Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 1 : Basic Concepts of Bio Chemistry and Cell Biology
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
Henderson–Hasselbalch equation
An
equation showing the relationship between a buffer’s pH and the relative
amounts of the buffer’s weak acid and its conjugate base is called as
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. Consider the dissociation of a weak acid (HA).
At equilibrium,
HA ↔H+ + A–
The
dissociation constant (Ka) is,
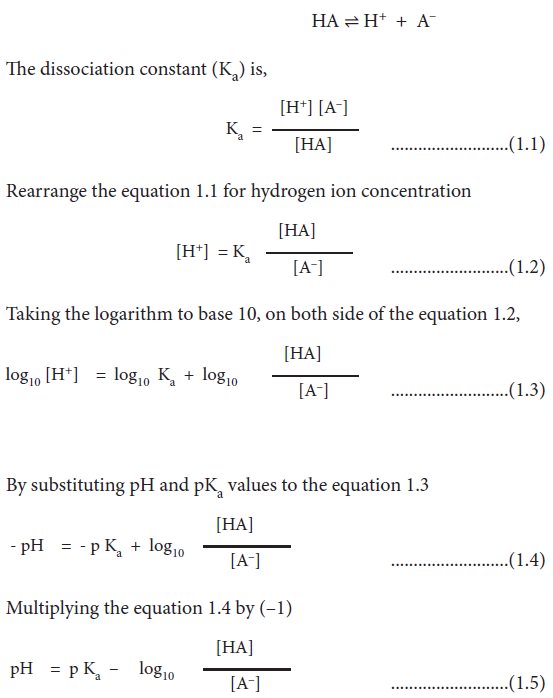
Reciprocating the log term of
equation 1.5
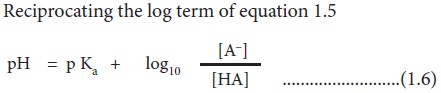
This form of the ionization constant
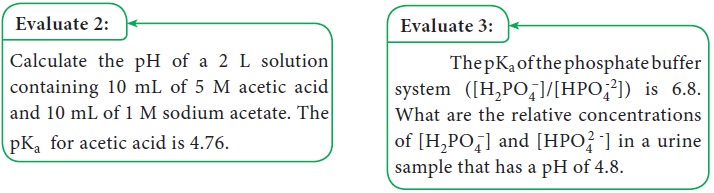
equation is called the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation (equation 1.6). It is
useful for calculating the pH of a weak acid solution containing its conjugate
base (salt). The other forms of the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation of weak acid
with its conjugate base are as follows:
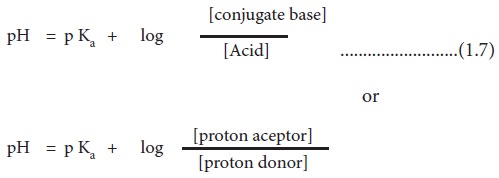
When the concentrations of weak acid
and its conjugate base or weak base and its conjugate acid are equal, the pH of
the solution equals the pKa of the buffer. This is evident from the
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
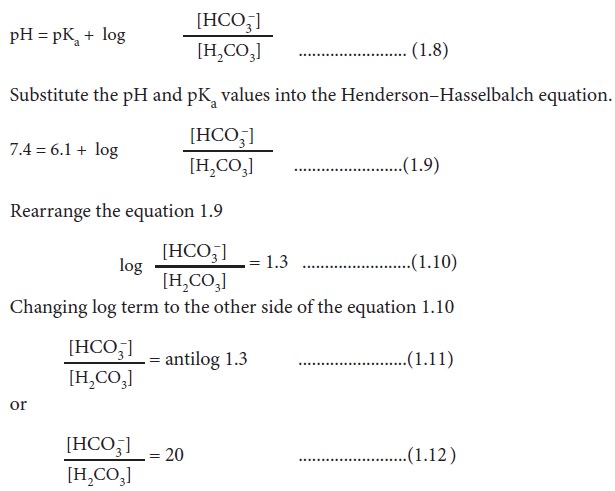
If the pKa of bicarbonate
buffer is 6.1 and the pH of blood is 7.4, then the ratio of bicarbonate to
carbonic acid ([HCO3–] / [H2CO3])
in blood is calculated by applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Related Topics