Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 10 : Types of Chemical Reactions
State of Equilibrium
STATE OF EQUILIBRIUM
In a reversible
reaction, both forward and backward reactions take place simultaneously. When
the rate of the forward reaction becomes equal to the rate of backward
reaction, then no more product is formed. This stage of the reaction is called ‘equilibrium
state’ . After this stage, no net change in the reaction can occur and
hence in the amount of the reactants and products. Since this equilibrium is
attained in a chemical reaction, it is called ‘Chemical Equilibrium’. Chemical
Equilibrium: It is state of a reversible chemical reaction in which no
change in the amount of the reactants and products takes place. At equilibrium,
Rate of forward reaction
= Rate of backward reaction
Explanation:
Initially the rate of
the forward reaction is
greater than the rate of the backward reaction. However, during the course of
reaction, the concentration of the reactants decreases and the concentration of
the products increases. Since the rate of a reaction is directly proportional
to the concentration, the rate of the forward reaction decreases with time,
whereas the rate of the backward reaction increases.
At a certain stage, both
the rates become equal. From this point onwards, there will be no change in the
concentrations of both the reactants and the products with time. This state is
called as equilibrium state.
Let us consider the
decomposition of calcium carbonate into lime and carbon dioxide. It is a
reversible reaction. The speed of each reaction can be determined by how
quickly the reactant disappears. If the reaction is carried out in a closed
vessel, it reaches a chemical equilibrium. At this stage,
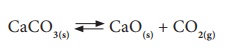
The rate of
decomposition of CaCO3 = The rate of combination of CaO and CO2
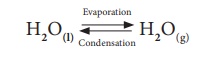
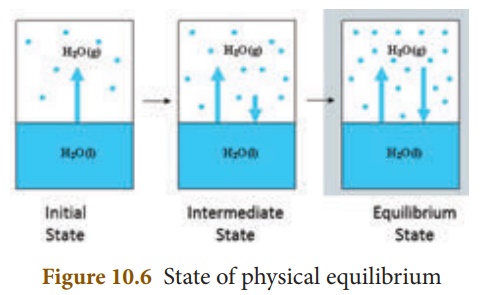
Not only chemical
changes, physical changes also may attain equilibrium. When water kept in a
closed vessel evaporates, it forms water vapour. No water vapour escapes out of
the container as the process takes place in a closed vessel. So, it builds up
the vapour pressure in the container. At one time, the water vapour condenses
back into liquid water and when the rate of this condensation becomes equal to
that of vapourisation, the process attains equilibrium.
At this stage, the
volume of the liquid and gaseous phases remain constant. Since it is a physical
change, the equilibrium attained is called ‘Physical Equilibrium’.
Physical equilibrium is a state of a physical change at which the volume of all
the phases remain unchanged.
Characteristics of equilibrium
·
In a chemical equilibrium, the rates of the forward and backward
reactions are equal.
·
The observable properties such as pressure, concentration, colour,
density, viscosity etc., of the system remain unchanged with time.
·
The chemical equilibrium is a dynamic equilibrium, because both
the forward and backward reactions continue to occur even though it appears
static externally.
·
In physical equilibrium, the volume of all the phases remain
constant.
Related Topics