Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller : 8086 System Bus Structure
Coprocessor configurations, Closely and Loosely Coupled Configuration
Coprocessor configurations
Coprocessor
Configuration:
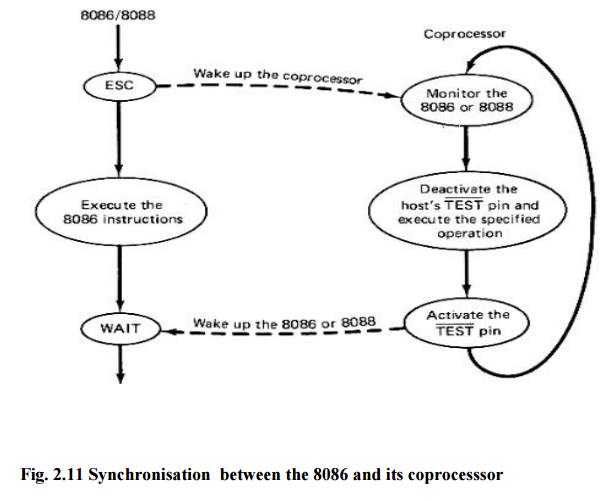
WAIT
instruction allows the processor to synchronize itself with external hardware,
eg., waiting for 8087 math co-processor.
When the
CPU executes WAIT waiting state.
TEST
input is asserted (low), the waiting state is completed and execution will
resume. ESC instruction:
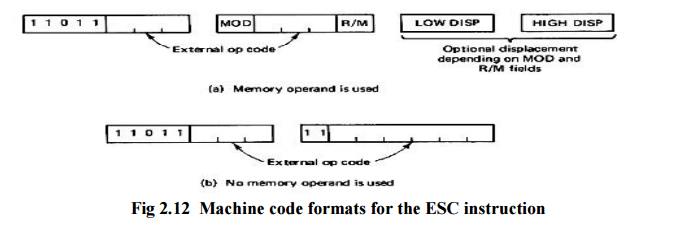
ESC
opcode, operand, opcode: immediate value recognizable to a coprocessor as an
instruction opcode
Operand:
name of a register or a memory address (in any mode)
When the
CPU executes the ESC instruction, the processor accesses the memory operand by
placing the address on the address bus.
If a
coprocessor is configured to share the system bus, it will recognize the ESC
instruction and therefore will get the opcode and the operand
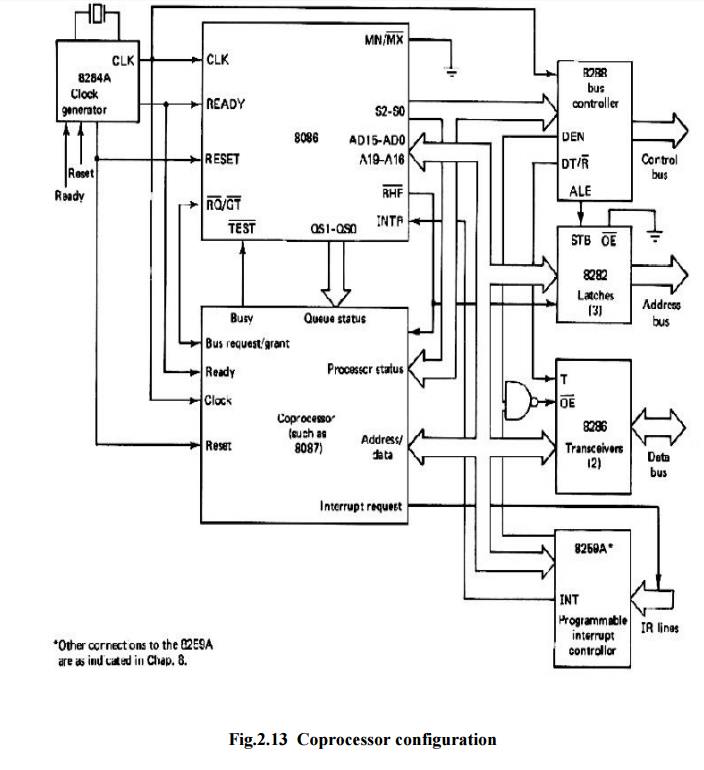
ü Coprocessor
cannot take control of the bus, it does everything through the CPU
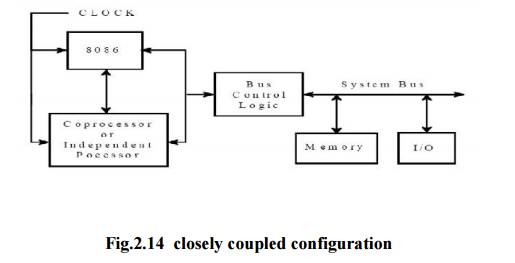
ü Closely
Coupled processor may take control of the bus independently - 8089 shares CPU’s
clock and bus control logic.
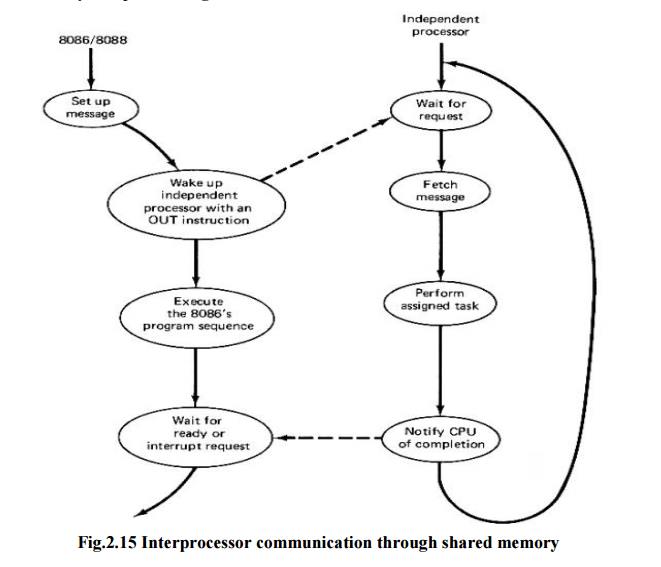
ü communication
with host CPU is by way of shared memory
ü host sets
up a message (command) in memory
ü independent
processor interrupts host on completion
ü Two
8086’s cannot be closely coupled
Closely Coupled Configuration
Loosely Coupled Configurations:
A loosely
coupled configuration provides the following advantages:
1. High
system throughput can be achieved by having more than one CPU.
2. The
system can be expanded in a modular form. Each bus master module is an
independent unit and normally resides on a separate PC board. Therefore, a bus
master module can be added or removed without affecting the other modules in
the system.
3. A failure
in one module normally does not cause a breakdown of the entire system and the
faulty module can be easily detected and replaced.
4. Each
bus master may have a local bus to access dedicated memory or I/O devices so
that a greater degree of parallel processing can be achieved. More than one bus
master module may have access to the shared system bus
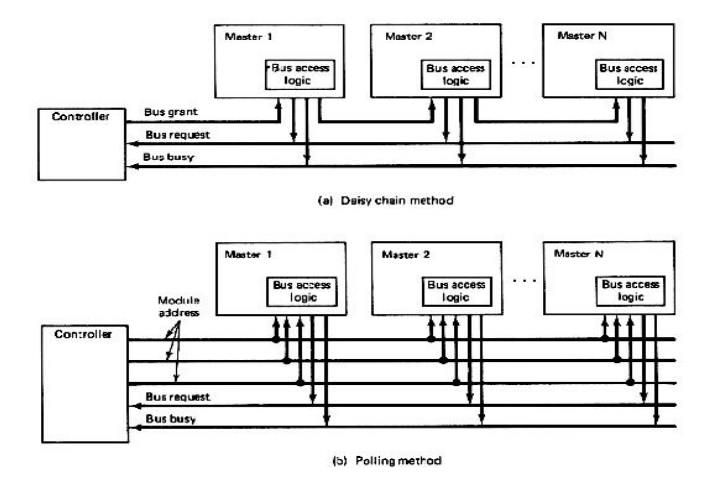
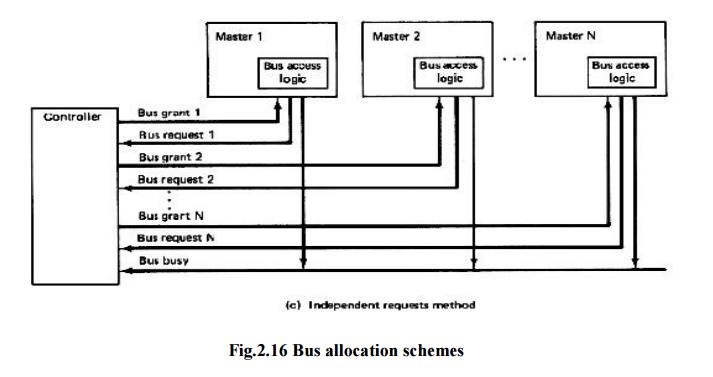
Extra bus control logic must be provided to resolve
the bus arbitration problem. The extra logic is called bus access logic and it
is its responsibility to make sure that only one bus master at a time has
control of the bus.
Simultaneous
bus requests are resolved on a priority
basis: There are three schemes for establishing priority:
1. Daisy
chaining.
2. Polling.
3. Independent
requesting
Related Topics