Electricity | Chapter 5 | 8th Science - Electroscope | 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 5 : Electricity
Electroscope
Electroscope
An electroscope is a scientific
instrument used to detect the presence of electric charge on body. In the year
1600, British physician William Gilbert invented the first electroscope. It is
the first electrical instrument. There are two types of electroscope: pith-ball
electroscope and gold-leaf electroscope. An electroscope is made out of
conducting materials, generally metal. It works on the principle that like
charges repel each other. In a simple electroscope two metal sheets are hung in
contact with each other. They are connected to a metal rod that extends
upwards, and ends in a knob at the end.
The first electroscope
developed in 1600 by William Gilbert was called versorium. The versorium was
simply a metal needle allowed to pivot freely on a pedestal. The metal would be
attracted to charged bodies brought near.
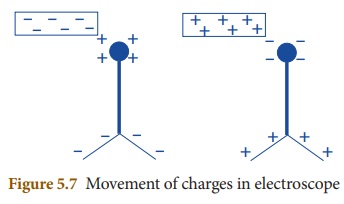
If you bring a charged object near
the knob, electrons will either move out of it or into it. This will result in
charges accumulating on the metal leaves inside the electroscope. If a
negatively charged object is brought near the top knob of the electroscope, it
causes free electrons in the electroscope to move down into the leaves, leaving
the top positive. Since both the leaves have negative charge, they repel each
other and move apart. If a positive object is brought near the top knob of the
electroscope, the free electrons in the electroscope start to move up towards
the knob. This means that the bottom has a net positive charge. The leaves will
spread apart again now.
Gold leaf electroscope
The gold-leaf electroscope was
developed in 1787 by a British scientist named Abraham Bennet. Gold and silver
are used in electroscope because they are the best conductors of electric
current.
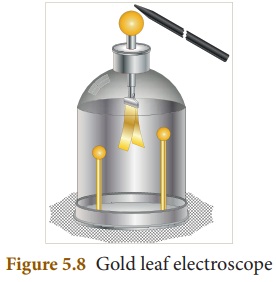
Structure
of Electroscope
It is made up of a glass jar. A
vertical brass rod is inserted into the jar through a cork. The top of the
brass rod has a horizontal brass rod or a brass disc. Two gold leaves are
suspended from the brass rod inside the jar.
Working
of Electroscope
When the brass disc of the
electroscope is touched by a charged object, electric charge gets transferred
to the gold leaf through the rod. This results in gold leaves moving away from
each other. This happens because both the leaves have similar charges.
Charging
Transfer of charge from one object
to another is called charging. In case of the gold leaves, charge is
transferred through the brass rods.
Electrical
discharge
The gold leaves resume their normal
position after some time. This happens because they lose their charge. This
process is called electrical discharge. The gold leaves would also be
discharged when someone touches the brass rod with bare hands. In that case,
the charge is transferred to the earth through the human body.
Related Topics