Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller : 8086 System Bus Structure
Internal Block Diagram of 80286
Internal Block Diagram of 80286
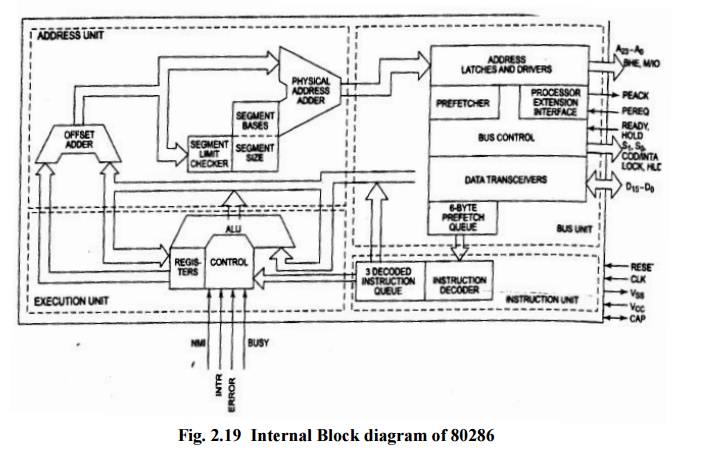
The CPU contain four functional blocks
1. Address Unit (AU)
2. Bus Init (BU)
3. Instruction Unit (IU)
4. Execution Unit (EU)
The address unit is responsible for calculating the physical address of instructions and data that the CPU wants to access. Also the address lines derived by this unit may be used to address different peripherals. The physical address computed by the address unit is handed over to the bus unit (BU) of the CPU. Major function of the bus unit is to fetch instruction bytes from the memory. Instructions are fetched in advance and stored in a queue to enable faster execution of the instructions. The bus unit also contains a bus control module that controls the prefetcher module. These prefetched instructions are arranged in a 6-byte instructions queue. The 6-byte prefetch queue forwards the instructions arranged in it to the instruction unit (IU). The instruction unit accepts instructions from the prefetch queue and an instruction decoder decodes
them one by one. The decoded instructions are latched onto a decoded instruction queue. The output of the decoding circuit drives a control circuit in the execution unit, which is responsible for executing the instructions received from decoded instruction queue. The decoded instruction queue sends the data part of the instruction over the data bus. The EU contains the register bank used for storing the data as scratch pad, or used as special purpose registers. The ALU, the heart of the EU, carries out all the arithmetic and logical operations and sends the results over the data bus or back to the register bank.
Related Topics