Chapter: Principles of Management : Organizing
Career development
CARRER DEVELOPMENT
Career development not only improves job performance but also
brings about the growth of the
personality. Individuals not only mature regarding their potential capacities
but also become better individuals.
Purpose of
development
Management
development attempts to improve managerial performance by imparting
Knowledge
Changing attitudes
Increasing skills
The major
objective of development is managerial effectiveness through a planned and a
deliberate process of learning. This provides for a planned growth of managers
to meet the future organizational needs.
Development Process:
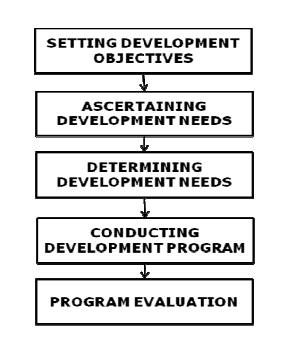
The
development process consists of the following steps
1. Setting Development Objectives:
It develops a framework from which executive
need can be determined.
2. Ascertaining Development Needs:
It aims at organizational planning &
forecast the present and future growth.
3. Determining Development Needs:
This consists of
Appraisal of present management talent
Management Manpower Inventory
The above two processes will determine the skill
deficiencies that are relative to the future needs of the organization.
4. Conducting Development Programs:
It is carried out on the basis of needs of different individuals,
differences in their attitudes and behavior, also their physical, intellectual
and emotional qualities. Thus a comprehensive and well conceived program is
prepared depending on the organizational needs and the time & cost
involved.
5. Program Evaluation:
It is an attempt to assess the value of training
in order to achieve organizational objectives.
TRAINING
Training is a process of learning a sequence of programmed behaviour. It
improves the employee's performance on the current job and prepares them for an
intended job.
Purpose of
Training:
To improve
Productivity: Training leads to increased operational productivity and
increased company profit.
To improve
Quality: Better trained workers are less likely to make operational mistakes.
To improve
Organizational Climate: Training leads to improved production and product
quality which enhances financial incentives. This in turn increases the overall
morale of the organization.
To
increase Health and Safety: Proper training prevents industrial accidents.
Personal
Growth: Training gives employees a wider awareness, an enlarged skill base and
that leads to enhanced personal growth.
Steps in Training Process:
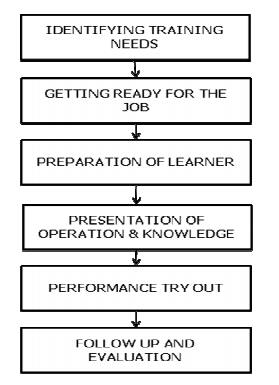
1)
Identifying Training needs: A training program is designed to assist in
providing solutions for specific operational problems or to improve performance
of a trainee.
Organizational determination and Analysis:
Allocation of resources that relate to organizational goal.
Operational Analysis: Determination of a
specific employee behaviour required for a particular task.
Man
Analysis: Knowledge, attitude and skill one must possess for attainment of
organizational objectives
Getting
ready for the job: The trainer has to be prepared for the job. And also who
needs to be trained - the newcomer or the existing employee or the supervisory
staff.
Preparation
of the learner:
Putting
the learner at ease
Stating
the importance and ingredients of the job
Creating
interest
Placing
the learner as close to his normal working position
Familiarizing
him with the equipment, materials and trade terms
Presentation
of Operation and Knowledge: The trainer should clearly tell, show, illustrate
and question in order to convey the new knowledge and operations. The trainee
should be encouraged to ask questions in order to indicate that he really knows
and understands the job.
Performance
Try out: The trainee is asked to go through the job several times. This
gradually builds up his skill, speed and confidence.
Follow-up:
This evaluates the effectiveness of the entire training effort
TRAINING METHODS
Training
methods can be broadly classified as on-the-job training and off-the-job
taining
a) On-the-job training
On the job
training occurs when workers pick up skills whilst working along side
experienced workers at their place of work. For example this could be the
actual assembly line or offices where the employee works. New workers may
simply “shadow” or observe fellow
employees to begin with and are often given instruction manuals or interactive
training programmes to work through.
b) Off-the-job training
This
occurs when workers are taken away from
their place of work to be trained. This may take place at training agency
or local college, although many larger firms also have their own training
centres. Training can take the form of lectures or self-study and can be used
to develop more general skills and knowledge that can be used in a variety of
situations.
The
various types of off-the-job training are
(i) Instructor presentation: The trainer orally
presents new information to the trainees, usually through lecture. Instructor
presentation may include classroom lecture, seminar, workshop, and the like.
Group
discussion: The trainer leads the group of trainees in discussing a topic.
Demonstration:
The trainer shows the correct steps for completing a task, or shows an example
of a correctly completed task.
Assigned
reading: The trainer gives the trainees reading assignments that provide new
information.
Exercise:
The trainer assigns problems to be solved either on paper or in real situations
related to the topic of the training activity.
Case
study: The trainer gives the trainees information about a situation and directs
them to come to a decision or solve a problem concerning the situation.
Role play:
Trainees act out a real-life situation in an instructional setting.
Field
visit and study tour: Trainees are given the opportunity to observe and
interact with the problem being solved or skill being learned.
Related Topics