Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller : 8086 System Bus Structure
System Design using 8086: Maximum mode 8086 system and timings
System Design using 8086: Maximum mode 8086 system
and timings
In the
maximum mode, the 8086 is operated by strapping the MN/MX* pin to ground. In
this mode, the processor derives the status signals S2*, S1* and S0*. Another
chip called bus controller derives the control signals using this status
information. In the maximum mode, there may be more than one microprocessor in
the system configuration.
The basic
functions of the bus controller chip IC8288, is to derive control signals like
RD* and WR* (for memory and I/O devices), DEN*, DT/R*, ALE, etc. using the
information made available by the processor on the status lines. The bus
controller chip has input lines S2*, S1* and S0* and CLK. These inputs to 8288
are driven by the CPU. It derives the outputs ALE, DEN*, DT/R*, MWTC*, AMWC*,
IORC*, IOWC* and AIOWC*. The AEN*, IOB and CEN pins are especially useful for
multiprocessor systems. AEN* and IOB are generally grounded. CEN pin is usually
tied to +5V.
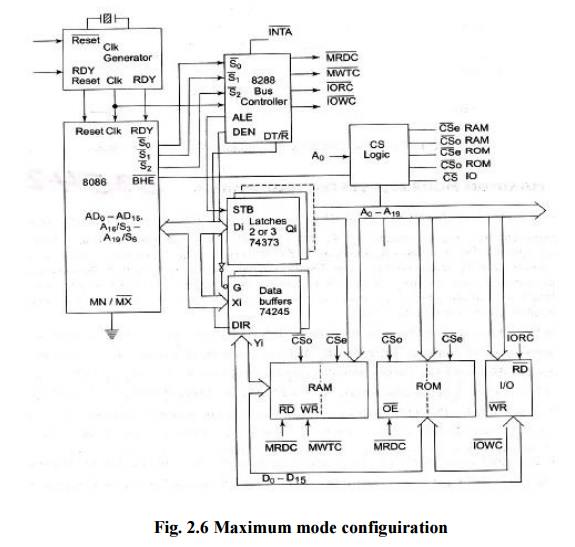
The
significance of the MCE/PDEN* output depends upon the status of the IOB pin. If
IOB is grounded, it acts as master cascade enable to control cascaded 8259A;
else it acts as peripheral data enable used in the multiple bus configurations.
INTA* pin
is used to issue two interrupt acknowledge pulses to the interrupt controller
or to an interrupting device.
IORC*,
IOWC* are I/O read command and I/O write command signals respectively.
These
signals enable an IO interface to read or write the data from or to the
addressed port. The MRDC*, MWTC* are memory read command and memory write
command signals respectively and may be used as memory read and write signals.
All these command signals instruct the memory to accept or send data from or to
the bus.
For both
of these write command signals, the advanced signals namely AIOWC* and AMWTC*
are available. They also serve the same purpose, but are activated one clock
cycle earlier than the IOWC* and MWTC* signals, respectively. The maximum mode
system is shown in fig. 2.1.
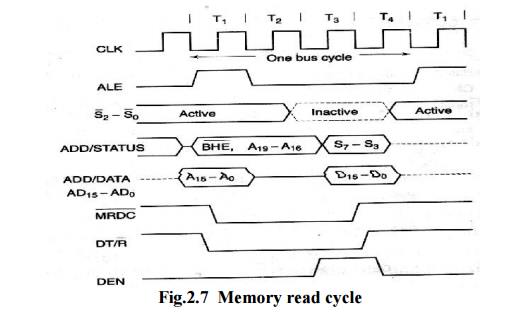
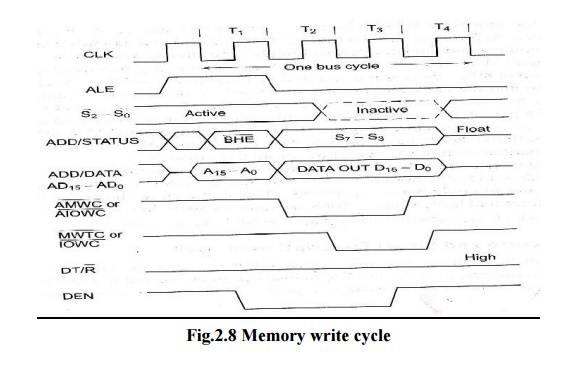
The
maximum mode system timing diagrams are also divided in two portions as read
(input) and write (output) timing diagrams. The address/data and address/status
timings are similar to the minimum mode. ALE is asserted in T1, just like
minimum mode. The only difference lies in the status signals used and the
available control and advanced command signals. The fig. 1.2 shows the maximum
mode timings for the read operation while the fig. 1.3 shows the same for the
write operation.
Related Topics