Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves - Space Wave Propagation | 12th Physics : UNIT 10b : Communication Systems
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 10b : Communication Systems
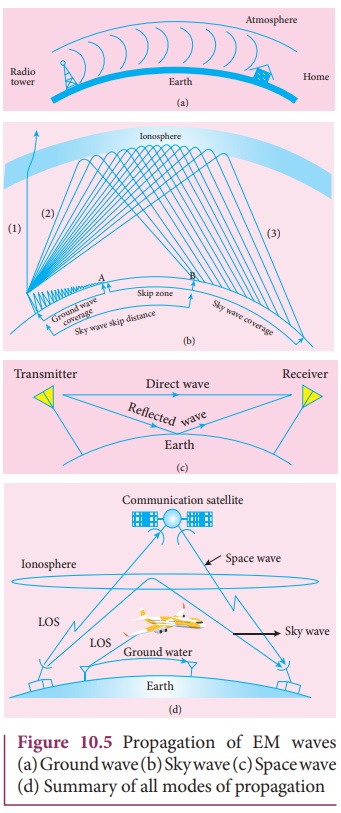
Space Wave Propagation
SPACE WAVE PROPAGATION
The process of sending and receiving information signal through
space is called space wave communication (Figure
10.5(c)). The electromagnetic waves of
very high frequencies above 30 MHz are called as space waves. These waves
travel in a straight line from the transmitter to the receiver. Hence, it is
used for a line of sight communication (LOS).
For high frequencies, the
transmission towers must be high enough so that the transmitted and received
signals (direct waves) will not encounter the curvature of the Earth and hence
travel with less attenuation and loss of signal strength. Certain waves reach
the receiver after getting reflected from the ground.
The communication systems like
television telecast, satellite communication and RADAR are based on space wave
propagation. Microwaves having high frequencies (super high frequency band) are
used against radio waves due to certain advantages: larger bandwidth, high data
rates, better directivity, small antenna size, low power consumption, etc.
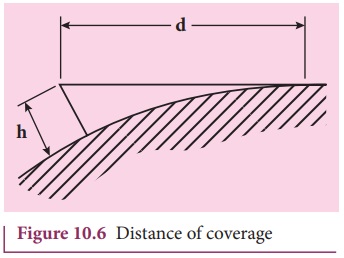
The range or distance (d) of
coverage of the propagation depends on the height (h) of the antenna given by
the equation,

where R is the radius of the Earth
and it is 6400 km.
The distance of coverage is shown pictorially
in Figure 10.6.
EXAMPLE 10.1
A transmitting antenna has a height
of
40 m and the height of the receiving antenna is 30
m. What is the maximum distance between them for line-of-sight communication?
The radius of the earth is 6.4×106 m.
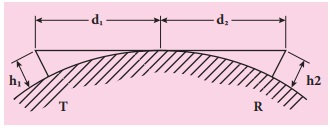
Solution:
The total distance d between the transmitting and receiving
antennas will be the sum of the individual distances of coverage.
d = d1 +d2
= √(2Rh) + √(2Rh2)
= √2√R (√h1 + √h2)
= √[2 × 6.4 ×106] × ( √40
+ √30 )
=16 ×102 √5 ×(6.32 + 5.48)
=42217m= 42.217 km
Related Topics