Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 1 : Basic Concepts of Bio Chemistry and Cell Biology
The unit of biological organisation: The Cell
The unit of biological
organisation: The Cell
Be it a
complex living organism or a non-living matter, they are comprised of several
basal units. If you are a living organism, you are based on the single block,
the cell. If you are non-living matter like a house, you are based on the
single block, the brick. Thus, simply, a cell is a basal building unit of an
organism. One of the first major discoveries in biology was made by Robert
Hooke (1665). He showed that the partition of the cork (plant tissue) into tiny
compartments, and termed them as ‘cellulae’, or cells. In 1838 Schleiden, a
German Botanist and his co-worker Theodor Schwann, have shown that organisms
are made up of cells surrounded by a thin layer. However, they failed to correctly
explain the generation of cells. Later, in 1857, Rudolph Virchow, a pathologist
demonstrated that cells can be formed. only by the division of pre-existing
cells. Yet, the question of first cell remains unanswered. Single cells may be
adapted to survive in many different types of environments, extending between
extremes of cold or heat, living in aerobic or anaerobic conditions, or even
surrounded by methane gas. Some single cells can live within other organisms.
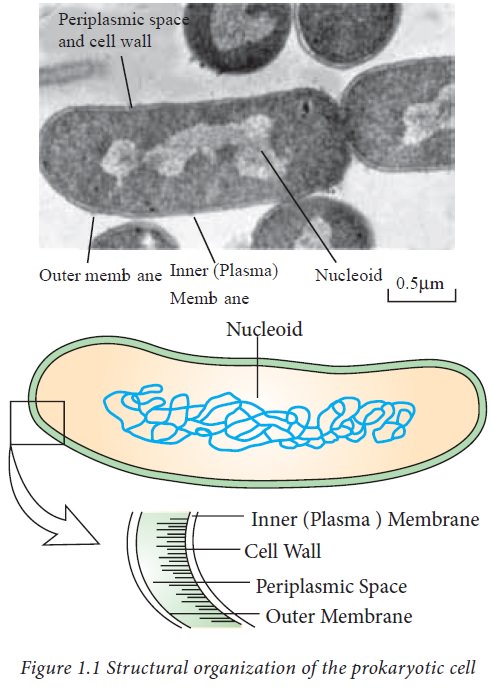
The cells of many of the organisms
are similar in size. Almost all cells maintain uniformity in size (1-2 μm in
diameter) and the bigger ones may be just 5-10 times larger. Why is such
uniformity in cell size maintained? The surface/volume ratio for any object of
any shape depends on its size. The complex biochemistry that takes place inside
the cell requires a significant volume and exchange with the external
environment. If the size is too large, then there will not be enough surface
for the exchange of substances with its environment and the process will not
occur. Thus, the size relates to the biochemical process i.e metabolism. An
unicellular bacterial cell has smaller size than that of the cells of higher
organisms as their metabolism is simple while a virion(viral particle) is
smaller than bacteria as they depend on their host for their survival. Yet,
there are unusual sizes such as very small bacteria which are 0.2 μm in length,
while cells of nervous systems of vertebrates are about a metre long.
Related Topics