Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Phloem transport distributes photoassimilates to the various sites of consumption and storage
Synthesis of the storage proteins occurs at the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesis of the storage proteins occurs at the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Seed storage proteins are formed by ribosomes at the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (Fig. 14.1). The newly synthesized proteins occur in the lumen of the ER, and the storage proteins are finally deposited in the pro-tein bodies. In the case of 2S-proteins and prolamins, the protein bodies are formed by budding from the ER. The globulins are mostly transferred from the ER by vesicle transfer via the Golgi apparatus , first to the vacuole, from which protein bodies are formed by fragmentation. There is also a pathway by which certain proteins (e.g., globulins in wheat endosperm) are transported directly by vesicle transfer from the ER to the vacuole without passing the Golgi apparatus.
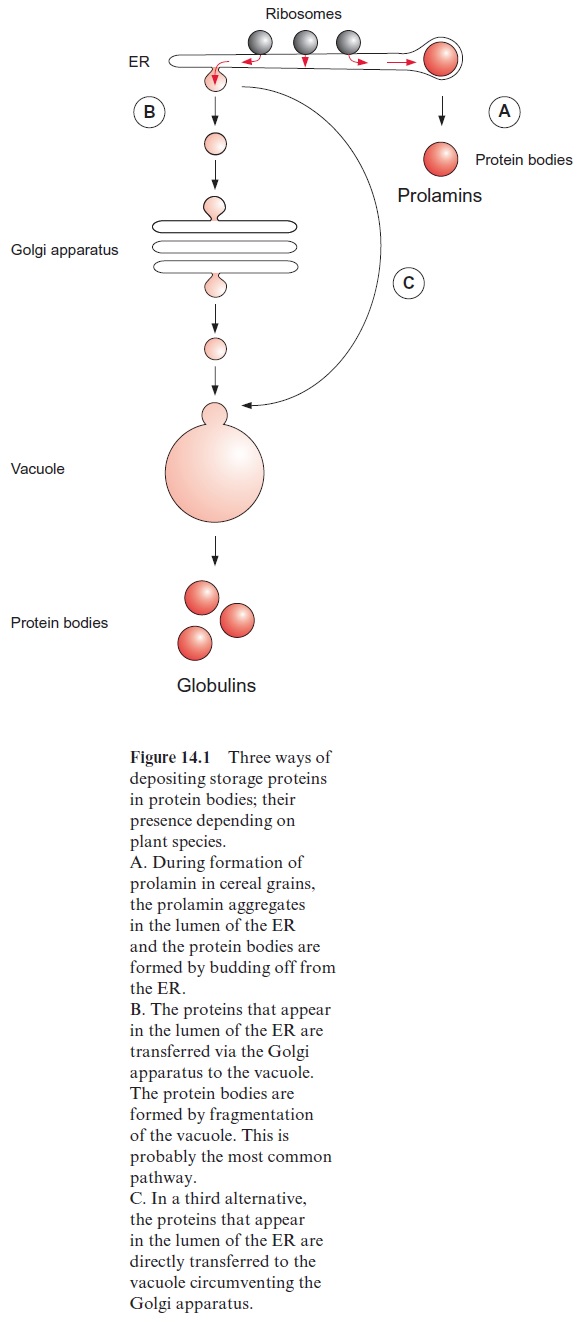
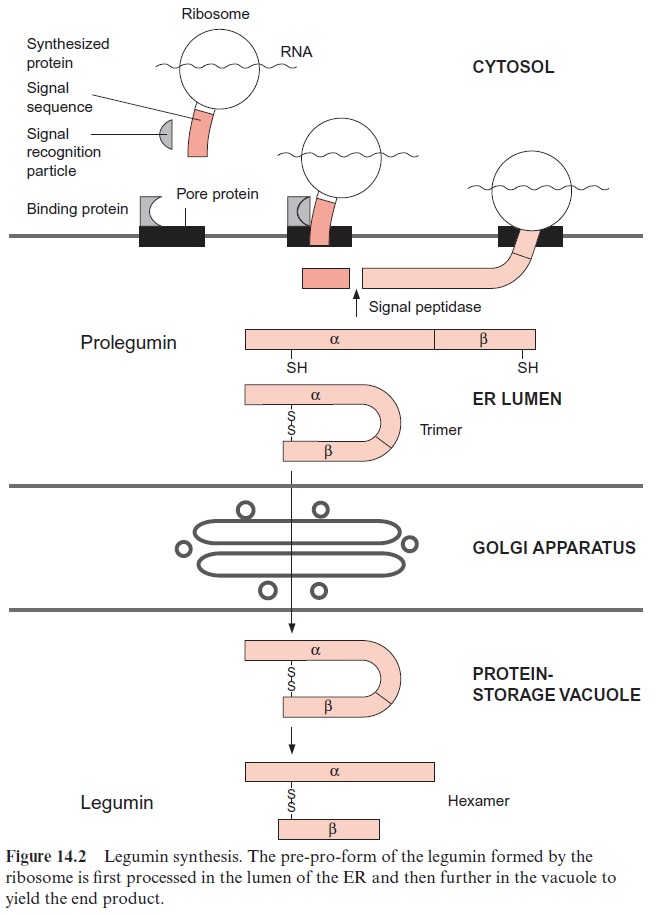
Figure 14.2 shows the formation of legumin in detail. The protein formed by the ribosome contains, at the N-terminus of the polypeptide chain, a hydrophobic section called a signal sequence. After the synthesis of this signal sequence, translation is attenuated, and the signal sequence forms a complex with three other components:
1. A signal recognition particle,
2. A binding protein attached at the ER membrane, and
3. A pore protein present in the ER membrane.
The formation of this complex anchors the ribosome on the ER mem-brane for the duration of protein synthesis and supports the continuation of translation. The newly formed protein chain (e.g., pre-pro-legumin) reaches the lumen of the ER. Immediately after the peptide chain enters the lumen, the signal sequence is removed by a signal peptidase located on the inside of the ER membrane. The remaining polypeptide, termed a pro-legumin, comprises the future α- and β-chains of the legumin. An S-S link-age within the pro-legumin is formed in the ER lumen. Three pro-legumin molecules form a trimer, facilitated by chaperones. A quality control occurs during this association: Trimers without the correct confor-mation are degraded. The trimers are transferred via the Golgi apparatus to the vacuoles, where the α- and β-chains are separated by a peptidase. The subunits of the legumins are now assembled tohexamers and are deposited in this form. The protein bodies, the final storage site of the legumins, are derived from fragmentation of the vacuole. The carbohydrate chains of gly-cosylated vicilins (e.g., of the phaesolins from the bean Phaseolus vulgaris) are processed in the Golgi apparatus.
The pre-pro-forms of newly synthesized 2S-proteins and prolamins, which occur in the lumen of the ER, also contain a signal sequence. Completion and aggregation of these proteins takes place in the lumen of the ER, from which the protein bodies are formed by budding.
Related Topics