Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 10 : Types of Chemical Reactions
Ionic Product of Water
IONIC PRODUCT OF WATER
Although pure water is
often considered as a non-conductor of electricity, precise measurements show
that it conducts electricity to a little extent. This conductivity of water has
resulted from the self-ionisation of water. Self-ionisation or auto ionisation
is a reaction in which two like molecules react to give ions. In the process of
ionisation of water, a proton from one water molecule is transferred to another
water molecule leaving behind an OH— ion. The proton gets
dissolved in water forming the hydronium ion as shown in the following
equation:
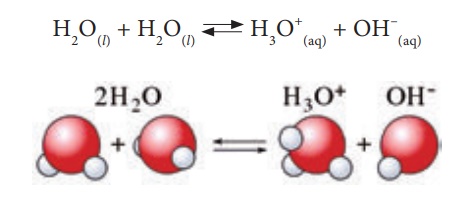
The hydronium ion formed
is a strong acid and the hydroxyl ion is a strong base. So as fast as they are
formed, they react again to produce water. Thus, it is a reversible reaction
and attains equilibrium very quickly. So, the extent of ionisation is very
little and the concentration of the ions produced is also very less. The
product of the concentration of the hydronium ion and the hydroxyl ion is
called ‘ionic product of water’. It is denoted as ‘Kw’.
It is mathematically expressed as follows:
Kw = [H3O+]
[OH−]
[H3O+]
may be simply written as [H+]. Thus the ionic product of water may
also be expressed as
Kw = [H+]
[OH−]
Its unit is mol2
dm−6. At 25° C, its value is
1.00 × 10−14.
Related Topics