wire, an LED light and a battery, and make a simple electric circuit. Take some
water in a glass and put the wires in the water as shown in the figure. Does
the LED bulb glow? What do you understand from this?
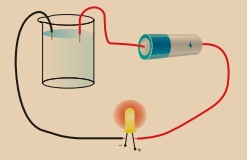
Answer: Yes, the LED bulb glows. From this activity we understood that liquids
also conduct electricity.
We know that electricity is
conducted by metals. This activity shows that liquids also conduct electricity.
When electric current is passed through a conducing solution, some chemical
reactions take place in the solution. This chemical reactions produce electrons
which conduct electricity. This is called chemical effect of electric current.
The decomposition of molecules of a solution into positive and negative ions on
passing an electric current through it, is called electrolysis. Electrolysis
has a number of applications. It is used in extraction and purification of
metals. The most general use of electrolyte is electroplating.
Electroplating
Electroplating is one of the most
common applications of chemical effects of electric current. The process of
depositing a layer of one metal over the surface of another metal by passing
electric current in called electroplating.
Activity 6
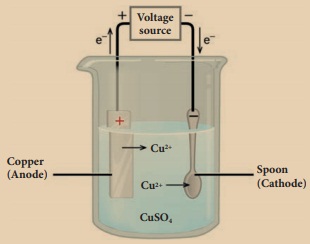
Take a glass jar and
fill it with copper sulphate solution. Take a copper metal plate and connect it
to the positive terminal of battery. Connect an iron spoon to the negative
terminal of the battery. Now, dip them in the copper sulphate solution. When
electric current is passed through the copper sulphate solution, you will find
that a thin layer of copper metal is deposited on the iron spoon and an
equivalent amount of copper is lost by the copper plate.
Electro plating is applied in many
fields. We use iron in bridges and automobiles to provide strength. However,
iron tends to corrode and rust. So, a coating of zinc is deposited on iron to
protect it from corrosion and formation of rust. Chromium has a shiny appearance.
It does not corrode. It resists scratches. But, chromium is expensive and it
may not be economical to make the whole object out of chromium. So, the objects
such as car parts, bath taps, kitchen gas burners, bicycle handlebars, wheel
rims are made from a cheaper metal and only a coating of chromium is deposited
over it.
2. Heating effect of current
Activity 7
Take a battery, a bulb, a switch and few connecting wires. Make an electric circuit as shown in the figure. Keep the switch in the ‘OFF’ position.

Does the bulb glow?
Answer: No, the bulb does not glow.
Now move the electric switch to the ‘ON’ position and let the bulb glow for a minute or so. Touch the bulb now. Do you feel the heat?
Answer: Yes, the bulb is hot because electrical energy is transformed
to heat energy. This is known as heating
effect of electric current.
When electric current passes through
a conductor, there is a considerable ‘friction’ between the moving electrons
and the molecules of the conductor. During this process, electrical energy is
transformed to heat energy. This is known as heating effect of electric
current. The heat produced depends on the amount of resistance offered by the
wire.
Copper wire offers very little
resistance and does not get heated up quickly. On the other hand, thin wires of
tungsten or nichrome which are used in bulbs offer high resistance and gets
heated up quickly. This is the reason why tungsten wire is used in the
filaments of the bulbs and nichrome wire is used as a heating element in
household heating appliances. Heating effect of electric current can be seen in
many devices. Some of them are given below.
Fuse
Fuse is a strip of alloy wire which is made up
of lead and tin with a very low melting point. This can be connected to the
circuit. The fuse is usually designed to take specific amount of current. When
current passing through the wire exceeds the maximum limit, it gets heated up.
Due to low melting point it melts quickly disconnecting the circuit. This
prevents damage to the appliances.

Electric
cookers
Electric cookers turn red hot when
electric current is passed through the coil. The heat energy produced is
absorbed by the cooking pot through conduction.
Electric
kettles
The heating element is placed at the
bottom of the kettle which contains water. The heat is then absorbed by the
liquid and distributed throughout the liquid by convection.
Electric
irons
When current flows through the heating element, the heat energy developed is conducted to the heavy metal base, raising its temperature.This energy is then used to press clothes.
Related Topics