Attributes, Need | Industrial Microbiology - Strain Improvement | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 6 : Industrial Microbiology
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 6 : Industrial Microbiology
Strain Improvement
Strain Improvement
Improvement
of the production strain(s) offers the great opportunities for cost reduction
without significant capital outlay in industries. Moreover, success in making
and keeping a fermentation industry competitive depends greatly on continuous
improvement of the production strain(s). Improvement usually resides in
increased yields of the desired metabolite. The science and technology of
manipulating and improving microbial strains, in order to enhance their
metabolic capacities for biotechnological applications, are referred to as
strain improvement.
Need for strain improvement
Microbes
exist in the nature produce certain compounds of biological interest. However
the industrial application of producing those compounds by natural strains is
not an economical one so, wild strains are changed by the changing their gene
pattern or by regulating their enzymes production. As a result, the specific
product is produced in excess.
Knowledge
of the function of enzymes, rate limiting steps in pathways, and environmental
factors controlling synthesis further helps in designing screening strategies.
Attributes of Improved strains
1. Assimilate
inexpensive and complex raw materials efficiently.
2. Alter
product ratios and eliminate impurities or by products in downstream
processing.
3. Reduce
demand on utilities during fermentation (air, cooling water, or power).
4. Provide
cellular morphology in a form suitable for product separation.
5. Create
tolerance to high product concentration.
6. Shorten
fermentation times.
7. Overproduce
natural products or bioactive molecules not synthesized naturally for example
insulin.
8. Excrete
the product to facilitate product recovery.
Generally wild strains of microorganisms produce low quantities of commercially important metabolites. So, genetic improvements have to be made and new strains need to be developed for any substantial increase in the product formation in a cost effective manner.
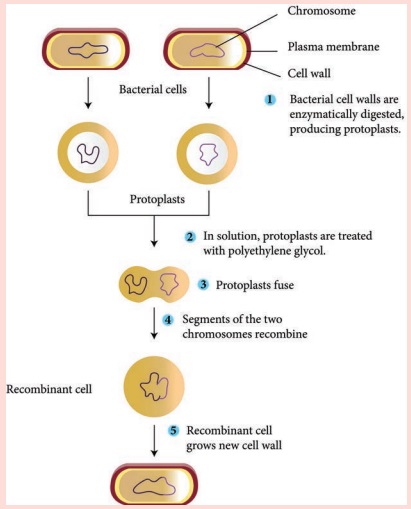
Protoplast fusion is defined as fusion of two different
protoplasts. A cell wall less nature of plant, bacteria, fungal is called
protoplast. It is re moved by either mechanical or enzymatic means. Protoplast
has nucleus other protoplasmic contents which are surrounded by cytoplasmic
membrane.
HOTS
An organism is isolated from soil, which is a very low yielding
one. How will you enhance the production activity?
The
following techniques at practical genomic level help to improve the microbial
strain. They are:
1. Selection
of mutants
2. Recombination
3. Regulation
4. Genetic
engineering
5. Protoplast
fusion
Related Topics