Chapter: Principles of Management : Organizing
Staffing: Recruitment and Selection
STAFFING
Staffing involves filling the positions needed in the organization
structure by appointing competent and qualified persons for the job.
The
staffing process encompasses man power planning, recruitment, selection, and
training.
a) Manpower requirements:
Manpower Planning which is also called as Human Resource Planning consists
of putting right number of people, right kind of people at the right place,
right time, doing the right things for which they are suited for the
achievement of goals of the organization. The primary function of man power
planning is to analyze and evaluate the human resources available in the
organization, and to determine how to obtain the kinds of personnel needed to
staff positions ranging from assembly line workers to chief executives.
b) Recruitment:
Recruitment is the process of finding and attempting to attract job
candidates who are capable of effectively filling job vacancies.
Job
descriptions and job specifications are important in the recruiting process
because they specify the nature of the job and the qualifications required of
job candidates.
c) Selection:
Selecting a suitable candidate can be the biggest challenge for any
organization. The success of an organization largely depends on its staff.
Selection of the right candidate builds the foundation of any organization's
success and helps in reducing turnovers.
d) Training and Development:
Training and Development is a planned effort to facilitate employee
learning of job-related behaviors in order to improve employee performance.
Experts sometimes distinguish between the terms “training” and “development”;
“training” denotes efforts to increase employee skills on present jobs, while
“development” refers to efforts oriented toward improvements relevant to future
jobs. In practice, though, the distinction is often blurred (mainly because
upgrading skills in present jobs usually improves performance in future jobs).
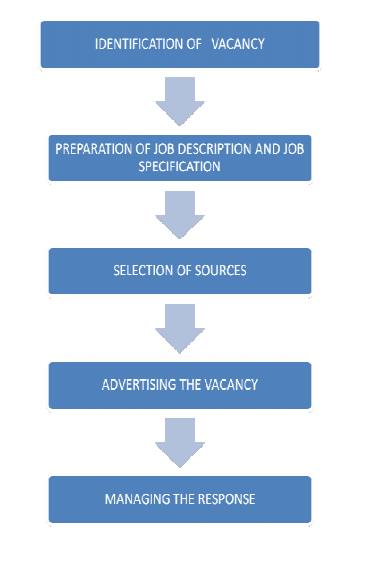
RECRUITMENT PROCESS
Recruitment is the process of finding and attempting to attract job
candidates who are capable of effectively filling job vacancies. The
recruitment process consists of the following steps
Identification of vacancy
Preparation of job description and job
specification
Selection of sources
Advertising the vacancy
Managing the response
a) Identification of vacancy:
The
recruitment process begins with the human resource department receiving
requisitions for recruitment from
any department of the company. These contain:
Posts to be filled
Number of persons
Duties to be performed
Qualifications required
Preparation of job description and job
specification:
A job
description is a list of the general tasks, or functions, and responsibilities
of a position. It may often include to whom the position reports,
specifications such as the qualifications or skills needed by the person in the
job, or a salary range. A job specification describes the knowledge, skills,
education, experience, and abilities you believe are essential to performing a
particular job.
c) Selection of sources:
Every organization has the option of choosing the candidates for its
recruitment processes from two kinds of sources: internal and external sources.
The sources within the organization itself (like transfer of employees from one
department to other, promotions) to fill a position are known as the internal
sources of recruitment. Recruitment candidates from all the other sources (like
outsourcing agencies etc.) are known as the external sources of the
recruitment.
d) Advertising the vacancy:
After choosing the appropriate sources, the vacancy is communicated to
the candidates by means of a suitable media such as television, radio,
newspaper, internet, direct mail etc.
e) Managing the response:
After receiving an adequate number of responses from job seekers, the
sieving process of the resumes begins. This is a very essential step of the
recruitment selection process, because selecting the correct resumes that match
the job profile, is very important. Naturally, it has to be done rather
competently by a person who understands all the responsibilities associated
with the designation in its entirety. Candidates with the given skill set are
then chosen and further called for interview. Also, the applications of
candidates that do not match the present nature of the position but may be
considered for future requirements are filed separately and preserved.
The
recruitment process is immediately followed by the selection process.
JOB ANALYSIS
Job Analysis is the process of describing and recording aspects of jobs and
specifying the skills and other
requirements necessary to perform the job.
The
outputs of job analysis are
Job description
Job specification
Job Description
A job
description (JD) is a written statement of what the job holder does, how it is
done, under what conditions it is done and why it is done. It describes what
the job is all about, throwing light on job content, environment and conditions
of employment. It is descriptive in nature and defines the purpose and scope of
a job. The main purpose of writing a job description is to differentiate the
job from other jobs and state its outer limits.
Contents
A job
description usually covers the following information:
Job title: Tells about the job title, code
number and the department where it is done.
Job summary: A brief write-up about what the job
is all about.
Job activities: A description of the tasks done,
facilities used, extent of supervisory help, etc.
Working conditions: The physical environment of
job in terms of heat, light, noise and other hazards.
Social environment: Size of work group and
interpersonal interactions required to do the job.
Job Specification
Job
specification summarizes the human characteristics needed for satisfactory job
completion. It tries to describe the key qualifications someone needs to
perform the job successfully. It spells out the important attributes of a
person in terms of education, experience, skills, knowledge and abilities
(SKAs) to perform a particular job. The job specification is a logical
outgrowth of a job description. For each job description, it is desirable to
have a job specification. This helps the organization to find what kinds of
persons are needed to take up specific jobs.
Contents
A job
specification usually covers the following information:
Education
Experience
Skill, Knowledge, Abilities
Work Orientation Factors
Age
SELECTION PROCESS
Selecting a suitable candidate can be the biggest challenge for any
organisation. The success of an organization largely depends on its staff.
Selection of the right candidate builds the foundation of any organization's
success and helps in reducing turnovers.
Though there is no fool proof selection procedure that will ensure low
turnover and high profits, the following steps generally make up the selection
process-

a) Initial Screening
This is
generally the starting point of any employee selection process. Initial
Screening eliminates unqualified applicants and helps save time. Applications
received from various sources are scrutinized and irrelevant ones are
discarded.
b) Preliminary Interview
It is used
to eliminate those candidates who do not meet the minimum eligibility criteria
laid down by the organization. The skills, academic and family background,
competencies and interests of the candidate are examined during preliminary
interview. Preliminary interviews are less formalized and planned than the
final interviews. The candidates are given a brief up about the company and the
job profile; and it is also examined how much the candidate knows about the
company. Preliminary interviews are also called screening interviews.
c) Filling Application Form
An
candidate who passes the preliminary interview and is found to be eligible for
the job is asked to fill in a formal application form. Such a form is designed
in a way that it records the personal as well professional details of the
candidates such as age, qualifications, reason for leaving previous job,
experience, etc.
d) Personal Interview
Most
employers believe that the personal interview is very important. It helps them
in obtaining more information about the prospective employee. It also helps
them in interacting with the candidate and judging his communication abilities,
his ease of handling pressure etc. In some Companies, the selection process
comprises only of the Interview.
e) References check
Most
application forms include a section that requires prospective candidates to put
down names of a few references. References can be classified into - former
employer, former customers, business references, reputable persons. Such
references are contacted to get a feedback on the person in question including
his behaviour, skills, conduct etc.
f) Background Verification
A
background check is a review of a person's commercial, criminal and
(occasionally) financial records. Employers often perform background checks on
employers or candidates for employment to confirm information given in a job
application, verify a person's identity, or ensure that the individual does not
have a history of criminal activity, etc., that could be an issue upon
employment.
g) Final Interview
Final
interview is a process in which a potential employee is evaluated by an
employer for prospective employment in their organization. During this process,
the employer hopes to determine whether or not the applicant is suitable for
the job. Different types of tests are conducted to evaluate the capabilities of
an applicant, his behaviour, special qualities etc. Separate tests are
conducted for various types of jobs.
h) Physical Examination
If all
goes well, then at this stage, a physical examination is conducted to make sure
that the candidate has sound health and does not suffer from any serious
ailment.
i) Job Offer
A
candidate who clears all the steps is finally considered right for a particular
job and is presented with the job offer. An applicant can be dropped at any
given stage if considered unfit for the job.
Related Topics