Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 10 : Types of Chemical Reactions
Rate of a Chemical Reaction
RATE OF A CHEMICAL
REACTION
So far we discussed
various types of chemical reactions and the nature of the reactants and
products. Let us consider the following reactions:
·
Rusting of iron
·
Digestion of food
·
Burning of petrol
·
Weathering of rock
How fast is each
reaction? Rank them from the slowest to fastest. How will you determine, which
is the fastest and which is the slowest? One of the ways to find out how fast a
reaction is as follows: Measure the amount of reactants or products before and
after a specific period of time. For example, let us assume that 100 g of a substance
‘A’ undergoes a reaction and after an hour 50 g of ‘A’ is left.![]()
![]()
A → Product
In another instance, 100
g of substance ‘C’ undergoes a reaction and after an hour, 20 g of ‘C’ is left.
C → Product
Can you say which is the
faster reaction? In the first reaction, 50 g of the reactant (A) is converted
into products whereas in the second reaction 80 g of the reactant is converted
into products in one hour. So, the second reaction is faster. This measurement
is called ‘the reaction rate’.
“Rate of a reaction is
the change in the amount or concentration of any one of the reactants or
products per unit time”.
Consider the following
reaction
A → B
The rate of this
reaction is given by
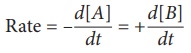
Where,
[A]– Concentration of A
[B]– Concentration of B
The negative sign
indicates the decrease in the concentration of A with time.
The postive sign
indicates the increase in the concentration of B with time.
Note: ‘[ ]’ represents the
concentration, ‘d’ represents the infinitesimal change in the concentration.
Why is reaction rate
important?
Faster the reaction,
more will be the amount of the product in a specified time. So, the rate of a
reaction is important for a chemist for designing a process to get a good yield
of a product. Rate of reaction is also important for a food processor who hopes
to slow down the reactions that cause food to spoil.
Factors influencing the rate of a reaction
Can the rate of a
reaction be changed? The rate of a reaction can be changed. For example, iron
gets rusted faster in an acid than in water. Important factors that affect rate
of a reaction are
i.
Nature of the reactants
ii.
Concentration of the reactants
iii.
Temperature
iv.
Catalyst
v.
Pressure
vi.
Surface area of the reactants
(i) Nature of the reactants
The reaction of sodium
with hydrochloric acid is faster than that with acetic acid. Do you know why?
Hydrochloric acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid and thus more reactive.
So, the nature of the reactants influence the reaction rate.
2Na(s)
+ 2HCl(aq) →
2NaCl(aq) + H2 (g) (fast)
2Na(s)
+ 2CH3COOH(aq) → 2CH3COONa(aq)
+ H2(g)(slow)
(ii) Concentration of the reactants
Changing the amount of
the reactants also increases the reaction rate. The amount of the substance
present in a certain volume of the solution is called ‘concentration’.
More the concentration, more particles per volume exist in it and hence faster
the reaction. Granulated zinc reacts faster with 2M hydrochloric acid than 1M
hydrochloric acid.
(iii) Temperature
Most of the reactions go
faster at higher temperature. Because adding heat to the reactants provides
energy to break more bonds and thus speed up the reaction. Calcium carbonate
reacts slowly with hydrochloric acid at room temperature. When the reaction
mixture is heated the reaction rate increases.
(iv)
Pressure

If the reactants are
gases, increasing their pressure increases the reaction rate. This is because,
on increasing the pressure the reacting particles come closer and collide
frequently.
(v) Catalyst
A catalyst is a
substance which increases the reaction rate without being consumed in the
reaction. In certain reactions, adding a substance as catalyst speeds up the
reaction. For example, on heating potassium chlorate, it decomposes into
potassium chloride and oxygen gas, but at a slower rate. If manganese dioxide
is added, it increases the reaction rate.
(vi) Surface area of the reactants
When solid reactants are
involve in a reaction, their powdered form reacts more readily. For example,
powdered calcium carbonate reacts more readily with hydrochloric acid than
marble chips. Because, powdering of the reactants increases the surface area
and more energy is available on collision of the reactant particles. Thus, the
reaction rate is increased.
You will study more
about reaction rate in you higher classes.
Related Topics