Industrial Microbiology - Industrially Important Microbes and their Products | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 6 : Industrial Microbiology
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 6 : Industrial Microbiology
Industrially Important Microbes and their Products
Industrially Important Microbes and their Products
Microorganisms
have the powerful capacity to produce numerous products, during their life
cycle. Flowchart 6.1 shows the production of valuable metabolic products during
the growth of microorganisms on a suitable medium under controlled
environmental conditions. Microbial products are often classified as primary
and secondary metabolites.
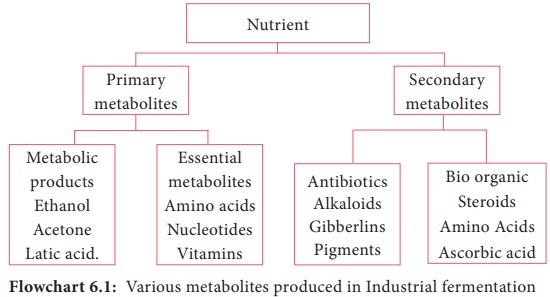
Primary
metabolites consist of compounds related to the synthesis by microbial cells in
the growth phase. Primary metabolites such as amino acids, vitamins, enzymes,
organic acids and nitrogenous bases are produced by wide variety of
microorganisms. These primary metabolites are essential for the growth of
microorganisms and they are produced during Logarithmic phase. Secondary
metabolites do not play a role in development, growth and reproduction of
microorganisms. They are produced at the end of growth phase near stationary
phase. They usually accumulate during the period of nutrient limitation or
waste product accumulation that follows the exponential phase. These compounds
have no direct relationship to the synthesis of cell materials and normal
growth. They are the end products of the primary metabolism. Products such as
steroids, alkaloids, antibiotics are secondary metabolites.
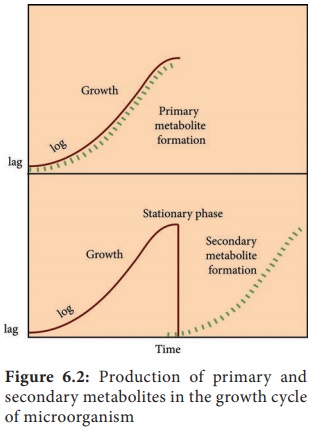
Excessive
production of the primary and secondary metabolites produced by the
microorganisms are useful in the large scale in industrial production. Unlike
primary metabolites, secondary metabolites are produced in small quantities and
their extraction is difficult (Figure 6.2).
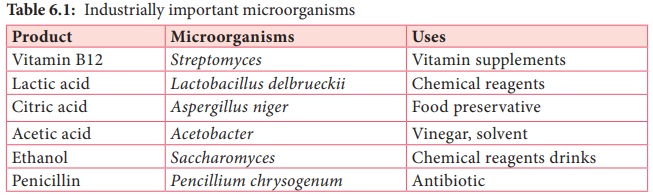
Some
industrially important products are,
• microbial cells (living or dead), microbial
biomass and components of microbial cells microbial metabolites
• intracellular
or extracellular enzymes
• modified
compounds that has been microbiologically transformed, and
• recombinant
products through the DNA recombinant technology. (Table 6.1 shows some
industrially important microorganisms)
The nutritional yeast is called food yeast. The yeast cells are
killed during manufacturing, and not alive in the final product. It is used in
cooking; it has a cheesy, nutty or savory flavour. Yeast S. cerevisiae is used
as food yeast. It is a vegan food, available in both fortified (with some
vitamins) and unfortified form.
The industrial production of commercial products is carried out by fermentation process. The term fermentation is defined scientifically in a strict sense as a biological process that occurs in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic). In industrial sense any process mediated by or involving microorganisms in which a product of economic value is obtained is called fermentation. The term Industrial fermentation also means large scale cultivation of microorganisms even though most of them are aerobic.
There are many microbiological processes thatoccurinthepresenceofair(aerobically) yielding incomplete oxidation products. Examples: i) the formation of acetic acid (vinegar) from alcohol by vinegar bacteria ii) citric acid from sugar by certain molds such as Aspergillus niger. These microbial processes are often referred to as fermentations, although they do not decompose in the absence of air.
Infobits.
The German Eduard Buchner, winner of the 1907 Nobel Prize in
chemistry, determined that fermentation was actually caused by a yeast
secretion that he termed zymase. The experiment for which Buchner won the Nobel
Prize consisted of producing a cell– free extract of yeast cells and showing
that this “press juice” could ferment sugar. This finding dealt yet another
blow to vitalism by demonstrating for the first time that fermentation could
occur outside living cells.
Related Topics