Types of Chemical Reactions - Book Back Questions with Answers | 10th Science : Chapter 10 : Types of Chemical Reactions
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 10 : Types of Chemical Reactions
Book Back Questions with Answers
Types of Chemical Reactions
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. H2(g) + Cl29(g) → 2HCl(g) is a
a. Decomposition Reaction
b. Combination Reaction
c. Single Displacement Reaction
d. Double Displacement Reaction
2. Photolysis is a decomposition reaction caused by ___________
a. heat
b. electricity
c. light
d. mechanical energy
3. A reaction between carbon and oxygen is represented by C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + Heat. In which of the type(s), the above reaction can be classified?
(i) Combination Reaction
(ii) Combustion Reaction
(iii) Decomposition Reaction
(iv) Irreversible Reaction
a. i and ii
b. i and iv
c. i, ii and iii
d. i, ii and iv
4. The chemical equation
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s)↓ + 2NaCl(aq)
represents which of the following types of reaction?
a. Neutralisation
b. Combustion
c. Precipitation
d. Single displacement
5. Which of the following statements are correct about a chemical equilibrium?
(i) It is dynamic in nature
(ii) The rate of the forward and backward reactions are equal at equilibrium
(iii) Irreversible reactions do not attain chemical equilibrium
(iv) The concentration of reactants and products may be different
a. i, ii and iii
b. i, ii and iv
c. ii, iii and iv
d. i, iii and iv
6. A single displacement reaction is represented by X(s) + 2HCl(aq) → XCl2(aq) + H2(g). Which of the following(s) could be X.
(i) Zn (ii) Ag (iii) Cu (iv) Mg.
Choose the best pair.
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. iii and iv
d. i and iv
7. Which of the following is not an “element + element → compound” type reaction?
a. C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
b. 2K(s) + Br2(l) → 2KBr(s)
c. 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g)
d. 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
8. Which of the following represents a precipitation reaction?
a. A(s) + B(s) → C(s) + D(s)
b. A(s) + B(aq) → C(aq) + D(l)
c. A(aq) + B(aq) → C(s) + D(aq)
d. A(aq) + B(s) → C(aq) + D(l)
9. The pH of a solution is 3. Its [OH–] concentration is
a. 1 × 10–3 M
b. 3 M
c. 1 × 10–11 M
d. 11 M
10. Powdered CaCO3 reacts more rapidly than flaky CaCO3 because of ___________.
a. large surface area
b. high pressure
c. high concentration
d. high temperature
II. Fill in the blanks
1. A reaction between an acid and a base is called neutralization.
2. When lithium metal is placed in hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas is evolved.
3. The equilibrium attained during the melting of ice is known as physical equilibrium.
4. The pH of a fruit juice is 5.6. If you add slaked lime to this juice, its pH Increases (increse/decrese)
5. The value of ionic product of water at 250 C is 1.00 x 10-14.
6. The normal pH of human blood is
7. Electrolysis is type of decomposition reaction
8. The number of products formed in a synthesis reaction is
9. Chemical volcano is an example for decomposition type of reaction
10. The ion formed by dissolution of H+ in water is called
III. Match the following
Identify the types of reaction
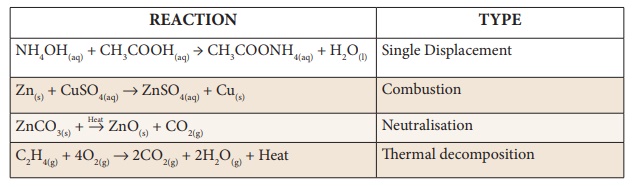
Answer:
1. Single Displacement
2. Combination
3. Neutralization
4. Thermal decomposition
IV. True or False: (If false give the correct statement)
1. Silver metal can displace hydrogen gas from nitric acid. - False
Silver metal will not be displace hydrogen gas from nitric acid.
2. The pH of rain water containing dissolved gases like SO3, CO2, NO2 will be less than 7. - True
3. At the equilibrium of a reversible reaction, the concentration of the reactants and the products will be equal.
At the equilibrium of a reversible reaction, there is no change in the concentration of the reactants and the products.
4. Periodical removal of one of the products of a reversible reaction increases the yield.
5. On dipping a pH paper in a solution, it turns into yellow. Then the solution is basic.
On dipping a pH paper in a solution, it turns into yellow. Then the solution is natural.
V. Short answer questions:
1. When an aqueous solution of potassium chloride is added to an aqueous solution of silver nitrate, a white precipitate is formed. Give the chemical equation of this reaction.
KCl + AgNO3 → KNO3 + AgCl ↓
2. Why does the reaction rate of a reaction increase on raising the temperature?
Increase in temperature provides energy to break more bonds and thus speeds up the reaction.
3. Define combination reaction. Give one example for an exothermic combination reaction.
A combination reaction is a reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a compound. It is otherwise called synthesis reaction or composition reaction.
Example: On burning magnesium in air, it combines with oxygen to form magnesium oxide. 2Mg(s)+ O2(g) → 2 MgO(s)
4. Differentiate reversible and irreversible reactions
Reversible Reaction
i. It can be reversed under suitable conditions
ii. Both forward and backward reactions take place simultaneously
iii. It attains equilibrium
iv. The reactants cannot be converted completely into products
v. It is relatively slow
Irreversible reaction
i. It cannot be reversed
ii. It is unidirectional. It proceeds only in forward direction
iii. Equilibrium is not attained
iv. The reactants can be completely converted into products
v. It is fast
VI. Answer in detail
1. What are called thermolysis reactions?
Answer:
In
this type of reaction, the reactant is decomposed by applying heat.
As
the molecule is dissociated by absorption of heat, it is otherwise called ‘Thermolysis’
2HgO(s)
____Heat→ 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
2. Explain the types of double displacement reactions with examples.
Answer:
There
are two major classes of double displacement reactions. They are
(i) Precipitation Reactions
(ii) Neutralization Reactions
(i) Precipitation Reactions : When aqueous solutions of
two compounds are mixed, if they react to form an insoluble compound and a
soluble compound, then it is called precipitation reaction.
Pb(NO3)2(aq)
+ 2KI(aq) → PbI2(s)
+ 2KNO3(aq)
(ii) Neutralization Reactions : Acid
reacts with the base to form a salt and water. It is called neutralization
reaction as both acid and base neutralise each other.
Acid
+ Base → Salt + Water
HCl(aq)
+ NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(I)
3. Explain the factors influencing the rate of a reaction
Answer:
Important
factors that affect rate of a reaction are:
(i) Nature of the reactants
(ii) Concentration of the reactants
(iii) Temperature
(iv) Catalyst
(v) Pressure
(vi) Surface area of the reactants
(i) Nature of the reactants : The reaction of sodium
with hydrochloric acid is faster than that with acetic acid. Hydrochloric acid
is stronger acid than acetic acid and thus more reactive. So the nature of the
reactants influence reaction rate.
2Na(s)
+ 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2(g)
fast
(ii) Concentration of the reactants: Changing
the amount of the reactants also increase the reaction rate. More the
concentration, more particles per volume exist in it and hence faster the
reaction.
(iii) Temperature : Increase in temperature provides
energy to break more bonds and thus speed up the reaction.
(iv) Pressure : If the reactants are gases,
increasing their pressure increases the reaction rate. Since on increasing
pressure the reacting particles come closer and collide frequently.
(v) Catalyst : A catalyst is a substance which
increase reaction rate without being consumed in the reaction. In certain
reactions, adding a substance as catalyst speeds up the reaction.
(vi) Surface area of
the reactants: When solid reactants are involved in a reaction,
their powdered form reacts more readily. Because powdering of the reactants
increases the surface area and more energy is available on collision of
reactant particles. Thus the reaction rate is increased.
4. How does pH play an important role in everyday life?
Answer:
(i) Living organisms can survive only in a narrow
range of pH change. Different body fluids have different pH values.
(ii) Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid which helps
in the digestion of food without harming the stomach. During indigestion, if
the stomach produces too much acid and this causes pain and irritation. pH of
the stomach fluid is approximately 2.0.
(iii) pH of the saliva normally ranges between 6.5 to
7.5.
(iv) When the pH of the mouth saliva falls below 5.5,
the enamel gets weathered.
(v) Toothpastes, which are generally basic are used
for cleaning the teeth that can neutralise the excess acid and prevent tooth
decay.
(vi) In agriculture, the pH of the soil is very
important. Citrus fruits require slightly alkaline soil, while rice requires
acidic soil and sugarcane requires neutral soil.
(vii) The pH of rain water is approximately 7, which
means that it is neutral and also represents its high purity. If the
atmospheric air is polluted with oxide gases of sulphur and nitrogen, they get
dissolved in the rain water and make its pH less than 7. Thus, if the pH of
rain water is less than 7, then it is called acid rain. When acid rain flows
into the rivers it lowers the pH of the river water also. The survival of
aquatic life in such rivers becomes difficult.
5. What is a chemical equilibrium? What are its characteristics?
Answer:
Chemical Equilibrium: It is state of a reversible
chemical reaction in which no change in the amount of reactants and products
takes place. At equilibrium,
Rate
of forward reaction = Rate of backward reaction
Characteristics of equilibrium :
(i) In chemical equilibrium, the rates of forward and
backward reactions are equal.
(ii) The observable properties such as pressure,
concentration, color, density, viscosity etc., of the system remain unchanged
with time.
(iii) The chemical equilibrium is a dynamic
equilibrium, because both the forward and backward reactions continue to occur
even though it appears static externally.
(iv) In physical equilibrium, the volume of all the
phases remain constant
VII. HOT questions
1. A solid compound ‘A’ decomposes on heating into ‘B’ and a gas ‘C’. On passing the gas ‘C’ through water, it becomes acidic. Identify A, B and C.
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 (Carbonic acid)
CaCO3 [A:Calcium carbonate] → CaO [B:Calcium oxide] + CO2 [C:Carbon di oxide]
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 (Carbonic acid)
A : CaCO3 : Calcium carbonate
B : CaO : Calcium oxide
C : CO2 : Carbon di oxide
2. Can a nickel spatula be used to stir copper sulphate solution? Justify your answer.
Nickel spatula cannot be used to stir the CuSO4 solution. Since Ni will displace Copper from CuSO4 solution and Cu will be deposited on the Nickel spatula.
VIII. Solve the following problems
1. Lemon juice has a pH 2, what is the concentration of H+ ions?
Solution
pH of lemon juice = 2
[HI] = ?
pH = -log10 [H+]
logl0[H+] = -2
[H+] = 10-2
= 0.01 mole litre-1
2. Calculate the pH of 1.0 ×10–4 molar solution of HNO3.
Solution
[H+] = 1.0 x 10-4
pH = -log10[H+]
= -log10 [1 x 10-4]
PH = -(log10 1 - 4 log1010)
= 0 + 4 x log1010
= 0 + 4 x 1
= 4
pH = 4
3. What is the pH of 1.0 × 10–5 molar solution of KOH?
Solution:
KOH(aq) ↔ K+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
One mole of KOH would give one mole of OH- ions.
[OH-] = 1 x 10-5 mol litre-1
pOH = -log10[OH-] = -log10[10-5]
= - (-5 x log1010) = - (-5) = 5
pH + pOH = 14
pH = 14 - pOH = 14-5 = 9
4. The hydroxide ion concentration of a solution is 1 × 10–11M. What is the pH of the solution?
Solution:
[OH-] = 1 x 10-11 M
pOH = -log10[OH-] = -log10[10-11]
= - (-11 x log1010) = - (-ll) = ll
pH + pOH = 14
pH = 14-pOH = 14-11 = 3
Related Topics