Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller : 8086 System Bus Structure
Internal Architecture of 80286
Internal Architecture of 80286
Register Organization of 80286
The 80286 CPU contains almost the same set of registers, as in 8086, namely
1. Eight 16-bit general purpose registers
2. Four 16-bit segment registers
3. 3. Status and control registers
4. 4.Instruction Pointer
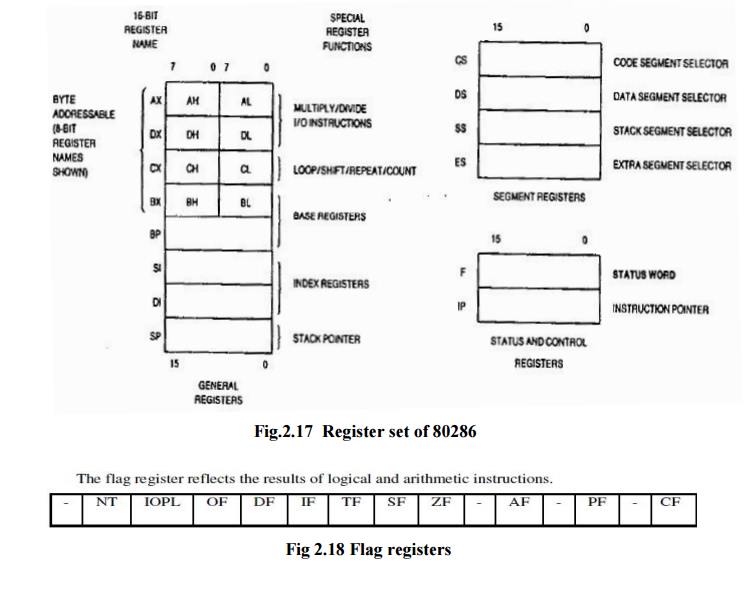
D2, D4, D6, D7 and D11 are called as status flag bits. The bits D8 (TF) and D9 (IF) are used for controlling machine operation and thus they are called control flags. The additional fields available in 80286 flag registers are:
1. IOPL - I/O Privilege Field (bits D12 and D13)
2. NT - Nested Task flag (bit D14)
3. PE - Protection Enable (bit D16)
4. MP - Monitor Processor Extension (bit D17)
5. EM - Processor Extension Emulator (bit D18)
6. TS – Task Switch (bit D19)
Protection Enable flag places the 80286 in protected mode, if set. This can only be cleared by resetting the CPU. If the Monitor Processor Extension flag is set, allows WAIT instruction to generate a processor extension not present exception.
Processor Extension Emulator flag if set, causes a processor extension absent exception and permits
the emulation of processor extension by the CPU.
Task Switch flag if set, indicates the next instruction using extension will generate exception 7, permitting the CPU to test whether the current processor extension is for the current task.
Machine Status Word (MSW)
The machine status word consists of four flags – PE, MO, EM and TS of the four lower order bits D19 to D16 of the upper word of the flag register. The LMSW and SMSW instructions are available in the instruction set of 80286 to write and read the MSW in real address mode.
Related Topics